Abstract
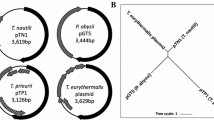
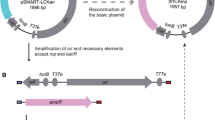
Among 21 human strains of Laribacter hongkongensis, small plasmids were observed in four strains, and large ones in six strains. The smallest, 3264-bp plasmid, pHLHK19, has only one ORF that encodes a putative replication initiator protein and a predicted origin of replication (ori) with a DnaA box, three 18-bp direct repeats and five pairs of inverted repeats. An Escherichia coli–L. hongkongensis shuttle vector was constructed by ligating the HindIII-digested pHLHK19, containing the replication initiator protein and ori of pHLHK19, to HindIII-digested pBK-CMV. This shuttle vector can propagate in E. coli and L. hongkongensis with good transformation efficiencies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Farmer JJ III, Gangarosa RE, Gangarosa EJ (2004) Does Laribacter hongkongensis cause diarrhoea, or does diarrhoea “cause” L. hongkongensis? Lancet 363:1923–1924
Inui M, Roh JH, Zahn K et al (2000) Sequence analysis of the cryptic plasmid pMG101 from Rhodopseudomonas palustris and construction of stable cloning vectors. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:54–63
Lau SK, Woo PC, Hui WT et al (2003) Use of cefoperazone MacConkey agar for selective isolation of Laribacter hongkongensis. J Clin Microbiol 41:4839–4841
Lau SK, Woo PC, Fan RY et al (2007) Seasonal and tissue distribution of Laribacter hongkongensis, a novel bacterium associated with gastroenteritis, in retail freshwater fish in Hong Kong. Int J Food Microbiol 113:62–66
Ni XP, Ren SH, Sun JR et al (2007) Laribacter hongkongensis isolated from a community-acquired gastroenteritis in Hangzhou City. J Clin Microbiol 45:255–256
Purdy D, O’Keeffe TA, Elmore M et al (2002) Conjugative transfer of clostridial shuttle vectors from Escherichia coli to Clostridium difficile through circumvention of the restriction barrier. Mol Microbiol 46:439–452
Qin X, Hartung JS (2001) Construction of a shuttle vector and transformation of Xylella fastidiosa with plasmid DNA. Curr Microbiol 43:158–162
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Simpson AJ, Reinach FC, Arruda P et al (2000) The genome sequence of the plant pathogen Xylella fastidiosa. The Xylella fastidiosa consortium of the organization for nucleotide sequencing and analysis. Nature 406:151–157
Smith MA, Bidochka MJ (1998) Bacterial fitness and plasmid loss: the importance of culture conditions and plasmid size. Can J Microbiol 44:351–355
Teng JL, Woo PC, Ma SS et al (2005) Ecoepidemiology of Laribacter hongkongensis, a novel bacterium associated with gastroenteritis. J Clin Microbiol 43:919–922
Woo PC, Kuhnert P, Burnens AP et al (2003) Laribacter hongkongensis: a potential cause of infectious diarrhea. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 47:551–556
Woo PC, Lau SK, Teng JL et al (2004) Association of Laribacter hongkongensis in community-acquired gastroenteritis with travel and eating fish: a multicentre case–control study. Lancet 363:1941–1947
Woo PC, Lau SK, Teng JL et al (2005a) Current status and future directions of Laribacter hongkongensis, a novel bacterium associated with gastroenteritis and traveller’s diarrhoea. Curr Opin Infect Dis 18:413–419
Woo PC, Ma SS, Teng JL et al (2005b) Construction of an inducible expression shuttle vector for Laribacter hongkongensis, a novel bacterium associated with gastroenteritis. FEMS Microbiol Lett 252:57–65
Yuen KY, Woo PC, Teng JL et al (2001) Laribacter hongkongensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel Gram-negative bacterium isolated from a cirrhotic patient with bacteremia and empyema. J Clin Microbiol 39:4227–4232
Acknowledgements
This work is partly supported by the Research Grant Council Grant (7357/04M); University Development Fund, The University of Hong Kong; and the Research Fund for the Control of Infectious Diseases of the Health, Welfare and Food Bureau of the Hong Kong SAR Government.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woo, P.C.Y., Ma, S.S.L., Teng, J.L.L. et al. Plasmid profile and construction of a small shuttle vector in Laribacter hongkongensis . Biotechnol Lett 29, 1575–1582 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9447-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9447-x