Abstract
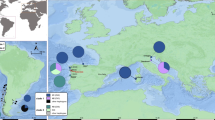
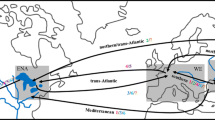
Knowledge about the spatial–temporal dynamics of biological invasions often remains incomplete, because precise information about the invaders’ arrival dates is rare. This applies to the quagga mussel, which has become one of the most successful invasive species in Western European freshwaters. We here used cryogenically stored Dreissena samples from the German Environmental Specimen Bank to reconstruct the colonization history of the quagga mussel in German river systems. Our retrospective genetic analysis significantly improved upon previous findings of when the quagga mussel arrived in Germany and can be used as chronological landmarks to reconstruct its range expansion. The discovery of Dreissena rostriformis in 2004 in the Rhine River near Koblenz presented the first record of this species not only in Germany, but also in Western Europe. Our results show that the quagga mussel had already invaded not only large parts of the Rhine and the Danube, but also the Elbe River. This demonstrates the value of cryobanked biological samples for the retrospective analysis of biological ‘pollution’ through alien invasive species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astanei I, Gosling E, Wilson J, Powell E (2005) Genetic variability and phylogeography of the invasive zebra mussel, Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas). Mol Ecol 14:1655–1666
Baldwin BS, Mayer MS, Dayton J, Pau N, Mendilla J, Sullivan M, Moore A, Ma A, Mills EL (2002) Comparative growth and feeding in zebra and quagga mussels (Dreissena polymorpha and Dreissena bugensis): implications for North American lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 59(4):680–694
bij de Vaate A (2010) Some evidence for ballast water transport being the vector of the quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis Andrusov, 1897) introduction into Western Europe and subsequent upstream dispersal in the River Rhine. Aquat Invasions 5(2):207–209
bij de Vaate A, Beisel J-N (2011) Range expansion of the quagga mussel Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) in Western Europe: first observation from France. Aquat Invasions 6(Supplement 1):S71–S74
Diggins TP (2001) A seasonal comparison of suspended sediment filtration by quagga (Dreissena bugensis) and zebra (D. polymorpha) mussels. J Great Lakes Res 27(4):457–466
Estoup A, Guillemaud T (2010) Reconstructing routes of invasion using genetic data: why, how and so what? Mol Ecol 19:4113–4130
Federal Environment Agency (2008) German Environmental Specimen Bank-Conception. Federal Environment Agency, Berlin
Feldheim KA, Brown JE, Murphy DJ, Stepien CA (2011) Microsatellite loci for dreissenid mussels (Mollusca: Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) and relatives: markers for assessing exotic and native populations. Mol Ecol Resour 11(4):725–732
Haybach A, Christmann K-H (2009) Erster Nachweis der Quaggamuschel Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) im Niederrhein von Nordrhein-Westfalen. Lauterbornia 67:69–72
Heiler KCM, Brandt S, Albrecht C, Hauffe T, Wilke T (2012) A new approach for dating introduction events of the quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis). Biol Invasions 14(7):1311–1316. doi:10.1007/s10530-011-0161-1
Heiler KCM, bij de Vaate A, Ekschmitt K, Ekschmitt K, vo PV, Albrecht C, Wilke T (2013) Reconstruction of the early invasion history of the quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis) in Western Europe. Aquat Invasions 8(1):53–57
Imo M, Seitz A, Johannesen J (2010) Distribution and invasion genetics of the quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis) in German rivers. Aquat Ecol 44(4):731–740
Lockwood JL, Hoopes MF, Marchetti MP (2007) Invasion ecology. Blackwell Publishing, Malden
Martens A, Grabow K, Schoolmann G (2007) Die Quagga-Muschel Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) am Oberrhein (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae). Lauterbornia 61:145–152
May B, Marsden JE (1992) Genetic identification of another invasive species of Dreissenid mussel in the Great Lakes. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 49:1501–1506
Mayer S, Rander A, Grabow K, Martens A (2009) Binnenfrachtschiffe als Vektoren der Quagga-Muschel Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov) im Rhein (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae). Lauterbornia 67:63–67
Molloy DP, bij de Vaate A, Wilke T, Giamberini L (2007) Discovery of Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov 1897) in Western Europe. Biol Invasions 9(7):871–874
Naish KA, Boulding EG (2001) Trinucleotide microsatellite loci for the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha, an invasive species in Europe and North America. Mol Ecol Notes 1:286–288
