Abstract
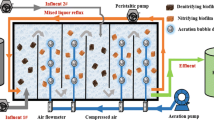
A membrane-aerated biofilm reactor (MABR) was developed to degrade acetonitrile (ACN) in aqueous solutions. The reactor was seeded with an adapted activated sludge consortium as the inoculum and operated under step increases in ACN loading rate through increasing ACN concentrations in the influent. Initially, the MABR started at a moderate selection pressure, with a hydraulic retention time of 16 h, a recirculation rate of 8 cm/s and a starting ACN concentration of 250 mg/l to boost the growth of the biofilm mass on the membrane and to avoid its loss by hydraulic washout. The step increase in the influent ACN concentration was implemented once ACN concentration in the effluent showed almost complete removal in each stage. The specific ACN degradation rate achieved the highest at the loading rate of 101.1 mg ACN/g-VSS h (VSS, volatile suspended solids) and then declined with the further increases in the influent ACN concentration, attributed to the substrate inhibition effect. The adapted membrane-aerated biofilm was capable of completely removing ACN at the removal capacity of up to 21.1 g ACN/m2 day, and generated negligible amount of suspended sludge in the effluent. Batch incubation experiments also demonstrated that the ACN-degrading biofilm can degrade other organonitriles, such as acrylonitrile and benzonitrile as well. Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis studies showed that the ACN-degrading biofilms contained a stable microbial population with a low diversity of sequence of community 16S rRNA gene fragments. Specific oxygen utilization rates were found to increase with the increases in the biofilm thickness, suggesting that the biofilm formation process can enhance the metabolic degradation efficiency towards ACN in the MABR. The study contributes to a better understanding in microbial adaptation in a MABR for biodegradation of ACN. It also highlights the potential benefits in using MABRs for biodegradation of organonitrile contaminants in industrial wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya A, Desai AJ (1997) Studies on utilization of acetonitrile by Rhodococcus erythropolis A10. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 13:175–178. doi:10.1023/A:1018585613448
Ahmed AE, Farooqui MYH (1982) Comparative toxicities of aliphatic nitriles. Toxicol Lett 12:157–163. doi:10.1016/0378-4274(82)90179-5
APHA (1998) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC
Aronstein BN, Maka A, Srivatava VJ (1994) Chemical and biological removal of cyanides from aqueous and soil containing systems. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41:700–707. doi:10.1007/BF00167288
Babu GRV, Wolfram JH, Marian JM, Chapatwala KD (1995) Pseudomonas marginalis: its degradative capability on organic nitriles and amides. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 43:739–745
Banerjee A, Sharma R, Banerjee UC (2002) The nitrile-degrading enzymes: current status and future prospects. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 60:33–44. doi:10.1007/s00253-002-1062-0
Beguin P, Chauvaux S, Miras I, Francois A, Fayolle F, Monot F (2003) Genes involved in the degradation of ether fuels by bacteria of the Mycobacterium/Rhodococcus group. Oil Gas Sci Technol 58:489–495. doi:10.2516/ogst:2003032
Bhalla TC, Miura A, Wakamoto A, Ohba Y, Furuhashi K (1992) Asymmetric hydrolysis of alpha aminonitriles to optically active amino acids by a nitrilase of Rhodococcus rhodochrous PA-34. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 37:184–190. doi:10.1007/BF00178168
Bhatti ZI, Toda H, Furukawa K (2002) p-Nitrophenol degradation by activated sludge attached on nonwovens. Water Res 36:1135–1142. doi:10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00292-5
Borucki MK, Peppin JD, White D, Loge F, Call DR (2003) Variation in biofilm formation among strains of Listeria monocytogenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:7336–7342. doi:10.1128/AEM.69.12.7336-7342.2003
Brindle K, Stephenson T (1996) The application of membrane biological reactors for the treatment of wastewaters. Biotechnol Bioeng 49:601–610. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0290(19960320)49:6<601::AID-BIT1>3.0.CO;2-S
