Abstract
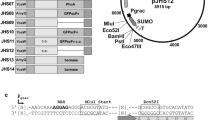
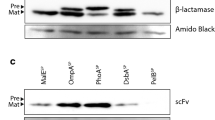
Bacterial expression of recombinant proteins containing disulfide bonds is facilitated by transport of the proteins to the periplasmic space. Several Pseudomonas fluorescens signal sequences have been identified that efficiently direct proteins to the periplasm and provide solubility and yield advantages over the production of proteins fused to the PelB signal sequence in E. coli. For a single chain antibody fragment, the final yield varied from about 1 g/l to 10 g/l when expression in P. fluorescens involved fusion to various P. fluorescens signal sequences.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvidsson RHA, Nordling M, Lundberg LG (1989) The azurin gene from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Cloning and characterization. Eur J Biochem 179:195–200
Bardwell J, Derman A, Belin D, Jander G, Prinz W, Martin N, Beckwith J (1994) Pathways of disulfide bond formation in proteins in vivo. In: Torriani-Gorini A, Yagil E, Silver S (eds) Phosphate in microorganisms: cellular and molecular biology. ASM Press, Washington DC, USA, pp 270–275
Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S (2004) Improved prediction of signal peptides: signalP 3.0. J Mol Biol 340:783–795
Bowers CW, Lau F, Silhavy TJ (2003) Secretion of LamB-LacZ by the signal recognition particle pathway of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 185:5697–5705
Calos MP, Miller JH (1980) The DNA sequence change resulting from the IQ1 mutation, which greatly increases promoter strength. Mol Gen Genet 183:559–560
De E, De Mot R, Orange N, Saint N, Molle G (1995) Channel-forming properties and structural homology of major outer membrane proteins from Pseudomonas fluorescens MFO and OE 28.3. FEMS Microbiol Lett 127:267–272
Derman AI, Beckwith J (1991) Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase fails to acquire disulfide bonds when retained in the cytoplasm. J Bacteriol 173:7719–7722
Georgiou G, Segatori L (2005) Preparative expression of secreted proteins in bacteria: status report and future prospects. Curr Opin Biotechnol 16:538–545
Heirwegh K, Edman P (1957) Purification and N-terminal determination of crystalline pepsin. Biochim Biophys Acta 24:219–220
Horton RM, Cai Z, Ho SN, Pease LR (1990) Gene splicing by overlap extension: tailor-made genes using the polymerase chain reaction. BioTechniques 8:528–530, 532, 534–535
Kajava AV, Zolov SN, Kalinin AE, Nesmeyanova MA (2000) The net charge of the first 18 residues of the mature sequence affects protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 182:2163–2169
Lee HC, Bernstein HD (2001) The targeting pathway of Escherichia coli presecretory and integral membrane proteins is specified by the hydrophobicity of the targeting signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3471–3476
Lei SP, Lin HC, Wang SS, Callaway J, Wilcox G (1987) Characterization of the Erwinia carotovora pelB gene and its product pectate lyase. J Bacteriol 169:4379–4383
Manoil C (2000) Tagging exported proteins using Escherichia coli alkaline phosphatase gene fusions. Meth Enzymol 326:35–47
Martineau P, Jones P, Winter G (1998) Expression of an antibody fragment at high levels in the bacterial cytoplasm. J Mol Biol 280:117–127
Martoglio B, Dobberstein B (1998) Signal sequences: more than just greasy peptides. Trends Cell Biol 8:410–415
Menne KML, Hermjakob H, Apweiler R (2000) A comparison of signal sequence prediction methods using a test set of signal peptides. Bioinformatics 16:741–742
Mergulhãoa FJM, Summersb DK, Monteiroa GA (2005) Recombinant protein secretion in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Adv 23:177–202
Retallack DM, Thomas TC, Shao Y, Haney KL, Resnick SM, Lee VD, Squires CH (2006) Identification of anthranilate and benzoate metabolic operons of Pseudomonas fluorescens and functional characterization of their promoter regions. Microb Cell Fact 5:1
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Schneider JC, Chew LC, Badgley AK, Ramseier TM (2005a) Improved bacterial expression systems for production of recombinant polypeptides utilizing auxotrophic selectable markers. U.S. Patent Application WO2005052151
Schneider JC, Jenings AF, Mun DM, McGovern PM, Chew LC (2005b) Auxotrophic markers pyrF and proC can replace antibiotic markers on protein production plasmids in high-cell-density Pseudomonas fluorescens fermentation. Biotechnol Prog 21:343–348
Sletta H, Nedal A, Aune TE, Hellebust H, Hakvag S, Aune R, Ellingsen TE, Valla S, Brautaset T (2004) Broad-host-range plasmid pJB658 can be used for industrial-level production of a secreted host-toxic single-chain antibody fragment in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:7033–7039
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FSL, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik J, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GKS, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01. Nature (London) 406:959–964
Yamano Y, Nishikawa T, Komatsu Y (1993) Cloning and nucleotide sequence of anaerobically induced porin protein E1 (OprE) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Mol Microbiol 8:993–1004
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the excellent technical assistance of Barbara Morach, Angel Salazar, Fareed Sajan, Michael Donahue, Tracey Thomas, Deborah Mun and Ping Xu. The authors would also like to thank Paul Roessler for critical review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Retallack, D.M., Schneider, J.C., Mitchell, J. et al. Transport of heterologous proteins to the periplasmic space of Pseudomonas fluorescens using a variety of native signal sequences. Biotechnol Lett 29, 1483–1491 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9415-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-007-9415-5