Abstract
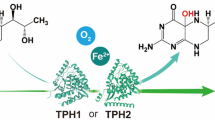
Hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase (H6H; EC 1.14.11.11) converts hyoscyamine to scopolamine in the last step of scopolamine biosynthetic pathway. The gene encoding H6H in Anisodus acutangulus was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli and the recombinant proteins fused with His-tag or GST-tag at its N-terminal were purified and then confirmed by Western bolt analysis. The biofunctional assay revealed that the His-AaH6H and GST-AaH6H converted hyoscyamine (40 mg/l) to scopolamine at 32 and 31 mg/l, respectively. This is the first report on AaH6H expression, purification and functional characterization facilitates further genetic improvement of scopolamine yield in A. acutangulus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardillo AB, Talou JR, Giulietti AM (2008) Expression of Brugmansia candida Hyoscyamine 6beta-Hydroxylase gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its potential use as biocatalyst. Microb Cell Fact 7:17
Hashimoto T, Yamada Y (1987) Purification and characterization of hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase from root cultures of Hyoscyamus niger. Eur J Biochem 164(2):277–285
Hashimoto T, Matsuda J, Yamada Y (1993) Two-step epoxidation of hyoscyamine to scopolamine is catalyzed by bifunctional hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase. FEBS Lett 329(1–2):35–39
Jouhikainen K, Lindgren L, Jokelainen T, Hiltunen R, Teeri T, Oksman-Caldentey KM (1999) Enhancement of scopolamine production in Hyoscyamus muticus L. hairy root cultures by genetic engineering. Planta 208:545–551
Kai GY, Chen JF, Li L, Zhou GY, Zhou LM, Zhang L, Chen YH, Zhao LX (2007) Molecular cloning and characterization of a new cDNA encoding hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase from root of Anisodus acutangulus. J Biochem Mol Biol 40(5):715–722
Kai GY, Zhang Y, Chen JF, Li L, Yan XM, Zhang R, Liao P, Lu X, Wang W, Zhou GY (2009a) Molecular characterization and expression analysis of two distinct putrescine N-methyltransferases from roots of Anisodus acutangulus. Physiol Plant 135(2):121–129
Kai GY, Li L, Jiang YX, Yan XM, Zhang Y, Lu X, Liao P, Chen JB (2009b) Molecular cloning, characterization of two tropinone reductases in Anisodus acutangulus and enhancement of tropane alkaloids production AaTRI transformed hairy roots. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 54(3):177–186
Liu T, Zhu P, Cheng KD, Meng C, He HX (2005) Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of hyoscyamine 6beta-hydroxylase from hairy roots of Anisodus tanguticus. Planta Med 71(3):249–253
Matsuda J, Okabe S, Hashimoto T, Yamada Y (1991) Molecular cloning of hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase, a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, from cultured roots of Hyoscyamus niger. J Biol Chem 266(15):9460–9464
Suzuki K, Yun DJ, Chen XY, Yamada Y, Hashimoto T (1999) An Atropa belladonna hyoscyamine 6-hydroxylase gene is differentially expressed in the root pericycle and anthers. Plant Mol Biol 40:141–152
Yun DJ, Hashimoto T, Yamada Y (1992) Metabolic engineering of medicinal plants: Transgenic Atropa belladonna with an improved alkaloid composition. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(24):11799–11803
Zarate R, El Jaber-Vazdekis N, Medina B, Ravelo AG (2006) Tailoring tropane alkaloid accumulation in transgenic hairy roots of Atropa baetica by over-expressing the gene encoding hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase. Biotechnol Lett 28(16):1271–1277
Zhang L, Ding RX, Chai YR, Bonfill M, Piñol MT, Xu TF, Pi Y, Wang ZN, Zhang HM, Kai GY, Liao ZH, Sun XF, Tang K (2004) Engineering tropane biosynthetic pathway in Hyoscyamus niger hairy root cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101(17):6786–6791
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Fund (30900110), National Transgenic Organism New Variety Culture Key Project (2009ZX08012-002B), Project from Ministry of Science and Technology of China (NC2010AE0075, NC2010AE0372), Shanghai Science and Technology Committee Project (10JC1412000, 09QH1401900, 06QA14038, 08391911800, 073158202, 075405117, 065458022, 05ZR14093), Kunshan Municipal Science & Technology Project (KS0914), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Fund (Y2080621), Program from Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (06DZ015, 09ZZ138), Fujian Science and Technology Committee Key Special Project (2008NZ0001-4), Leading Academic Discipline Project of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (J50401) and Project from Shanghai Normal University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kai, G., Liu, Y., Wang, X. et al. Functional identification of hyoscyamine 6β-hydroxylase from Anisodus acutangulus and overproduction of scopolamine in genetically-engineered Escherichia coli . Biotechnol Lett 33, 1361–1365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0575-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-011-0575-y