Abstract
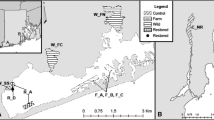
Aquaculture can promote the introduction of non-indigenous species (NIS) into wild marine environments. In addition, NIS aquaculture escapees may hybridize with closely-related native species introducing foreign alleles to their gene pool. To quantify the influence of mussel aquaculture on the native community in British Columbia we sampled mussels from fourteen locations on Vancouver Island. There are two native species in this region, M. trossulus and M. californianus, and two farmed NIS, Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis, both originally from Europe. DNA was extracted from mussel tissue and the mitochondrial cytochrome c oxydase subunit 1 (COI) gene was sequenced. One nuclear locus that exhibits different alleles for M. edulis, M. galloprovincialis and M. trossulus (Glu-5′) was also characterized, using PCR, in order to identify heterozygotes. We found the proportion of NIS introgression depended primarily on farm density. Other habitat traits such as the degree of exposure to the open sea and, to a minor extent, salinity, contributed significantly to explain the distribution of introgressed individuals. Different habitat preference of NIS and native species, and marine currents, provide additional explanations for the distribution of alien and native species along Vancouver Island coasts. As a whole, our results suggest that native M. trossulus populations are more introgressed by M. galloprovincialis genes in open habitats.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Addison JA, Ort BS, Mesa KA, Pogson GH (2008) Range-wide genetic homogeneity in the California sea mussel (Mytilus californianus): a comparison of allozymes, nuclear DNA markers, and mitochondrial DNA sequences. Mol Ecol 17:4222–4232
Anderson AS, Bilodeau AL, Gilg MR, Hilbish TJ (2002) Routes of introduction of the Mediterranean mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) to Puget Sound and Hood Canal. J Shellfish Res 21:75–79
Bayne BL (1965) Growth and delay of metamorphosis of the larvae of Mytilus edulis (L.). Ophelia 2:1–47
Beaumont AR, Abdul-Matin AKM, Seed R (1993) Early development, survival and growth in pure and hybrid larvae of Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis. J Molluscan Stud 59:120–123
Bell EC, Gosline JM (1997) Strategies for life in flow: tenacity, morphometry, and probability of dislodgment of two Mytilus species. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 159:197–208
Bierne N, David P, Boudry P, Bonhomme F (2002) Assortative fertilization and selection at larval stage in the mussels Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis. Evolution 56:292–298
Bierne N, Borsa P, Daguin C, Jollivet D, Viard F, Bonhomme F, David P (2003) Introgression patterns in the mosaic hybrid zone between Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis. Mol Ecol 12:447–461
Bierne N, Bonhomme F, Boudry P, Szulkin M, David P (2006) Fitness landscapes support the dominance theory of post-zygotic isolation in the mussels Mytilus edulis and M. galloprovincialis. Proc R Soc B 273:1253–1260
Blanchfield PJ, Tate LS, Podemski CL (2009) Survival and behaviour of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) released from an experimental aquaculture operation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 66(11):1976–1988
Braby CE, Somero GN (2006) Ecological gradients and relative abundance of native (Mytilus trossulus) and invasive (Mytilus galloprovincialis) blue mussels in the California hybrid zone. Mar Biol 148(6):1249–1262
Carlton JT (1992) Introduced marine and estuarine mollusks of North America: an end-of-the-20th-century perspective. J Shellfish Res 11(2):489–505
Carlton JT (1996) Pattern, process, and prediction in marine invasion ecology. Biol Conserv 78:97–106
