Abstract
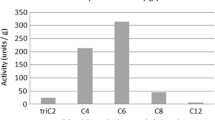
Lipases and esterases are frequently used in dairy production processes to enhance the buttery flavour of the end product. Short chain fatty acids, and especially butanoic acid, play a key role in this and different enzymes with specificity towards short chain fatty acids are commercially available as potent flavouring tools. We have compared six lipases/esterases associated with buttery flavour production. Although specificity to short chain fatty acids was ascribed to each enzyme, clear differences in free fatty acid profiles were found when these enzymes were applied on cream. Candida cylindraceae lipase was the most useful enzyme for buttery flavour production in cream with the highest yield of free fatty acids (57 g oleic acid 100 g−1 fat), no release of long chain fatty acids and specificity towards butanoic acid.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok P, Sailas B, Carlos RS et al (1999) The realm of microbial lipases in biotechnology. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 29:119–131
Chowdary GV, Prapulla SG (2003) Enzymatic synthesis of ethyl hexanoate by transesterifiation. Int J Food Sci Technol 38:127–133
Gerhartz W (ed) (1990) Enzymes in industry: production and applications. VCH-Verlagsgesselschaft, Weinheim
Ha JK, Lindsay RC (1993) Release of volatile branched chain and other fatty acids from ruminant milk fats by various lipases. J Dairy Sci 76: 677–690
Jensen RG (1992) Chapter 5: fatty acids in milk and dairy products. In: Chow CK (ed) Fatty acids in foods and their health implications. Marcel Dekker Inc, New York
Kinsella JE (1975) Butter flavour. Food Technol 5:82–98
Kovac A, Stadler P, Haalck L et al (1996) Hydrolysis and esterification of acylglycerols and analogues in aqueous medium catalyzed by microbial lipases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1301:57–66
Nini L, Sarda L, Comeau L et al (2001) Lipase-catalysed hydrolysis of short-chain substrates in solution and in emulsion: a kinetic study. Biochim Biophys Acta 1534:34–44
Patel MT, Nagarajan R, Kilara A (1996) Hydrolysis of milk fat by lipase in solvent-free phospholipids reverse micellar media. J Food Sci 61: 33–38
Pleiss J (2000) Molecular basis of specificity and stereoselectivity of microbial lipases toward triacylglycerols. In: Bornscheyer TU (ed) Enzymes in lipid modification. Wiley-VCH, Germany
Sailas B, Ashok P (1998) Candida rugosa lipases: molecular biology and versatility in biotechnology. Yeast 14:947–1087
Schieberle P, Gassenmeier K, Guth H et al (1993) Character impact odour compounds of different kinds of butter. Lebensm Wiss Technol 26:347–356
Schmid RD, Verger R (1998) Lipases: interfacial enzymes with attractive applications. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 37:1608–1633
Walstra P, Geurts TJ, Noomen A, Jellema A, Van Boekel MAJS (1999) Dairy technology: principles of milk properties and processes. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York
Walstra P, Jenness R (eds) (1984) Dairy chemistry and physics. Wiley & Sons, New York
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Institute for the Promotion of Innovation by Science and Technology in Flanders (Brussels, Belgium). The authors are grateful to Campina Milk Fat Products N.V. (Klerken, Belgium) for the provision of the standardised cream.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saerens, K., Descamps, D. & Dewettinck, K. Release of short chain fatty acids from cream lipids by commercial lipases and esterases. Biotechnol Lett 30, 311–315 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9541-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9541-0