Abstract
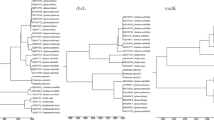
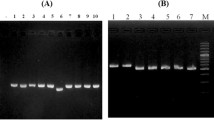
Dendrobium plants are important commercial herbs in China, widely used in traditional medicine and ornamental horticulture. In this study, sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers were applied to molecular phylogeny analysis and species identification of 31 Chinese Dendrobium species. Fourteen SRAP primer pairs produced 727 loci, 97% of which (706) showed polymorphism. Average polymorphism information content of the SRAP pairs was 0.987 (0.982–0.991), showing that plenty of genetic diversity exists at the interspecies level of Chinese Dendrobium. The molecular phylogeny analysis (UPGMA) grouped the 31 Dendrobium species into six clusters. We obtained 18 species-specific markers, which can be used to identify 10 of the 31 species. Our results indicate the SRAP marker system is informative and would facilitate further application in germplasm appraisal, evolution, and genetic diversity studies in the genus Dendrobium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aneja B, Yadav N, Chawla V, Yadav R (2012) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) molecular marker system and its applications in crop improvement. Mol Breed 30(4):1635–1648
Bao X, Shun Q, Chen L (2001) The medicinal plants of Dendrobium (Shi-hu) in China. Shanghai Medicinal University Press and Fudan University Press, Shanghai
Botstein D, White RL, Skolnick M, Davis RW (1980) Construction of a genetic linkage map in man using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Am J Hum Genet 32(3):314–331
Budak H, Shearman RC, Parmaksiz I, Gaussoin RE, Riordan TP, Dweikat I (2004) Molecular characterization of Buffalo grass germplasm using sequence-related amplified polymorphism markers. Theor Appl Genet 108(2):328–334
Cai XY, Feng ZY, Zhang XX, Xu W, Hou BW, Ding XY (2011) Genetic diversity and population structure of an endangered Orchid (Dendrobium loddigesii Rolfe) from China revealed by SRAP markers. Sci Hortic 129(4):877–881
Carlsward BS, Stern WL, Judd WS, Lucansky TW (1997) Comparative leaf anatomy and systematics in Dendrobium, sections Aporum and Rhizobium (Orchidaceae). Int J Plant Sci 158(3):332–342
Ding G, Zhang DZ, Ding XY, Zhou Q, Zhang WC, Li XX (2008) Genetic variation and conservation of the endangered Chinese endemic herb Dendrobium officinale based on SRAP analysis. Plant Syst Evol 276(3–4):149–156
Ferriol M, Pico B, Nuez F (2003) Genetic diversity of a germplasm collection of Cucurbita pepo using SRAP and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 107(2):271–282
Ferriol M, Pico B, de P, Nuez F (2004) Molecular diversity of a germplasm collection of squash (Cucurbita moschata) determined by SRAP and AFLP markers. Crop Sci 4:653–664
Huang LK, Bughrara S, Zhang XQ, Bales-Arcelo C, Bin X (2011) Genetic diversity of switchgrass and its relative species in Panicum genus using molecular markers. Biochem Syst Ecol 39(4):685–693
Lau DTW, Shaw PC, Wang J, But PPH (2001) Authentication of medicinal Dendrobium species by the internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA. Planta Med 67(5):456–460
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103(2–3):455–461
Lu JJ, Wang S, Zhao HY, Liu JJ, Wang HZ (2012a) Genetic linkage map of EST-SSR and SRAP markers in the endangered Chinese endemic herb Dendrobium (Orchidaceae). Genet Mol Res 11(4):4654–4667
Lu JJ, Zhao HY, Suo NN, Wang S, Shen B, Wang HZ, Liu JJ (2012b) Genetic linkage maps of Dendrobium moniliforme and D. officinale based on EST-SSR, SRAP, ISSR and RAPD markers. Sci Hortic 137:1–10
Morris MW, Stern WL, Judd WS (1996) Vegetative anatomy and systematics of subtribe Dendrobiinae (Orchidaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 120(2):89–144
Mutlu N, Boyaci FH, Gocmen M, Abak K (2008) Development of SRAP, SRAP-RGA, RAPD and SCAR markers linked with a Fusarium wilt resistance gene in eggplant. Theor Appl Genet 117(8):1303–1312
Nei M, Li WH (1979) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76(10):5269–5273
Rahman M, McVetty PB, Li G (2007) Development of SRAP, SNP and multiplexed SCAR molecular markers for the major seed coat color gene in Brassica rapa L. Theor Appl Genet 115(8):1101–1107
Rogers SO, Bendich AJ (1985) Extraction of DNA from milligram amounts of fresh, herbarium and mummified plant tissues. Plant Mol Biol 5(2):69–76
Rohlf F (1997) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy and multivariate analysis system, version 2.2. Applied Biostatistics, New York
Stern WL, Morris MW, Judd WS (1994) Anatomy of the thick leaves in Dendrobium section Rhizobium (Orchidaceae). Int J Plant Sci 155(6):716–729
Suman A, Kimbeng CA, Edmé SJ, Veremis J (2008) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP) markers for assessing genetic relationships and diversity in sugarcane germplasm collections. Plant Genet Res 6(03):222
Tsi ZH, Chen SC, Luo YB, Zhu GH (1999) Orchidaceae (3). Flora Republicae Popularis Sinicae. Science Press, Beijing
Wang H-Z, Feng S-G, Lu J-J, Shi N-N, Liu J-J (2009) Phylogenetic study and molecular identification of 31 Dendrobium species using inter-simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers. Sci Hortic 122(3):440–447
Weir BS (1990) Genetic data analysis. Methods for discrete population genetic data. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, p 377
Xue D, Feng S, Zhao H, Jiang H, Shen B, Shi N, Lu J, Liu J, Wang H (2010) The linkage maps of Dendrobium species based on RAPD and SRAP markers. J Genet Genomics (Yi chuan xue bao) 37(3):197–204
Yue GH, Lam-Chan LT, Hong Y (2006) Development of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers and their use in identification of Dendrobium varieties. Mol Ecol Notes 6(3):832–834
Acknowledgments
This research was funded in part by the National Natural Science Foundation (No. 31070298, 30870180), the Zhejiang Scientific and Technological Program (2008C12081), the Hangzhou Scientific and Technological Program (20101032B25), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Q13H280036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S.G. Feng and J.J. Lu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, SG., Lu, JJ., Gao, L. et al. Molecular Phylogeny Analysis and Species Identification of Dendrobium (Orchidaceae) in China. Biochem Genet 52, 127–136 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9633-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9633-6