Abstract
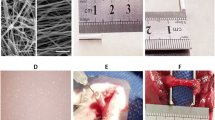
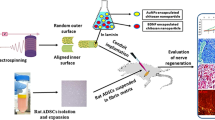
Immunophilin ligand FK506 has been treated as adjunct therapy for nerve repair due to its potent neurotrophic and neuroprotective actions. It was hypothesized that FK506 releasing from biodegradable chitosan guide provided better nerve regenerative response than the guide with no FK506. The drug was entrapped in the semi-permeable wall of chitosan guide with the drug-loading of 647 μg/g. Rat sciatic nerve defect model treated with FK506-releasing chitosan guide showed more mature appearance of myelinated fibers 8 weeks after surgery; furthermore, the motor functional reinnervation occurred, the amplitude and velocity of compound muscle action potentials reached 60% and 73% with respect to the normal. Thus, FK506-releasing chitosan guide should be acted as a long-lasting delivery device of immunosuppressive and neuroregenerative agent for peripheral nerve repair.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alluin O, Wittmann C, Marqueste T et al (2009) Functional recovery after peripheral nerve injury and implantation of a collagen guide. Biomaterials 30:363–373
Chavez-Delgado ME, Gomez-Pinedo U, Feria-Velasco A et al (2005) Ultrastructural analysis of guided nerve regeneration using progesterone- and pregnenolone-loaded chitosan prostheses. J Biomed Mater Res 74B:589–600
Chen B, Song YX, Liu ZJ (2009) Promotion of nerve regeneration in peripheral nerve by short-course FK506 after end-to-side neurorrhaphy. J Surg Res 152:303–310
Cheng MY, Cao WL, Gao Y et al (2003) Studies on nerve cell affinity of biodegradable modified chitosan films. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 14:1155–1167
Chunasuwankul R, Ayrout C, Dereli Z et al (2002) Low dose discontinued FK506 treatment enhances peripheral nerve regeneration. Int Surg 87:274–278
Ciardelli G, Chiono V (2006) Materials for peripheral nerve regeneration. Macromol Biosci 6:13–26
Freier T, Koh HS, Kazazian K, Shoichet MS (2005) Controlling cell adhesion and degradation of chitosan films by N-acetylation. Biomaterials 26:5872–5878
Gold BG, Katoh K, Storm-Dickerson T (1995) The immunosuppressant FK506 increases the rate of axonal regeneration in rat sciatic nerve. J Neurosci 15:7509–7516
Jiang MR, Zhuge XM, Yang YM et al (2009) The promotion of peripheral nerve regeneration by chitooligosaccharides in the rat nerve crush injury model. Neurosci Lett 454:239–243
Lyons WE, George EB, Dawson TM et al (1994) Immunosuppressant FK506 promotes neurite outgrowth in cultures of PC12 cells and sensory ganglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:3191–3195
Navarro X, Udina E, Ceballos D, Gold BD (2001) Effects of FK506 on nerve regeneration and reinnervation after graft or tube repair of long gaps. Muscle Nerve 24:905–915
Sakurai E, Nozake M, Okabe K et al (2003) Scleral plug of biodegradable polymers containing tacrolimus (FK506) for experimental uveitis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:4845–4852
Sosa I, Reyes O, Kuffler DP (2005) Immunosuppressants: neuroprotection and promoting neurological recovery following peripheral nerve and spinal cord lesions. Exp Neurol 195:7–15
Udina E, Rodriguez FJ, Verdu E et al (2004) FK506 enhances regeneration of axons across long peripheral nerve gaps repaired with collagen guides seeded with allogeneic Schwann cells. Glia 47:120–129
Yang YM, Ding F, Wu J et al (2007) Development and evaluation of silk fibroin-based nerve grafts used for peripheral nerve regeneration. Biomaterials 28:5526–5535
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Aihua Xu for assistance in manuscript preparation and Fujisawa Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (Osaka, Japan) for the generous gift of FK506. This study was supported by Knowledge Innovation Project of The Chinese Academy of Sciences (KJCX2-YW-210-02) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 20736006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10529_2010_287_MOESM1_ESM.docx
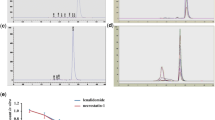
Supplementary material 1 (DOCX 25 kb) Supplementary Figure Fourier transformation infrared spectra of (a) FK506, (b) chitosan guide and (c) FK506-loaded chitosan guide; chitosan showed characteristic band of amide-I (1655 cm−1) and amino (1599 cm−1) in the spectra of (b) and (c), and there was no shift for other bands such as 1159 cm−1 for C–O–C stretch and C–N stretch, 1026 cm−1 for C–O skeletal vibration. It could be presented that the structure of chitosan guide does not change significantly with or without FK506
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Wang, W., Wei, G. et al. Immunophilin FK506 loaded in chitosan guide promotes peripheral nerve regeneration. Biotechnol Lett 32, 1333–1337 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0287-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-010-0287-8