Abstract
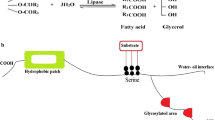
Lipase was pretreated with soybean oil in order to allow fatty acids to bond to the active site before immobilization. This pretreated lipase exhibited steric hindrance around the active site such that during immobilization, covalent bonds were formed between the carrier and the lipase region far from the active site. The activity of the pretreated lipase immobilized covalently on a silica gel was 530 U/g-matrix, which is 16 times higher than that of the immobilized non-pretreated lipase. In addition, the immobilized lipase activity was maintained at levels exceeding 90% of its original activity after 10 reuses.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balcao VM, Paiva AL, Malcata FX (1996) Bioreactors with immobilized lipases: state of the art. Enz Microb Technol 18:392–416
Kwon DY, Rhee JS (1986) A simple and rapid colorimetric method for determination of free fatty acids for lipase assay. J Am Oil Chem Soc 63:89–92
Murty VR, Bhat J, Muniswaran PKA (2002) Hydrolysis of oils by using immobilized lipase enzyme: a review. Biotechnol Bioproc Eng 7:57–66
Noor INJ, Omar IC (2000) Dependency of water availability on the esterifying activity of Candida cylindracea in organic solvent. J Microbiol Biotechnol 10:99–102
Park SW, Kim YI, Chung KH, Kim SW (2001a) Improvement of stability of immobilized GL-7-ACA acylase through modification with glutaraldehyde. Proc Biochem 37:153–163
Park SW, Kim YI, Chung KH, Kim SW (2001b) Quantitative analysis of the degree of silanization by the ninhydrin method and its application to the immobilization of GL-7-ACA acylase and cellulolytic enzyme. J Microbiol Biotechnol 11:199–203
Park SW, Lee J, Hong SI, Kim SW (2003) Immobilization of glutaryl-l-7-aminocephalospoanic acid acylase on silica gel and enhancement of its stability. Appl Biochem Biotech 104:185–198
Rocha JMS, Gil MH, Garcia FAP (1998) Effect of additives on the activity of a covalently immobilized lipase in organic media. J Biotechnol 66:61–67
Schoemaker HE, Mink D, Wubbolts MG (2003) Dispelling the myths—biocatalysis in industrial synthesis. Science 299:1694–1697
Soares CMF, Santana MHA, Zanin GM, Castro HFD (2003) Covalent coupling method for lipase immobilization on controlled pore silica in the presence of nonenzymatic proteins. Biotechnol Prog 19:803–807
Tischer W, Wedekind F (1999) Immobilized enzymes: methods and applications. Top Curr Chem 200:95–126
Wehtje E, Adlercreutz P, Mattiasson B (1993) Improved activity retention of enzymes deposited on solid supports. Biotechnol Bioeng 41:171–178
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by research grant 2003-N-BI03-P-01 from the Korea Energy Management Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D.H., Kim, J.M., Kang, S.W. et al. Pretreatment of lipase with soybean oil before immobilization to prevent loss of activity. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1965–1969 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9181-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9181-9