Abstract
Objectives
Neurosporene is a carotene and an intermediate in the synthesis of lycopene from phytoene. Its content in carotenogenic organisms is very low; hence, the complete assignments of its spectroscopic data, including NMR, are insufficient.
Results
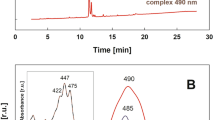
A purple bacterium of Rhodobacter sphaeroides G1C mutant had only one carotenoid. This carotenoid was extracted and purified using silica gel, DEAE-Toyopearl and C18-HPLC columns. It was identified using its absorption spectra, mass spectra, and 1H- and 13C-NMR spectra, including two-dimensional spectral analyses.
Conclusion
The major carotenoid in the Rhodobacter sphaeroides G1C mutant was identified as neurosporene (7,8-dihydro-ψ,ψ-carotene) using spectroscopic measurements, including complete assignments of its 1H- and 13C-NMR spectral data.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H (2004) Carotenoids handbook. Birkhäuser, Basel
Englert G (1995) NMR spectroscopy. In: Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H (eds) Carotenoids vol. 1B, spectroscopy. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 147–260
Harada J, Nagashima KVP, Takaichi S, Misawa N, Matsuura K, Shimada K (2001) Phytoene desaturase, CrtI, of the purple photosynthetic bacterium, Rubrivivax gelatinosus, produces both neurosporene and lycopene. Plant Cell Physiol 42:1112–1118
Ramaprasad EVV, Sasikala Ch, Ramana ChV (2013) Neurosporene is the major carotenoid accumulated by Rhodobacter viridis JA737. Biotechnol Lett 35:1093–1097
Sasa T, Suda S, Watanabe MM, Takaichi S (1992) A yellow marine Chlamydomonas: morphology and pigment composition. Plant Cell Physiol 33:527–534
Scolnik P, Walker MA, Marrs BL (1980) Biosynthesis of carotenoids derived from neurosporene in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. J Biol Chem 255:2427–2432
Takaichi S (2000) Characterization of carotenes in a combination of a C18 HPLC column with isocratic elution and absorption spectra with a photodiode-array detector. Photosynth Res 65:93–99
Takaichi S (2009) Distribution and biosynthesis of carotenoids. In: Hunter CN, Daldal F, Thurnauer MC, Beatty JT (eds) The purple phototrophic bacteria. Springer, New York, pp 97–117
Takaichi S (2014) General methods for identification of carotenoids. Biotechnol Lett 36:1127–1128
Takaichi S, Shimada K (1992) Characterization of carotenoids in photosynthetic bacteria. Methods Enzymol 213:374–385
Supporting information
Supplementary Fig. 1—1H-1H COSY spectrum of the carotenoid in CDCl3.
Supplementary Fig. 2—NOESY spectrum of the carotenoid in CDCl3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takaichi, S., Maoka, T. Identification and spectroscopic characterization of neurosporene. Biotechnol Lett 37, 2027–2031 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1884-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1884-3