Casey E, Syron E (2008) Membrane-aerated biofilms for high rate biotreatment: performance appraisal, engineering principles, scale-up, and development requirements. Environ Sci Technol 42:1833–1844. doi:10.1021/es0719428
Casey E, Glennon B, Hamer G (1999) Review of membrane aerated biofilm reactors. Resour Conserv Recycl 27:203–215. doi:10.1016/S0921-3449(99)00007-5
Dhillon JK, Shivaraman N (1999) Biodegradation of organic and alkali cyanide compounds in a trickling filter. Indian J Environ Prot 19:805–810
Dias JCT, Rezende RP, Linardi VR (2001) Bioconversion of nitriles by Candida guilliermondii CCT 7202 cells immobilized in barium alginate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:757–761. doi:10.1007/s002530100681
DiGeronimo MJ, Antoine AD (1976) Metabolism of acetonitrile and propionitrile by Nocardia rhodochrous LL 100-21. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:900–906
Endo I, Watanabe I (1989) Nitrile hydratase of Rhodococcus sp. N-774: purification and characterization. FEBS Lett 243:61–64. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(89)81218-9
Fang HHP, Liu H (2002) Effect of pH on hydrogen production from glucose by a mixed culture. Bioresour Technol 82:87–93. doi:10.1016/S0960-8524(01)00110-9
Fayolle F, Vandecasteele JP, Monot F (2001) Microbial degradation and fate in the environment of methyl tert-butyl ether and related fuel oxygenates. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 56:339–349. doi:10.1007/s002530100647
Freitas dos Santos LM, Livingston AG (1995) Membrane-attached biofilms for VOC wastewater treatment. I: novel in situ biofilm thickness technique. Biotechnol Bioeng 47:82–89. doi:10.1002/bit.260470110
García Encina PA, Hidalgo MD (2005) Influence of substrate feed patterns on biofilm development in anaerobic fluidized bed reactors (AFBR). Process Biochem 40:2509–2516. doi:10.1016/j.procbio.2004.10.007
Håkansson K, Welander U, Mattiasson B (2005) Degradation of acetonitrile through a sequence of microbial reactors. Water Res 39:648–654. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2004.10.016
Henahan JF, Idon JD (1971) Setting the world of nitrile chemistry afire. Chem Eng News 49:16–18
Johammsen FR, Levinskas GJ, Bertean PE, Rodwell DE (1986) Evaluation of teratogenic potential of three aliphatic nitriles in the rat. Fundam Appl Toxicol 7:33–40. doi:10.1016/0272-0590(86)90194-6
Kao CM, Chen KF, Liu JK, Chou SM, Chen SC (2006) Enzymatic degradation of nitriles by Klebsiella oxytoca. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:228–233. doi:10.1007/s00253-005-0129-0
Kobayashi M, Yanaka N, Nagasawa T, Yamada H (1990) Purification and characterization of a novel nitrilase of Rhodococcus rhodochrous K 22 that acts on aliphatic nitriles. J Bacteriol 172:4807–4815
Kowalchuk GA, Stephen JR, DeBoer W, Prosser JI, Embley TM, Woldendorp JW (1997) Analysis of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria of the beta subdivision of the class Proteobacteria in coastal sand dunes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and sequencing of PCR-amplified 16S ribosomal DNA fragments. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:1489–1497
Langdanhl BR, Bisp P, Ingvorse K (1996) Nitrile hydrolysis by Rhodococcus eryhropolis BL1, an acetonitrile-tolerant stain isolated from a marine sediment. Microbiology 142:145–154
LaPara TM, Cole AC, Shanahan JW, Semmens MJ (2006) The effects of organic carbon, ammonia-nitrogen, and oxygen partial pressure on the stratification of membrane-aerated biofilms. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 33:315–323. doi:10.1007/s10295-005-0052-5
Li TG, Liu JX, Bai RB, Ohandja DG, Wong FS (2007) Biodegradation of organonitriles by adapted activated sludge consortium with acetonitrile-degrading microorganisms. Water Res 41:3465–3473. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2007.04.033
Manolov T, Kristina H, Benoit G (2005) Continuous acetonitrile degradation in a packed-bed bioreactor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 66:567–574
Millette D, Butler BJ, Frind EO, Comeau Y, Samon R (1998) Substrate interaction during aerobic biodegradation of creosote-related compounds in columns of sandy aquifer material. J Contam Hydrol 29:165–183. doi:10.1016/S0169-7722(97)00015-6
