Abstract
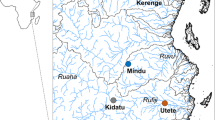
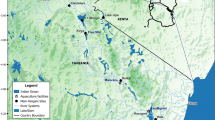
Sometime between 2010 and 2012, Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) invaded the remote Lake Kutubu, in the Southern Highlands of Papua New Guinea, apparently as a result of flooded aquaculture ponds. The subsequent burgeoning population of Tilapia has had apparent impacts on the RAMSAR-listed lakes’ ecology, but paradoxically may be benefiting endemic fish and crustaceans in the lake that have been under severe threat of extinction due to sustenance overfishing. Here, we explore options for eradicating or adaptively managing the invasive Tilapia population, and conclude that it is logistically and socially feasible to use low-risk genetic (chromosomal) technology to establish a non-self-sustaining population in the lake as an alternative protein source for local communities that causes minimal environmental damage while reducing exploitation rates on endemic taxa that have already driven at least three to apparent extinction.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur RI et al (2010) Assessing impacts of introduced aquaculture species on native fish communities: Nile tilapia and major carps in SE Asian waters. Aquaculture 299:81–88
Attayde JL, Brasil J, Menescal RA (2011) Impacts of introducing Nile tilapia on the fisheries of a tropical reservoir in North-eastern Brazil. Fish Manag Ecol 18:437–443
Bacharach E et al (2016) Characterization of a novel orthomyxo-like virus causing mass die-off of tilapia. MBio 7(2):e00431-16. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00431-16
Baroiller JF et al (1995) Treatment and sex chromosomes govern sex ratios of the mouthbrooding cichlid fish Oreochromis niloticus. J Exp Zool 273:216–223
Barria A et al (2020) Genetic parameters for resistance to Tilapia Lake Virus (TiLV) in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 522:735126
Bax N, Thresher RE (2009) Ecological, behavioral, and genetic factors influencing the recombinant control of invasive pests. Ecol Appl 19:873–888
Benedict MQ, Robinson AS (2003) The first releases of transgenic mosquitoes: an argument for the sterile insect technique. Trends Parasitol 19:349–355
Beveridge MCM, Baird DJ (2000) Diet, feeding and digestive physiology. In: Beveridge MCM, McAndrew BJ (eds) Tilapias: biology and exploitation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 59–88
Beveridge MCM, McAndrew BJ (eds) (2000) Tilapias: biology and exploitation. Springer, Dordrecht
Bhjuel RC, Litte DC, Hossain A (2007) Reproductive performance and the growth of pre-stunted and normal Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) broodfish at varying feeding rates. Aquaculture 272:71–79
Bhujel RC (2000) A review of strategies for the management of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) broodfish in seed-production systems, especially hapa-based systems. Aquaculture 181:37–59
Bramick U et al (1995) Testing of triploid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) under tropical pond conditions. Aquaculture 137:343–353
Corlett RT (2017) A bigger toolbox: biotechnology in biodiversity conservation. Trends Biotechnol 35:55–65
D’Cruz R (2008) Lake Kutubu catchment management plan. WWF Kikori River Programme. Aonyx Environmental, Malaysia
Dudgeon D, Smith REW (2006) Exotic species, fisheries and conservation of freshwater biodiversity in tropical Asia: the case of the Sepik River, Papua New Guinea. Aquat Conserv Mar Freshw Ecosyst 16:203–215
El Gamel A-RA et al (1999) Induction of triploidy and tetraploidy in Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J World Aquacult Soc 30:269–275
Eraz AT et al (2004) Sex ratios in the progeny of androgenetic and gynogenetic YY male Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. Aquaculture 232:205–214
Galemoni de Graaf GJF, Huisman EA (2013) Reproductive biology of pond reared Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. Aquacult Res 30:25–33
Galizi R et al (2014) A synthetic sex ratio distortion system for the control of the human malaria mosquito. Nature Comm. 5:3977
Gomez-Marquez JL et al (2008) Age and growth of the tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Perciformes: Cichlidae) from a shallow tropical lake in Mexico. Int J Trop Biol 56:875–884