Carriker MR (1992) Introductions and transfers of molluscs: risk considerations and implications. J Shellfish Res 11:507–510
Castillo AGF, Ayllon F, Moran P, Izquierdo JI, Martinez JL, Beall E, Garcia-Vazquez E (2008) Interspecific hybridization and introgression are associated with stock transfers in salmonids. Aquaculture 278:31–36
Comesaña AS, Toro JE, Innes DJ, Thompson RJ (1999) A molecular approach to the ecology of a mussel (Mytilus edulis–M. trossulus) hybrid zone on the east coast of Newfoundland Canada. Mar Biol 133:213–221
Consuegra S, Phillips N, Gajardo G, de Leaniz CG (2011) Winning the invasion roulette: escapes from fish farms increase admixture and facilitate establishment of non-native rainbow trout. Evol Appl 4:660–671
Couceiro L, López L, Ruiz JM, Barreiro R (2012) Population structure and range expansion: the case of the invasive gastropod Cyclope neritea in northwest Iberian Peninsula. Integr Zool 7(3):286–298
Daguin C, Borsa P (2000) Genetic relationships of Mytilus galloprovincialis Lamarck populations worldwide: evidence from nuclear-DNA markers. Geol Soc Lond Spec Pub 177(1):389–397
Danancher D, Garcia-Vazquez E (2011) Genetic population structure in flatfishes and potential impact of aquaculture and stock enhancement on wild populations in Europe. Rev Fish Biol Fish 21(3):441–462
Davenne E, Masson D (2001) Water Properties in the Straits of Georgia and Juan de Fuca. Publication of oceanographic processes of interest, 41p. Available online at the Department of Fisheries and Oceans of Canada website (www.pac.dfo-mpo.gc.ca/science/oceans/cotesud-southcoast/JdFG_e.pdf). Last access: 2013/07/07
Dias PJ, Dordor A, Tulett D, Piertney S, Davies IM, Snow M (2009) Survey of mussel (Mytilus) species at Scottish shellfish farms. Aquac Res 40:1715–1722
Didham RK, Tylianakis JM, Gemmell NJ, Rand TA, Ewers RM (2007) Interactive effects of habitat modification and species invasion on native species decline. Trends Ecol Evol 22:489–496
Distel DL (2000) Phylogenetic relationships among Mytilidae (Bivalvia): 18S rRNA data suggest convergence in mytilid plans. Mol Phylogenet Evol 15:25–33
Elliott J, Holmes K, Chambers R, Leon K, Wimberger P (2008) Differences in morphology and habitat use among the native mussel Mytilus trossulus, the non-native M. galloprovincialis, and their hybrids in Puget Sound Washington. Mar Biol 156:39–53
Excoffier L, Lischer HEL (2010) Arlequin suite ver 3.5: a new series of programs to perform population genetics analyses under Linux and Windows. Mol Ecol Res 10:564–567
Fitzpatrick BM, Johnson JR, Kump DK, Shaffer HB, Smith JJ, Voss SR (2009) Rapid fixation of non-native alleles revealed by genome-wide SNP analysis of hybrid tiger salamanders. BMC Evol Biol 9:176
Fleming IA, Gross MR (1993) Breeding success of hatchery and wild coho salmon (Oncorhynchus kisutch) in competition. Ecol Appl 3(2):230–245
Folmer O, Black M, Hoeh W, Lutz R, Vrijenhoek R (1994) DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol Mar Biol Biotech 3(5):294–299
Geller JB (1999) Decline of a native mussel masked by sibling species invasion. Conserv Biol 13:661–664
Geller JB, Carlton JT, Powers DA (1994) PCB-based detection of mtDNA haplotypes of native and invading mussels on the northeastern Pacific coast: latitudinal pattern of invasion. Mar Biol 119:243–249
Gilg MR, Hilbish TJ (2003) The geography of marine larval dispersal: coupling genetics with fine-scale physical oceanography. Ecology 84:2989–2998
Gosling EM (1992) Genetics of Mytilus. In: Gosling E (ed) The mussel Mytilus: ecology, physiology, genetics and culture. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 309–382
Grosholz ED (2002) Ecological and evolutionary consequences of coastal invasions. Trends Ecol Evol 17:22–27