Orlova MI, Muirhead JR, Antonov PI, Shcherbina GK, Starobogatov YI, Biochino GI, Therriault TW, MacIsaac HJ (2004) Range expansion of quagga mussels Dreissena rostriformis bugensis in the Volga River and Caspian Sea basin. Aquat Ecol 38(4):561–573
Orlova MI, Therriault TW, Antonov PI, Shcherbina GK (2005) Invasion ecology of quagga mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis): a review of evolutionary and phylogenetic impacts. Aquat Ecol 39(4):401–418
Pathy DA, Mackie GL (1993) Comparative shell morphology of Dreissena polymorpha, Mytilopsis leucophaeata, and the “quagga” mussel (Bivalvia: Dreissenidae) in North America. Can J Zool 71:1012–1023
Popa OP, Popa LO (2006) The most westward European occurrence point for Dreissena bugensis (Andrusov 1897). Malacol Bohemoslov 5:3–5
Ram JL, Karim AS, Banno F, Kashian DR (2012) Invading the invaders: reproductive and other mechanisms mediating the displacement of zebra mussels by quagga mussels. Invertebr Reprod Dev 56(1):21–32. doi:10.1080/07924259.2011.588015
Ricciardi A, Whoriskey FG (2004) Exotic species replacement: shifting dominance of dreissenid mussels in the Soulanges Canal, upper St. Lawrence River, Canada. J N Am Benthol Soc 23(3):507–514
Schöll F, Eggers TO, Haybach A, Gorka M, Klima M, König B (2012) Verbreitung von Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) in Deutschland (Mollusca: Bivalvia). Lauterbornia 74:111–115
Son MO (2007) Native range of the zebra mussel and quagga mussel and new data on their invasions within the Ponto-Caspian region. Aquat Invasions 2(3):147–184
Stepien CA, Grigorovich IA, Gray MA, Sullivan TJ, Yerga-Woolwine S, Kalayci G (2013) Evolutionary, biogeographic, and population genetic relationships of dreissenid mussels, with revision of component taxa. In: Nalepa T, Schloesser D (eds) Quagga and zebra mussels: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 403–444
Thomas G, Hammouti N, Seitz A (2011) New polymorphic microsatellite loci for the zebra mussel Dreissena polymorpha (Pallas, 1771), a common bioindicator. J Shellfish Res 30(1):123–126
van der Velde G, Platvoet D (2007) Quagga mussels Dreissena rostriformis bugensis (Andrusov, 1897) in the Main River (Germany). Aquat Invasions 2(3):261–264
van der Velde G, Rahagopal S, bij de Vaate A (2010) From zebra mussel to quagga mussel: an introduction to the Dreissenidae. In: van der Velde G, Rahagopal S, bij de Vaate A (eds) The zebra mussel in Europe. Backhuys Publishers Margraf Publishers, Leiden Weikersheim, pp 1–10
Wagner G, Bartel M, Klein R, Neitzke M, Nentwich K, Quack M (2003) Guideline for sampling and sample treatment zebra mussel (Dreissena polymorpha). In: Agency FE (ed) Guidelines for sampling, transport, storage and chemical characterisation of environmental- and human organ samples. Federal Environment Agency, Berlin
Williamson M (1996) Biological invasions. Chapman & Hall, London
Wilson AB, Boulding EG, Naish KA (1999) Characterization of tri- and tetranucleotide microsatellite loci in the invasive mollusk Dreissena bugensis. Mol Ecol 8:692–693
Wong WH, Holdren GC, Tietjen T, Gerstenberger S, Moore B, Turner K, Wilson DC (2013) Effects of invasive quagga mussels (Dreissena rostriformis bugensis) on chlorophyll and water clarity in Lakes Mead and Havasu of the lower Colorado River Basin, 2007–2009. In: Nalepa T, Schloesser D (eds) Quagga and zebra mussels: biology, impacts, and control, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 495–508
Zhulidov AV, Kozhara AV, Scherbina GH, Nalepa TF, Protasov A, Afanasiev SA, Pryanichnikova EG, Zhulidov DA, Gurtovaya TY, Pavlov DF (2010) Invasion history, distribution, and relative abundances of Dreissena bugensis in the old world: a synthesis of data. Biol Invasions 12(7):1923–1940
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the contributions of all past and present partners to the routine operations of the German Environmental Specimen Bank. The continuous funding by the German Federal Ministry for the Environment, Nature Conservation, Building and Nuclear Safety and the organization by the Federal Environment Agency is gratefully acknowledged. Furthermore we want to thank the Federal Environment Agency (A. Körner) for the clearance of Dreissena subsamples and Dr. H. Rüdel from the Fraunhofer Institute for Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology for the swift provision of the homogenates. Valentin Mingo helped substantially during the genetic studies in the laboratory. We also want to thank our ESB project team Trier for the assistance with sampling and data acquisition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paulus, M., Teubner, D., Hochkirch, A. et al. Journey into the past: using cryogenically stored samples to reconstruct the invasion history of the quagga mussel (Dreissena rostriformis) in German river systems. Biol Invasions 16, 2591–2597 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-014-0689-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10530-014-0689-y