Abstract
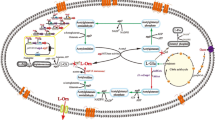
Metabolic engineering has been used to improve l-ornithine biosynthesis in Escherichia coli W3110. l-Ornithine production increased from 0.3 to 3.2 mg/g (dry cell weight) when the primary l-ornithine biosynthetic pathway was optimized by disrupting the pathway transcription repressor, thereby increasing the expression of the genes involved in the pathway, and by preventing conversion of l-ornithine into citrulline. When a feedback-resistant N-acetylglutamate synthetase gene (argA214) was placed under the control of the arabinose-inducible promoter, either in the chromosome or on a multicopy plasmid in the cell, the combination of overexpression of argA214 with an argF argI argR triple knockout mutation had an additive effect on l-ornithine production but only when exogenous glutamate was present. When speF (which encodes ornithine decarboxylase) and proB (which encodes γ-glutamyl kinase) were inactivated to prevent the conversion of l-ornithine to putrescine and to block the biosynthesis of a side branch of l-ornithine, respectively, l-ornithine production was further enhanced approxi. 140% from 5.5 to 13.2 mg/g (dry cell weight).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Applebaum DM, Dunlap JC, Morris DR (1977) Comparison of the biosynthetic and biodegradative ornithine decarboxylase of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry 16:1580–1584
Charlier D, Roovers F, Van Vliet F, Boyen A, Cunin R, Nakamura Y, Glansdorff N, Pierard A (1992) Arginine regulon of Escherichia coli K-12. A study of repressor-operator interactions and of in vitro binding affinities versus in vivo repression. J Mol Biol 226:367–386
Chinard FP (1952) Photometric estimation of proline and ornithine. J Biol Chem 199:91–95
Choi DK, Ryu WS, Choi CY, Park YH (1996) Production of l-ornithine by arginine auxotrophic mutants of Brevibacterium ketoglutamicum in dual substrate-limited continuous culture. J Ferment Bioeng 81:216–219
Cunin R, Glansdorff N, Pierard A, Stalon V (1986) Biosynthesis and metabolism of arginine in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 50:314–352
Datsenko KA, Wanner BL (2000) One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6640–6645
Güldener U, Susanne H, Thomas F, Beinhauer J, Hegemann JH (1996) A new efficient gene disruption cassette for repeated use in budding yeast. Nucleic Acids Res 24:2519–2524
Jensen KF (1993) The Escherichia coli K-12 “wild type” W3110 and MG1655 have an rph frameshift mutation that leads to pyrimidine starvation due to low pyrF expression levels. J Bacteriol 175:3401–3407
Kim SY, Cho JY (2005) A modified PCR-directed gene replacements method using λ-Red recombination functions in Escherichia coli. J Microbiol Biotechnol 15:1346–1352
Kiupakis AK, Reitzer L (2002) ArgR-independent induction and ArgR-dependent superinduction of the astCADBE operon in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 184:2940–2950
Legrain C, Stalon V, Glansdorff N (1976) Escherichia coli ornithine carbamoyltransferase isoenzymes: evolutionary significance and the isolation of λargF and λargI transducing bacteriophages. J Bacteriol 128:35–38
Maas W (1994) The arginine repressor of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev 58:631–640
Palmeros B, Wild J, Szybalski W, Le Borgne S, Hernández-Chávez G, Gosset G, Valle F, Bolivar F (2000) A family of removable cassettes designed to obtain antibiotic-resistant-free genomic modifications of Escherichia coli and other bacteria. Gene 247:255–264
Panagiotidis CA, Blackburn S, Low KB, Canellakis ES (1987) Biosynthesis of polyamines in ornithine decarboxylase, arginine decarboxylase, and agmatine ureohydrolase deletion mutants of Escherichia coli strain K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4423–4427
Rajagopal BS, DePonte J, Tuchman M, Malamy MH (1998) Use of inducible feedback-resistant N-acetylglutamate synthetase (argA) genes for enhanced arginine biosynthesis by genetically engineered Escherichia coli K-12 strains. 1998. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1805–1811
Salvatore F, Cimino F, Maria C, Cittadini D (1964) Mechanism of the protection by l-ornithine-l-aspartate mixture and by l-arginine in ammonia intoxication. Arch Biochem Biophys 107:499–503
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Schneider BL, Kiupakis AK, Reitzer L (1998) Arginine catabolism and the arginine succinyltransferase pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 180:4278–4286
Smith LT (1985) Characterization of a γ-glutamyl kinase from Escherichia coli that confers proline overproduction and osmotic tolerance. J Bacteriol 164:1088–1093
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by Sangji University Research Fund 2005.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, YJ., Cho, JY. Genetic manipulation of a primary metabolic pathway for l-ornithine production in Escherichia coli . Biotechnol Lett 28, 1849–1856 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9163-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9163-y