Abstract
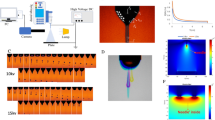
Bio-electrospraying (BES) is a technique for directly jetting living cells that has significant implications for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. However, the effect of BES on human adipose-derived stem cells (hASCs) remains unknown. Here, we show that an hASC suspension was successfully electrosprayed via a continuous, stable and linearly directed electrospray at 10 kV and at 3 ml/h. Morphological observations and Trypan Blue and CCK-8 assays revealed that the cells remained viable and proliferated at a rate similar to that of the controls (0 kV). However, at 20 kV, BES became unstable and cell viability was reduced. Moreover, hASCs electrosprayed at 10 kV retained their multilineage potential, successfully differentiating into chondrogenic, osteogenic and neurogenic lineages. Thus, BES does not significantly affect cell morphology, viability or multipotency.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 February 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-021-03102-4
References
Chen W, Han Y, Chen Y, Xie JX (1998) Field-induced electroconformational damages in cell membrane proteins: a new mechanism involved in electrical injury. Bioelectrochem Bioenerg 47:237–245
Davalos RV, Rubinsky B (2008) Temperature considerations during irreversible electroporation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 51:5617–5622
DeBruin KA, Krassowska W (1999) Modeling electroporation in a single cell. I. Effects of field strength and rest potential. Biophys J 77:1213–1224
Jaworek A, Krupa A (1999) Classification of the modes of EHD spraying. J Aerosol Sci 30:873–893
Jayasinghe SN (2007) Bio-electrosprays: the development of a promising tool for regenerative and therapeutic medicine. Biotechnol J 8:934–937
Jayasinghe SN (2011) Bio-electrosprays: from bio-analytics to a generic tool for the health sciences. Analyst 136:878–890
Lin Y, Wang T, Wu L, Jing W, Chen X, Li Z, Liu L, Tang W, Zheng X, Tian W (2007) Ectopic andin situ bone formation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells in biphasic calcium phosphate nanocomposite. J Biomed Mater Res A 81:900–910
Mongkoldhumrongkul N, Flanagan JM, Jayasinghe SN (2009) Direct jetting approaches for handling stem cells. Biomed Mater 4:15–18
Patel AS, Smith A, Attia RQ, Mattock K, Humphries J, Lyons O, Saha P, Modarai B, Jayasinghe SN (2012) Encapsulation of angiogenic monocytes using bio-spraying technology. Integr Biol 4:628–632
Selimović S, Jonghyun O, Hojae B, Dokmeci M, Khademhosseini A (2012) Microscale strategies for generating cell-encapsulating hydrogels. Polymers 4:1554–1579
Shin JY, Park J, Jang HK, Lee TJ, La WG, Bhang SH, Kwon KI, Kwon OH, Kim BS (2012) Efficient formation of cell spheroids using polymer nanofibers. Biotechnol Lett 34:795–803
Ye C, Hu P, Ma MX, Xiang Y, Liu RG, Shang XW (2009) PHB/PHBHHx scaffolds and human adipose-derived stem cells for cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials 30:4401–4406
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, DeUgarte DA, Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P, Hedrick MH (2002) Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4279–4295
Acknowledgments
We thank Mr. Li Rui and Luo Wanlun for their academic support. This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (81360232), the Key Project of Chinese Ministry of Education (2012156), and the Department of Science and Technology (G20107015, 20103166, LG2012008) and the Department of Education (2009143) of Guizhou Province.
Supporting Information
Supplementary Table 1—Sequences of the primers for the analyzed genes
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, C., He, Z., Lin, Y. et al. Bio-electrospraying is a safe technology for delivering human adipose-derived stem cells. Biotechnol Lett 37, 449–456 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1693-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1693-0