Molin S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2003) Gene transfer occurs with enhanced efficiency in biofilms and induces enhanced stabilization of the biofilm structure. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:255–261. doi:10.1016/S0958-1669(03)00036-3
Moy BYP, Tay JH, Toh SK, Liu Y, Tay STL (2002) High organic loading influences the physical characteristics of aerobic sludge granules. Lett Appl Microbiol 34:407–412. doi:10.1046/j.1472-765X.2002.01108.x
Muñoz R, Jacinto M, Guieysse B, Mattiasson B (2005) Combined carbon and nitrogen removal from acetonitrile using algal-bacterial bioreactors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 67:699–707. doi:10.1007/s00253-004-1811-3
Muyzer G, Dewaal EC, Uitterlinden AG (1993) Profiling of complex microbial populations by denaturing gradient gel-electrophoresis analysis of polymerase chain reaction-amplified genes-coding for 16s ribosomal-RNA. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:695–700
Nawaz MS, Chapatwala KD (1991) Simultaneous degradation of acetonitrile and biphenyl by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Microbiol 37:411–418
Nawaz MS, Chapatwala KD, Wolfram JH (1989) Degradation of acetonitrile by Pseudomonas putida. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:2267–2274
Nawaz MS, Davis JW, Wolfram JH, Chapatwala KD (1991) Degradation of organic cyanides by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 28:865–875. doi:10.1007/BF02922656
Pollak P, Romender G, Hagedorn F, Gelbke HP (1991) In: Elvers B, Hawkins S, Schulz G (eds) Ullman’s encyclopedia of industrial chemistry, vol A17, 5th edn. Wiely-VCH, Weinheim, pp 363–376
Rishell S, Casey E, Glennon B, Hamer G (2004) Mass transfer analysis of a membrane aerated reactor. Biochem Eng J 18:159–167. doi:10.1016/j.bej.2003.08.005
Rothemund C, Amann R, Klugbauer S, Manz W, Bieber C, Schleifer K-H, Wilderer PA (1996) Microflora of 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degrading biofilms on gas permeable membranes. Syst Appl Microbiol 19:608–615
Spain JC, Van Veld PA (1983) Adaptation of natural microbial communities to degradation of xenobiotic compounds: effects of concentration, exposure time, inoculum and structure. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:428–435
Springael D, Peys K, Ryngaert A, Van Roy S, Hooyberghs L, Ravatn R, Heyndrickx M, van der Meer JR, Vandecasteele C, Mergeay M, Diels L (2002) Community shifts in a seeded 3-chlorobenzoate degrading membrane biofilm reactor: indications for involvement of in situ horizontal transfer of the clcelement from inoculum to contaminant bacteria. Environ Microbiol 4:70–80. doi:10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00267.x
Tay STL, Zhuang WQ, Tay JH (2005) Start-up, microbial community analysis and formation of aerobic granules in a tert-butyl alcohol degrading sequencing batch reactor. Environ Sci Technol 39:5774–5780. doi:10.1021/es050278x
Terada A, Yuasa A, Tsuneda S, Hirata A, Katakai A, Tamada M (2005) Elucidation of dominant effect on initial bacterial adhesion onto polymer surfaces prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 43:99–107. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2005.03.016
Tolker-Nielsen T, Molin S (2000) Spatial organization of microbial biofilm communities. Microb Ecol 40:75–84
Wang CC, Lee CM, Chen LJ (2004) Removal of nitriles from synthetic wastewater by acrylonitrile utilizing bacteria. J Environ Sci Health Part A: Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 39:1767–1779. doi:10.1081/ESE-120037876
Watanabe K, Teramoto M, Futamata H, Harayama S (1998) Molecular detection, isolation, and physiological characterization of functionally dominant phenol-degrading bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4396–4402
Yi S, Zhuang WQ, Wu B, Tay STL, Tay JH (2006) Biodegradation of p-nitrophenol by aerobic granules in a sequencing batch reactor. Environ Sci Technol 40:2396–2401. doi:10.1021/es0517771
Zhang T, Fang HH (2001) Phylogenetic diversity of a SRB-rich marine biofilm. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:437–440. doi:10.1007/s002530100770
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Bai, R., Ohandja, DG. et al. Biodegradation of acetonitrile by adapted biofilm in a membrane-aerated biofilm reactor. Biodegradation 20, 569–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9246-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-008-9246-7