Abstract
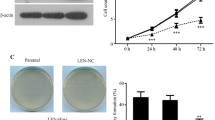
Inhibition of c-MYC has been considered as a potential therapy for lymphoma treatment. We explored a lentiviral vector-mediated small interfering RNA (siRNA) expression vector to stably reduce c-MYC expression in B cell line Jijoye cells and investigated the effects of c-MYC downregulation on cell growth, cell cycle, and apoptosis in vitro. The expression of c-MYC mRNA and protein levels were inhibited significantly by c-MYC siRNA. The c-MYC downregulation resulted in the inhibition of cell proliferation and cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase, which was associated with decreased expression of cyclin B and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) and increased expression of CDK inhibitor p21 proteins. In addition, downregulation of c-MYC induced cell apoptosis characterized by DNA fragmentation and caspase-3 activation. Taken together, these results suggest that lentiviral vector-mediated siRNA for c-MYC may be a promising approach for targeting c-MYC in the treatment of Burkitt lymphoma.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravin A, Tuschl T (2005) Identification and characterization of small RNAs involved in RNA silencing. FEBS Lett 579(26):5830–5840
Aukema SM, Siebert R, Schuuring E, van Imhoff GW, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Boerma EJ, Kluin PM (2011) Double-hit B-cell lymphomas. Blood 117(8):2319–2331
Baluchamy S, Rajabi HN, Thimmapaya R, Navaraj A, Thimmapaya B (2003) Repression of c-MYC and inhibition of G1 exit in cells conditionally overexpressing p300 that is not dependent on its histone acetyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(16):9524–9529
Blum KA, Lozanski G, Byrd JC (2004) Adult Burkitt leukemia and lymphoma. Blood 104(10):3009–3020
Bosher JM, Labouesse M (2000) RNA interference: genetic wand and genetic watchdog. Nat Cell Biol 2(2):E31–E36
Busch K, Keller T, Fuchs U, Yeh RF, Harbott J, Klose I, Wiemels J, Novosel A, Reiter A, Borkhardt A (2007) Identification of two distinct MYC breakpoint clusters and their association with various IGH breakpoint regions in the t(8;14) translocations in sporadic Burkitt-lymphoma. Leukemia 21(8):1739–1751
Cao X, Bennett RL, May WS (2008) c-MYC and caspase-2 are involved in activating Bax during cytotoxic drug-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 283(21):14490–14496
Dang CV (2012) MYC on the path to cancer. Cell 30–149(1):22–35
Dang CV, Lewis BC (1997) Role of oncogenic transcription factor c-MYC in cell cycle regulation, apoptosis and metabolism. J Biomed Sci 4(6):269–278
Dropulić B (2011) Lentiviral vectors: their molecular design, safety, and use in laboratory and preclinical research. Hum Gene Ther 22(6):649–657
Gartel AL, Shchors K (2003) Mechanisms of c-MYC-mediated transcriptional repression of growth arrest genes. Exp Cell Res 283(1):17–21
Gustafson WC, Weiss WA (2010) Myc proteins as therapeutic targets. Oncogene 29(9):1249–1259
Herkert B, Eilers M (2010) Transcriptional repression: the dark side of myc. Genes Cancer 1(6):580–586
Hoffman B, Liebermann DA (2008) Apoptotic signaling by c-MYC. Oncogene 27(50):6462–6472
Hong J, Zhao Y, Huang W (2006) Blocking c-MYC and stat3 by E. coli expressed and enzyme digested siRNA in mouse melanoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348(2):600–605
Hotti A, Järvinen K, Siivola P, Hölttä E (2000) Caspases and mitochondria in c-Myc-induced apoptosis: identification of ATM as a new target of caspases. Oncogene 19(19):2354–2362
Joos S, Falk MH, Lichter P, Haluska FG, Henglein B, Lenoir GM, Bornkamm GW (1992) Variable breakpoints in Burkitt lymphoma cells with chromosomal t(8;14) translocation separate c-MYC and the IgH locus up to several hundred kb. Hum Mol Genet 1:625–632
Jung P, Hermeking H (2009) The c-MYC-AP4-p21 cascade. Cell Cycle 8(7):982–989
Kabilova TO, Vladimirova AV, Chernolovskaya EL, Vlassov VV (2006) Arrest of cancer cell proliferation by dsRNAs. Ann NY Acad Sci 1091:425–436
Kangas A, Nicholson DW, Hölttä E (1998) Involvement of CPP32/Caspase-3 in c-Myc-induced apoptosis. Oncogene 16(3):387–398
Klapproth K, Wirth T (2010) Advances in the understanding of MYC-induced lymphomagenesis. Br J Haematol 149(4):484–497
