Abstract
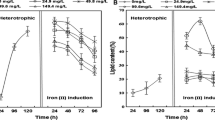
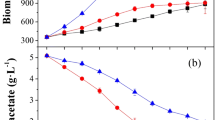
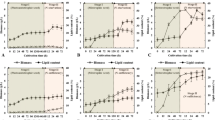
A heterotrophic-Na+ induction (HNI) two-step regime was developed to enhance lipid accumulation in oleaginous Chlorella vulgaris. C. vulgaris was cultivated heterotrophically to a biomass of 7.8 g l−1 in 120 h. The cells were re-suspended in fresh media supplemented with 0.5 M NaCl followed by 12 h growth to accumulate lipid to 53.4 % (w/w). The lipid productivity (625 mg l−1 day−1) achieved with HNI was better than that using heterotrophy alone (405 mg l−1 day−1). To promote possible applications of HNI strategy in other microalgal species, the lipid triggers and potential molecular pathways associated with lipid biosynthesis were investigated. Malic enzyme and acyl-CoA-binding protein were key metabolic checkpoints found to modulate lipid biosynthesis in cells. These results provide the foundation to develop high-lipid engineering miroalgae for industrialization of biodiesel.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babuskin S, Radhakrishnan K, Babu PAS, Sivarajan M, Sukumar M (2014) Effect of photoperiod, light intensity and carbon sources on biomass and lipid productivities of Isochrysis galbana. Biotechnol Lett 23:1539–1545
Choi YE, Hwang H, Kim HS, Ahn JW, Jeong WJ, Yang JW (2013) Comparative proteomics using lipid over-producing or less-producing mutants unravels lipid metabolisms in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Bioresour Technol 145:108–115
Dehesh K, Tai H, Edwards P, Byrne J, Jaworski JG (2001) Overexpression of 3-ketoacyl-acyl-carrier protein synthase IIIs in plants reduces the rate of lipid synthesis. Plant Physiol 125:1103–1114
Du CX, Fan HF, Guo SR, Tezuka K, Li J (2010) Proteomic analysis of cucumber seedling roots subjected to salt stress. Phytochemistry 71:1450–1459
Gaspa ML, Jesch SA, Viswanatha R, Antosh AL, Brown WJ, Kohlwein SD, Henry SA (2008) A block in endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi trafficking inhibits phospholipid synthesis and induces neutral lipid accumulation. J Biol Chem 283:25735–25751
Guarnieri MT, Nag A, Yang S, Pienkos PT (2013) Proteomic analysis of Chlorella vulgaris: potential targets for enhanced lipid accumulation. J Proteomics 93:245–253
Hu Q, Sommerfeld M, Jarvis E, Ghirardi M, Posewitz M, Seibert M, Darzins A (2008) Microalgal triacylglycerols as feedstocks for biofuel production: perspectives and advances. Plant J 54:621–639
Jiang Y, Yang B, Harris NS, Deyholos MK (2007) Comparative proteomic analysis of NaCl stress-responsive proteins in Arabidopsis roots. J Exp Bot 57:3591–3607
Li YJ, Fei XW, Deng XD (2012) Novel molecular insights into nitrogen starvation-induced triacylglycerols accumulation revealed by differential gene expression analysis in green algae Micractinium pusillum. Biomass Bioenerg 42:199–211
Li YQ, Mu JX, Chen D, Han FX, Xu H, Kong F, Xie F, Feng B (2013) Production of biomass and lipid by the microalgae Chlorella protothecoides with heterotrophic-Cu(II) stressed (HCuS) coupling cultivation. Bioresour Technol 148:283–292
Lu Y, Zhai Y, Liu MS, Wu QY (2010) Biodiesel production from algal oil using cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) as feedstock. J Appl Phycol 22:573–578
Lu N, Wei D, Jiang XL, Chen F, Yang ST (2012) Regulation of lipid metabolism in the snow alga Chlamydomonas nivalis in response to NaCl stress: an integrated analysis by cytomic and lipidomic approaches. Process Biochem 47:1163–1170
Mérida I, Ávila-Flores A, Merino E (2008) Diacylglycerol kinase: at the hub of cell signalling. Biochem J 409:1–18
Ratledge C (2014) The role of malic enzyme as the provider of NADPH in oleaginous microorganisms: a reappraisal and unsolved problems. Biotechnol Lett 36:1557–1568
Sheng J, Kim HW, Badalamenti JP, Zhou C, Sridharakrishnan S, Krajmalnik-Brown R, Rittmann BE, Vannela R (2011) Effects of temperature shifts on growth rate and lipid characteristics of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803 in a bench-top photobioreactor. Bioresour Technol 102:11218–11225
Takagi M, Karseno Yoshida T (2006) Effect of salt concentration on intracellular accumulation of lipids and triacylglyceride in marine microalgae Dunaliella cells. J Biosci Bioeng 101:223–226
Wang DZ, Li C, Zhang Y, Wang YY, He ZP, Lin L, Hong HS (2012) Quantitative proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins in the toxicity-lost mutant of Alexandrium catenella (Dinophyceae) in the exponential phase. J Proteomics 75:5564–5577
Wei AL, Zhang XW, Wei D, Chen G, Wu QY, Yang ST (2009) Effects of cassava starch hydrolysate on cell growth and lipid accumulation of the heterotrophic microalgae Chlorella protothecoides. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:1383–1389
Wijffels RH, Barbosa MJ (2010) An outlook on microalgal biofuels. Science 329:769–799
Yeesang C, Cheirsilp B (2011) Effect of nitrogen, salt, and iron content in the growth medium and light intensity on lipid production by microalgae isolated from freshwater sources in Thailand. Bioresour Technol 102:3034–3040
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (21306161), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation Funded Project (2012M521531 and 2014T70775), and Hunan Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (13JJ3062).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Mu, J., Chen, D. et al. Proteomics analysis for enhanced lipid accumulation in oleaginous Chlorella vulgaris under a heterotrophic-Na+ induction two-step regime. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1021–1030 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1758-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1758-0