Hall A (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: Paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4(1):9
Heath DD, Rawson PD, Hilbish TJ (1995) PCR-based nuclear markers identify alien blue mussel Mytilus spp. genotypes on the west coast of Canada. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 52:2621–2627
Herlinveaux RH, Tully JP (1961) Some oceanographic features of Juan de Fuca Strait. J Res Bd Canada 18(6):1027–1071
Hilbish TJ (1999) Genetic and ecological consequences of contact between species of Mytilus: lessons from California, Puget Sound and Europe. Bull Aquac Assoc Canada 99:14–16
Hilbish TJ, Mullinax A, Dolven SI, Meyer A, Koehn RK, Rawson PD (2000) Origin of the antitropical distribution pattern in the marine mussels (Mytilus spp.): routes and timing of transequatorial migration. Mar Biol 136:69–77
Hilbish TJ, Carson E, Plante J, Weaver L, Gilg M (2002) Distribution of Mytilus edulis, M. galloprovincialis, and their hybrids in open-coast populations of mussels in southwestern England. Mar Biol 140(1):137–142
Hilbish TJ, Brannock PM, Jones KR, Smith AB, Bullock BN, Wethey DS (2010) Historical changes in the distributions of invasive and endemic marine invertebrates are contrary to global warming predictions: the effects of decadal climate oscillations. J Biogeogr 37:423–431
Hindar K, Ryman N, Utter F (1991) Genetic effects of cultured fish on natural fish populations. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 48:945–957
Horreo JL, Machado-Schiaffino G, Griffiths AM, Bright D, Stevens JR, Garcia-Vazquez E (2014) Long-term effects of stock transfers: synergistic introgression of allochthonous genomes in salmonids. J Fish Biol. doi:10.1111/jfb.12424
Huxel GR (1999) Rapid displacement of native species by invasive species: effects of hybridization. Biol Cons 89:143–152
Inoue K, Waite JH, Matsuoka M, Odo S, Harayama S (1995) Interspecific variations in adhesive protein sequences of Mytilus edulis, M. galloprovincialis, and M. trossulus. Biol Bull 189(3):370–375
Kenchington E, Landry D, Bird CJ (1995) Comparison of taxa of the mussel Mytilus (Bivalvia) by analysis of the nuclear small-subunit rRNA gene sequence. Can J Fish Aquatic Sci 52(12):2613–2620
Koehn RK (1991) The genetics and taxonomy of species in the genus Mytilus. Aquaculture 94:125–145
Lallias D, Stockdale R, Boudry P, Lapègue S, Beaumont AR (2009) Characterization of ten microsatellite loci in the blue mussel Mytilus edulis. J Shellfish Res 28:547–551
Lamaze FC, Sauvage C, Marie A, Garant D, Bernatchez L (2012) Dynamics of introgressive hybridization assessed by SNP population genomics of coding genes in stocked brook charr (Salvelinus fontinalis). Mol Ecol 21:2877–2895
Lewis PN, Riddle MJ, Hewitt CL (2004) Management of exogenous threats to Antarctica and the sub-Antarctic Islands: balancing risks from TBT and non-indigenous marine organisms. Marine Poll Bull 49:999–1005
Linde AR, Izquierdo JI, Moreira J, Garcia-Vazquez E (2008) Invasive Tilapia juveniles are associated with degraded river habitats. Aquat Conserv 18(6):891–895
Lowe S, Browne M, Boudjelas S, De Poorter M (2000) 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species. A selection from the Global Invasive Species Database. Published by The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) a specialist group of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the World Conservation Union (IUCN), 12pp
Lowe MR, Wu W, Peterson MS, Brown-Peterson NJ, Slack WT et al (2012) Survival, growth and reproduction of non-native Nile Tilapia II: fundamental niche projections and invasion potential in the Northern Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 7(7):e41580
Mallet J (2005) Hybridization as an invasion of the genome. Trends Ecol Evol 20(5):229–237
