Abstract
Objective
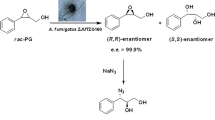
To produce (S)-3-hydroxy-1-(3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-4-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-1-one (S)-1 from 4-oxo-4-[3-(trifluoromethyl)-5,6-dihydro [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl)-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-one (2) by microbial bioreduction.
Results
A new isolate of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes reduced enantioselectively prochiral ketone 2 to chiral alcohol (S)-1. Whole cells of the bacterium were tolerant towards 20 % (v/v) DMSO and 10 g 2/l. Under the optimal conditions, the preparative-scale bioreduction yielded (S)-1 at 90 % yield and >99 % ee. Cells could be re-used with the yield and ee of product being 45 % and >99 %, respectively, after five cycles.
Conclusion
Bioreduction using whole cells of P. pseudoalcaligenes is an attractive approach to produce (S)-1, as a chiral intermediate of the anti-diabetic drug, sitagliptin.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bornscheuer UT, Huisman GW, Kazlauskas RJ, Lutz S, Moore JC, Robins K (2012) Engineering the third wave of biocatalysis. Nature 485:185–194
Davies SG, Ai MF, Lv L, Roberts PM, Thomson JE (2012) Asymmetric synthesis of (-)-(R)- sitagliptin. Tetrahed Lett 53:3052–3055
Hansen KB, Balsells J, Dreher S, Hsiao Y, Kubryk M, Palucki M, Rivera N, Steinhuebel D, Armstrong JD, Askin D, Grabowski EJJ (2005) First generation process for the preparation of the DPP-IV inhibitor sitagliptin. Org Pro Res Dev 9:634–639
Hansen KB, Yi H, Xu F, Rivera N, Clausen A, Kubryk M, Krska S, Rosner T, Simmons B, Balsells J, Ikemoto N, Sun Y, Spindler F, Malan C, Grabowski EJJ, Armstrong JD (2009) Highly efficient asymmetric synthesis of sitagliptin. J Am Chem Soc 131:8798–8804
Karasik A, Aschner P, Katzeff H, Davies MJ, Stein PP (2008) Sitagliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes: a review of recent clinical trials. Curr Med Res Opin 24:489–496
Kim D, Wang L, Beconi M, Eiermann GJ, Fisher MH et al (2005) (2R)-4-oxo-4-[3-(trifleotometh-yl)-5,6-dihydro[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-a]pyrazin-7(8H)-yl]-1-(2,4,5-trifluorophenyl)butan-2-amine: a potent, orally active dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Med Chem 48:141–151
Kumar S, Nei M, Dudley J, Tamura K (2008) MEGA: a biologist-centric software for evolutionary analysis of DNA and protein sequences. Brief Bioinform 9:299–306
Lee M, Rhee MK (2015) Sitagliptin for Type 2 diabetes: a 2015 update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 13:597–610
Liu F, Yu WS, Ou WH, Wang XK, Ruan LB, Li LM, Peng XJ, Tao XH, Pan XH (2010) The asymmetric synthesis of Sitagliptin, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J Chem Res 34:230–232
Ni Y, Xu JH (2002) Asymmetric reduction of aryl ketones with a new isolate Rhodotorula sp. AS 2.2241. J Mol Catal B Enzym 18:233–241
Pan XH, Li XJ, Lu QL, Yu WS, Li WJ, Zhang QH, Deng F, Liu F (2013) Efficient synthesis of sitagliptin phosphate, a novel DPP-IV inhibitor, via a chiral aziridine intermediate. Tetrahed Lett 54:6807–6809
Patel RN (2013) Biocatalytic synthesis of chiral alcohols and amino acids for development of pharmaceuticals. Biomolecules 3:741–777
Reetz MT (2011) Laboratory evolution of stereoselective enzymes: a prolific source of catalysts for asymmetric reactions. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:138–174
Savile CK, Janey JM, Mundorff EC, Moore JC, Tam S, Jarvis WR, Colbeck JC, Krebber A, Fleitz FJ, Brands J, Devine PN, Huisman GW, Hughes GJ (2010) Biocatalytic asymmetric synthesis of chiral amines from ketones applied to sitagliptin manufacture. Science 329:305–309
Soni P, Banerjee UC (2005) Biotransformations for the production of the chiral drug (S)-Duloxetine catalyzed by a novel isolate of Candida tropicalis. Appl Microbiol Biot 67:771–777
Yokoh H, Kobayashi K, Sato Y, Takemoto M, Uchida D, Kanatsuka A, Kuribayashi N, Terano T, Hashimoto N, Sakurai K, Hanaoka H, Ishikawa K, Onishi S, Yokote K (2015) Efficacy and safety of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin compared with alpha-glucosidase inhibitor in japanese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin or pioglitazone alone (study for an ultimate combination therapy to control diabetes with sitagliptin-1): a multicenter, randomized, open-label, non-inferiority trial. J Diabet Investig 6:182–191
Zeng LL, Ding YJ, Zhang GC, Song HR, Hu WH (2009) A practical synthesis of trifluorophenyl R-amino acid: The key precursor for the new anti-diabetic drug sitagliptin. Chin Chem Lett 20:1397–1399
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the Application Development Progam Chongqing Municipality (CSTC2013yykfa10017).
Supporting Information
Details of the microbial screening procedure.
Supplementary Table 1—Microorganisms screened for the reduction of 2 to (5)-1.
Supplementary Table 2—Morphological characterization, biochemical and physiological characteristics of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes XW-40.
Supplementary Fig. 1—Neighbor-joining phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences shows the relationship of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes XW-40 and its related taxa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Xia, S., He, C. et al. Highly enantioselective production of a chiral intermediate of sitagliptin by a novel isolate of Pseudomonas pseudoalcaligenes . Biotechnol Lett 38, 841–846 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2051-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2051-1