Kuttler F, Mai S (2006) c-MYC, genomic instability and disease. Genome Dyn 1:171–190
Lin CP, Liu JD, Chow JM, Liu CR, Liu HE (2007) Small-molecule c-MYC inhibitor, 10058–F4, inhibits proliferation, downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase and enhances chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs 18(2):161–170
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the \( {2^{-\Updelta \Updelta {\text{C}}}}_{\text{T}} \) method. Methods 25:402–408
Llano M, Gaznick N, Poeschla EM (2009) Rapid, controlled and intensive lentiviral vector-based RNAi. Methods Mol Biol 485:257–270
Magrath I (1990) The pathogenesis of Burkitt’s lymphoma. Adv Cancer Res 55:133–270
Morrish F, Neretti N, Sedivy JM, Hockenbery DM (2008) The oncogene c-MYC coordinates regulation of metabolic networks to enable rapid cell cycle entry. Cell Cycle 7(8):1054–1066
Morrish F, Isern N, Sadilek M, Jeffrey M, Hockenbery DM (2009) c-MYC activates multiple metabolic networks to generate substrates for cell-cycle entry. Oncogene 28(27):2485–2491
Nigris F, Balestrieri ML, Napoli C (2006) Targeting c-MYC, Ras and IGF cascade to treat cancer and vascular disorders. Cell Cycle 5(15):1621–1628
Obaya AJ, Kotenko I, Cole MD, Sedivy JM (2002) The proto-oncogene c-MYC acts through the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor P21(Kip1) to facilitate the activation of Cdk4/6 and early G(1) phase progression. J Biol Chem 277(34):31263–31269
Pajic A, Spitkovsky D, Christoph B, Kempkes B, Schuhmacher M, Staege MS, Brielmeier M, Ellwart J, Kohlhuber F, Bornkamm GW, Polack A, Eick D (2000) Cell cycle activation by c-MYC in a Burkitt lymphoma model cell line. Int J Cancer 87(6):787–793
Peterson CW, Ayer DE (2011) An extended Myc network contributes to glucose homeostasis in cancer and diabetes. Front Biosci 17:2206–2223
Radziszewska A, Schroer SA, Choi D, Tajmir P, Radulovich N, Ho JC, Wang L, Liadis N, Hakem R, Tsao MS, Penn LZ, Evan GI, Woo M (2009) Absence of caspase-3 protects pancreatic β-cells from c-Myc-induced apoptosis without leading to tumor formation. J Biol Chem 284(16):10947–10956
Salaverria I, Siebert R (2011) The gray zone between Burkitt’s lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma from a genetics perspective. J Clin Oncol 29(14):1835–1843
Schiffer CA (2001) Treatment of high-grade lymphoid malignancies in adults. Semin Hematol 38(4 Suppl 10):22–26
Schlee M, Schuhmacher M, Hölzel M, Laux G, Bornkamm GW (2007) c-MYC impairs immunogenicity of human B cells. Adv Cancer Res 97:167–188
Slack GW, Gascoyne RD (2011) MYC and aggressive B-cell lymphomas. Adv Anat Pathol 18(3):219–228
Sobolewski C, Cerella C, Dicato M, Diederich M (2011) Cox-2 inhibitors induce early c-MYC downregulation and lead to expression of differentiation markers in leukemia cells. Cell Cycle 10(17):2978–2993
Steidl C, Gascoyne RD (2011) The molecular pathogenesis of primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 118(10):2659–2669
Tomita N (2011) BCL2 and MYC dual-hit lymphoma/leukemia. J Clin Exp Hematop 51(1):7–12
Vermeulen K, Berneman ZN, Van Bockstaele DR (2003) Cell cycle and apoptosis. Cell Prolif 36(3):165–175
Yap CS, Peterson AL, Castellani G, Sedivy JM, Neretti N (2011) Kinetic profiling of the c-MYC transcriptome and bioinformatic analysis of repressed gene promoters. Cell Cycle 10(13):2184–2196
Zimonjic DB, Keck-Waggoner C, Popescu NC (2001) Novel genomic imbalances and chromosome translocations involving c-MYC gene in Burkitt’s lymphoma. Leukemia 15(10):1582–1588
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Qingdao Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 2012-1-3-2-5-nsh), the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation, China (Grant No. Y2008C170) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31100824).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, A., Ye, J., Zhang, K. et al. Lentiviral Vector-Mediated siRNA Knockdown of c-MYC: Cell Growth Inhibition and Cell Cycle Arrest at G2/M Phase in Jijoye Cells. Biochem Genet 51, 603–617 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9590-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-013-9590-0