Martinez-Lage A, Rodríguez F, González-Tizón A, Prats E, Cornudella L, Méndez J (2002) Comparative analysis of different satellite DNAs in four Mytilus species. Genome 45:922–929
Masson D, Cummins PF (2004) Observations and modelling of seasonal variability in the Straits of Georgia and Juan de Fuca. J Mar Res 62:491–516
McDonald JH, Seed R, Koehn RK (1991) Allozymes and morphometric characters of three species of Mytilus in the northern and southern hemispheres. Mar Biol 11(1):323–333
McQuaid CD, Phillips TE (2000) Limited wind-driven dispersal of intertidal mussel larvae: in situ evidence from the plankton and the spread of invasive species Mytilus galloprovincialis in South Africa. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 201:211–220
Methratta ET, Menzie CA, Wickwire WT, Richkus WA (2013) Evaluating the risk of establishing a self-sustaining population of non-native oysters through large-scale aquaculture in Chesapeake Bay. Hum Ecol Risk Assess 19(5):1234–1252
Meyer CP, Paulay G (2005) DNA Barcoding: error rates based on comprehensive sampling. PLoS Biol 3(12):e422
Molnar JL, Gamboa RL, Revenga C, Spalding RD (2008) Assessing the global threat of invasive species to marine biodiversity. Front Ecol Environ 6:485–492
Morris RH, Abbott DL, Haderlie EC (1980) Intertidal invertebrates of California. Stanford University Press, Stanford
Naylor RL, Goldburg RJ, Primavera JH, Kautsky N, Beveridge MC, Clay J, Folke C, Lubchenco J, Mooney H, Troell M (2000) Effect of aquaculture on world fish supplies. Nature 405:1017–1024
Pysek P, Jarošík V, Hulme PE, Kühn I, Wild J, Arianoutsou M, Bacher S, Chiron F, Didžiulis V, Essl F, Genovesi P, Gherardi F, Hejda M, Kark S, Lambdon PW, Desprez-Loustau M-L, Nentwig W, Pergl J, Poboljšaj K, Rabitsch W, Roques A, Roy DB, Shirley S, Solarz W, Vilà M, Winter M (2010) Disentangling the role of environmental and human pressures on biological invasions across Europe. Proc Ntl Acad Sci USA 107(27):12157–12162
Quesada H, Gallagher C, Skibinski DAG, Skibinski DOF (1998) Patterns of polymorphism and gene flow of gender-associated mitochondrial DNA lineages in European mussel populations. Mol Ecol 7:1041–1051
Rawson PD, Hilbish TJ (1995) Distribution of male and female mtDNA lineages in populations of blue mussels, Mytilus trossulus and M. galloprovincialis, along the Pacific coast of North America. Mar Biol 124:245–250
Rawson PD, Joyner KL, Meetze K, Hilbish TJ (1996) Evidence for intragenic recombination within a novel genetic marker that distinguishes mussels in the Mytilus edulis species complex. Heredity 77(6):599–607
Rawson PD, Agrawal V, Hilbish TJ (1999) Hybridization between the blue mussels Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. trossulus along the Pacific coast of North America: evidence for limited introgression. Mar Biol 134:201–211
Rhymer JM, Simberloff D (1996) Extinction by Hybridization and Introgression. Ann Rev Ecol Syst 27:83–109
Riginos C, Cunningham CW (2005) Invited Review: local adaptation and species segregation in two mussel (Mytilus edulis × Mytilus trossulus) hybrid zones. Mol Ecol 14:381–400
Robinson TB, Griffiths CL, McQuaid C, Rius M (2005) Marine alien species of South Africa: status and impacts. Afr J Mar Sci 27:297–306
Saavedra C, Stewart DT, Stanwood RR, Zouros E (1996) Species-specific segregation of gender-associated mitochondrial DNA types in an area where two mussel species (Mytilus edulis and M. trossulus) hybridize. Genetics 143:1359–1367
Santaclara FJ, Espiñeira M, Cabado AG, Aldasoro A, Gonzalez-Lavín N, Vieites JM (2006) Development of a method for the genetic identification of mussel species belonging to Mytilus, Perna, Aulacomya, and other genera. J Agric Food Chem 54:8461–8470