Gutierrez JB, Teem JL (2006) A model describing the effect of sex-reversed YY fish in an established wild population: the use of a Trojan Y chromosome to cause extinction of an introduced exotic species. J Theor Biol 241:333–341
Gwahaba JJ (1973) Effects of fishing on the Tilapia nilotica (Linne’ 1757) population in Lake George, Uganda over the past 20 years. Afr J Ecol 11:317–328
Haley N, May RJ (eds) (2007) Conflict and resource development in the Southern Highlands of Papua New Guinea. ANU E Press, Canberra. http://epress.anu.edu.au/conflict_citation.html
Hamilton JB, Walter RO, Daniel RM, Mestler GE (1969) Competition for mating between ordinary and supermale Japanese medaka fish. Anim Behav 17:168–176
Harris AF et al (2012) Successful suppression of a field mosquito population by sustained release of engineered male mosquitoes. Nat Biotech 30:828–830
Herbst EC (2002) Induction of tetraploidy in zebrafish Danio rerio and Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Master’s Thesis, Louisiana State University
Husen MA (2014) Impact of invasive alien fish, Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) on native fish catches of sub-tropical lakes (Phewa, Begnas and Rupa) of Pokhara Valley, Nepal. In: Thapa GJ, Subedi N, Pandey MR, Thapa SK, Chapagain NR, Rana A (eds) Proceedings of the international conference on invasive alien species management, pp 112–122. National Trust for Nature Conservation, Nepal
Hydrobiology (2012) The artisianal fishery in Lake Kutubu, Southern Highlands, Papua New Guinea. Hydrobiology Pty. Ltd., Milton
Hydrobiology (2015) Lake Kutubu fish surveys. Draft report. Hydrobiology Pty. Ltd., Milton
Iles TD (1973) Dwarfing or stunting in the genus Tilapia (Cichlidae) a possibly unique recruitment mechanism. J Cons Int Explor Mer 164:247–254
Imbun BY, Smith PT (2018) Recent developments at Lake Kutubu: impacts on the fish and the Foe. Fishes Sahul 31:1224–1238
Jalabert B, Moreau J, Planquette L, Billard R (1974) Determinisme du sexe chez Tilapia macrochir and Tilapia nilotica: action de la methyltestosterone dans l’alimentation des alevins sur la differenciation sexuelle; proportion des sexes dans la descendance des “mbles inversbs”. An. Biol Anim Biochim Biophys 14:729–739
Jansen MD, Dong HT, Mohan CV (2019) Tilapia Lake Virus: a threat to the global tilapia industry? Rev Aquacult 11:725–739
Jenkins, A. 2007. A rapid ecological health assessment of Lake Kutubu Ramsar Site and the status of endemic fish populations. Consultancy report. Wetlands International
Karayucel I et al (2003) Thermal and hormonal feminization of all male YY Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus L. Israeli J Aquacult Bamidgeh 55:114–122
Kendall D, Ford RM (2017) The role of social license in conservation. Conserv Biol 32:493–495
Kirankumar S, Pandian TJ (2003) Production of an androgenetic tiger barb, Puntius tertazona. Aquaculture 228:37–51
Krafsur ES (1998) Sterile insect technique for suppressing and eradicating insect population: 55 years and counting. J Agricult Entomol 15:303–317
Lacroix R et al (2012) Open field release of genetically engineered sterile male Aedes aegypti in Malaysia. PLoS ONE 7(8):e42771. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0042771
Leary T (1997) Subsistence catch monitoring—Lake Kutubu, Southern Highlands Province, PNG, September 1995–February 1997, World Wildlife Fund, Kikori ICDP
Lilley JH, Callinan RB, Chinabut S, Kanchanakhan S, MacRae IH, Phillips MJ (1998) Epizootic ulcerative syndrome (EUS) technical handbook. The Aquatic Animal Health Research Institute, Bangkok, p 88
Little DC, Hulata G (2000) Strategies for tilapia seed production. In: Beveridge MCM, McAndrew BJ (eds) Tilapias: biology and exploitation. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 267–326
Manasi E (2011) Fish audit survey report for Lake Kutubu—Southern Highlands Province. World Wide Fund for Nature. P.O. Box 8280, Boroko, NCD, PNG
Nakamura M, Nozu R, Ijiri S, Kobayashi T, Hirai T, Yamaguchi Y, Seale A, Lerner DT, Grau GE (2015) Sexual characteristics of high-temperature sterilized male Mozambique tilapia, Oreochromis mossambicus. Zool Lett 1:21
Ogutu-Ohwayo R, Hecky RE (1991) Fish introductions in Africa and some of their implications. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48(Suppl. 1):8–12
Pradeep PJ et al (2012) Effects of triploidy induction on growth and masculinization of red tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters, 1852) x Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758). Aquaculture 344–349:181–187