Shields JL, Barnes P, Heath DD (2008) Growth and survival differences among native, introduced and hybrid blue mussels (Mytilus spp.): genotype, environment and interaction effects. Mar Biol 154:919–928
Shields JL, Heath JW, Heath DD (2010) Marine landscape shapes hybrid zone in a broadcast spawning bivalve: introgression and genetic structure in Canadian west coast Mytilus. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 399:211–223
Stachowicz JJ, Fried H, Osman RW, Whitlatch RB (2002) Biodiversity, invasion resistance, and marine ecosystem function: reconciling pattern and process. Ecology 83:2575–2590
Suchanek TH (1981) The role of disturbance in the evolution of life history strategies in the intertidal mussels Mytilus edulis and Mytilus californianus. Oecologia 50:143–152
Suchanek TH (1985) Mussels and their role in structuring rocky shore communities. In: Moore PG, Seed R (eds) The Ecology of Rocky Coasts. Hodder & Stoughton, London, pp 70–96
Suchanek TH, Geller JB, Kreiser BR, Mitton JB (1997) Zoogeographic distributions of the sibling species Mytilus galloprovincialis and M. trossulus (Bivalvia: mytilidae) and their hybrids in the North Pacific. Biol Bull 193:187–194
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control región of mitocondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzes. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Thomsen J, Casties I, Pansch C, Körtzinger A, Melzner F (2013) Food availability outweighs ocean acidification effects in juvenile Mytilus edulis: laboratory and field experiments. Glob Change Biol 19:1017–1027
Toro J, Innes DJ, Thompson RJ (2004) Genetic variation among life-history stages of mussels in a Mytilus edulis - M. trossulus hybrid zone. Mar Biol 145:713–725
Veliz D, Duchesne P, Bourget E, Bernatchez L (2006) Stable genetic polymorphism in heterogeneous environments: balance between asymmetrical dispersal and selection in the acorn barnacle. J Evol Biol 19:589–599
Waugh J (2007) DNA barcoding in animal species: progress, potential and pitfalls. BioEssays 29:188–197
Wonham MJ (2004) Mini-Review: distribution of the Mediterranean mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis (Bivalvia: Mytilidae) and hybrids in the northeast Pacific. J Shellfish Res 23(2):535–543
Wood AR, Beaumont AR, Skibinski DOF, Turner G (2003) Analysis of a nuclear-DNA marker for species identification of adults and larvae in the Mytilus edulis complex. J Molluscan Stud 69:61–66
Zbawicka M, Drywa A, Śmietanka B, Wenne R (2012) Identification and validation of novel SNP markers in European populations of marine Mytilus mussels. Mar Biol 159:1347–1362
Zouros E, Oberhauser Ball A, Saavedra C, Freeman KR (1994) An unusual type of mitochondrial DNA inheritance in the blue mussel Mytilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:7463–7467
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to A. Burrill, E. Hertz, Z. Mueller and L. Wiwchar for their assistance with sample collection. We are also thankful to Dr. H. Gurney-Smith for helping with her field knowledge. EGV was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Education (Grant PRX12/00217). VCP held a Cajastur Mobility Grant 2011/2012. This project was supported by the Principado de Asturias (Grant SV-PA-13-ECOEMP-41; GRUPIN14-093) and the Spanish National Grant MINECO CGL2013-42415-R, in collaboration with the Campus of Excellence of the University of Oviedo, and the Liber Ero endowment (FJ) and by NSERC (Canada) Discovery Grants (JST, FJ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crego-Prieto, V., Ardura, A., Juanes, F. et al. Aquaculture and the spread of introduced mussel genes in British Columbia. Biol Invasions 17, 2011–2026 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0853-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-015-0853-z