Pullin RSV, Palomares ML, Casal CV, Day MM, Pauly D (1997) Environmental impacts of tilapias. In: Fitzsimmons K (ed) Tilapia aquaculture—proceedings from the fourth international symposium on Tilapia in aquaculture. Northeast regional agricultural engineering service cooperative extension, Ithaca, New York. vol 2, p 554–570
Redford KH, Adams W, Mace GM (2013) Synthetic biology and conservation of nature: wicked problems and wicked solutions. PLoS Biol 11(4):e1001530. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1001530
Rougeot C et al (2007) Sex determination in Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus: effect of high temperature during embryogenesis on sex ratio and sex differentiation pathway. Aquaculture 272(Supplement 1):S306–S307
Sanches FHC, Miyai CA, Costa TM, Christofoletti RA, Volpato GL, Barret RE (2012) Aggressiveness overcomes body-size effects in fights staged between invasive and native fish species with overlapping niches. PLoS ONE 7(1):e29746. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0029746
Scott AG et al (1989) The ‘YY’ supermale in Oreochromis niloticus (L.) and its potential in aquaculture. Aquaculture 78:237–251
Shackleton CM et al (2007) Assessing the effects of invasive alien species on rural livelihoods: case examples and a framework from South Africa. Hum Ecol 35:113–127
Shelton A, Roush R, Wang P, Zhao JZ (2007) Resistance to insect pathogens and strategies to manage resistance: an update. In: Lacey LA, Kaya HK (eds) Field manual of techniques in invertebrate pathology. Springer, Dordrecht
Smith PT (ed) (2007) Aquaculture in Papua New Guinea, Status of freshwater fish farming. ACIAR, Canberra
Smith PT, Imbun BY, Duarte FP (2015) Impacts of a fish kill at Lake Kutubu, Papua New Guinea. Pac Sci 70(1):21–33
Starling F et al (2002) Contribution of omnivorous tilapia to eutrophication of a shallow tropical reservoir: evidence from a fish kill. Freshwater Biol. 47:2443–2452
Sustainability Council of New Zealand (2018) A constitutional moment: gene drive and international governance. www.sustainabilitynz.org. Accessed 3 Sept 2018
Thammatorn W, Rawiwan P, Surachetpong W (2019) Minimal risk of tilapia lake virus transmission via frozen tilapia fillets. J Fish Dis 42:3–9
Thresher RE et al (2014a) Sex-ratio-biasing constructs for the control of invasive lower vertebrates. Nat Biotechnol 32:424–427
Thresher RE, Hayes K, Bax NJ, Teem J, Benfey TJ, Gould F (2014b) Genetic control of invasive fish: technological options and its role in integrated pest management. Biol Invasions 16:1201–1216
van Wilgen BW, Richardson DM (2012) Three centuries of managing introduced conifers in South Africa: benefits, impacts, changing perceptions and conflict resolution. J Environ Manag 106:56–68
Zambrano L et al (2006) Invasive potential of common carp (Cyprinus carpio) and Nile tilpaia (Oreochromis niloticus) in American freshwater systems. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 63:1903–1910
Acknowledgements
We thank Oil Search for initiating these studies, particularly Megan Christensen, General Manager Stakeholder Engagement and Social Responsibility, the Oil Search personnel who organised and participated in the various meetings and visits, particularly Keron Kilip, Cornelius Soagai, Paul Sapake, James Pambori, Cassander Garong and Max Haro, and the staff of the NFA for assisting with the visits to the hatcheries, particularly Lina Pandihau and Billy Kerowa. We also gratefully acknowledge the active engagement of the stakeholder representatives from CEPA, particularly Fabian Taimbari, the NFA, particularly Gideon Pama and Lina Pandihau, and the most importantly the WMA committee, particularly the chairman Lawrence Kage, at the stakeholder meetings. The study simply would not have been possible without that support and interest from all involved in progressing these concepts for Tilapia management.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thresher, R.E., Smith, R. & Cutajar, J. Optimizing the impacts of an invasive species on the threatened endemic biota of a remote RAMSAR site: Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) in Lake Kutubu, Papua New Guinea. Biol Invasions 22, 2661–2670 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-020-02289-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-020-02289-3