Abstract
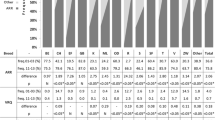
Allele and genotype frequency distributions of prion protein (PrP) polymorphisms at three codons, 136, 154, and 171, in East Asian sheep were determined by PCR–RFLP analysis using 553 animals from nine local breeds of the northern group and four local breeds of the southern group. Based on the genotype distribution, the risk score for scrapie was estimated. Among the local breeds, ARQ appeared predominantly (0.7701–1), followed by ARH and ARR. From such a biased allele distribution, it was difficult to ascertain the prevalent genetic relationships. A marked difference in allele frequencies between the northern and southern groups was seen (P < 0.0001). The East Asian sheep had ARQ at the highest frequency (0.8834); in European sheep it was 0.5317. According to an assessment of scrapie risk in the PrP genotype classes, the predominant ARQ/ARQ in East Asian sheep corresponded to the risk score of R4. This finding suggests that East Asian sheep have a high level of genetic susceptibility to scrapie.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aucoutturier P, Carp RI, Carnaud C, Wisniewski T (2000) Prion disease and immune system. Clinic Immunol 96:79–85
Belt PBGM, Muileman IH, Schreuder BEC, Bos-de Ruijter J, Gielkens ALJ, Smits MA (1995) Identification of five allelic variants of the sheep PrP gene and their association with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol 76:509–517
Bossers A, Screuder BEC, Muileman JH, Belt PBGM, Smits MA (1996) PrP genotype contributes to determining survival times of sheep with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol 77:2669–2673
Bossers A, de Vries R, Smits MA (2000) Susceptibility of sheep for scrapie as assessed by in vitro conversion of nine naturally occurring variants of PrP. J Virol 74:1407–1414
Clouscard C, Beaudry P, Elsen JM, Milan D, Dussaucy M, Bounneau C, Schelcher, Chatelain J, Launay JM, Laplanche JL (1995) Different allelic effects of the codons 136 and 171 of the prion protein gene in sheep with natural scrapie. J Gen Virol 76:2097–2101
Dawson M (1997) PrP genotyping (scrapie gene testing) as an aid to the control of scrapie. State Vet J 7:16–17
Dawson M, Hoinville L, Hosie BD, Hunter N (1998) Guidance on the use of PrP genotyping as an aid to the control of clinical scrapie. Vet Rec 142:623–625
Drögemüller C, Leeb T, Distl O (2001) PrP genotype frequencies in German breeding sheep and the potential to breed for resistance to scrapie. Vet Rec 149:349–352
Elsen JM, Amigues Y, Schelcher F, Ducrocq V, Andreoletti O, Eyechenne F, Vu Tien Khang J, Poivey JP, Lantier F, Laplanche JL (1999) Genetic susceptibility and transmission factors in scrapie: detailed analysis of an epidemic in a closed flock of Romanov. Arch Virol 144:431–445
Garcia-Crespo D, Oporto B, Gomez N, Nagore D, Benedicto L, Juste RA, Hurtado A (2004) PrP polymorphisms in Basque sheep breeds determined by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism and real-time PCR. Vet Rec 154:717–722
Goldmann W, Hunter N, Foster JD, Salbaum JM, Beyreuther K, Hope J (1990) Two alleles of a neural protein gene linked to scrapie in sheep. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:2476–2480
Goldmann W, Hunter N, Benson G, Foster JD, Hope J (1991) Different scrapie-associated fibril proteins (PrP) are encoded by lines of sheep selected for different alleles of the Sip gene. J Gen Virol 72:2411–2417
Goldmann W, Hunter N, Smith G, Foster JD, Hope J (1994) PrP genotype and agent effects in scrapie: change in allelic interaction with different isolates of agent in sheep, a natural host of scrapie. J Gen Virol 75:989–995
Gombojav A, Ishiguro N, Horiuchi M, Serjmyadag D, Byambaa B, Shinagawa M (2003) Amino acid polymorphisms of PrP gene in Mongolian sheep. J Vet Med Sci 65:75–81
Hunter N (1998) Scrapie. Mol Biotechnol 9:225–234
Hunter N, Goldmann W, Benson G, Foster JD, Hope J (1993) Swaledale sheep affected by natural scrapie differ significantly in PrP genotype frequencies from healthy sheep and those selected for reduced incidence of scrapie. J Gen Virol 74:1025–1031
Hunter N, Goldmann W, Smith G, Hope J (1994) The association of a codon 136 PrP gene variant with the occurrence of natural scrapie. Arch Virol 137:171–177
Laplanche JL, Chatelain J, Westaway D, Thomas S, Dussaucy M, Brugere-Picoux J, Launay JM (1993) PrP polymorphisms associated with natural scrapie discovered by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Genomics 15:30–37
Nei M (1973) Analysis of gene diversity in subdivided population. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3321–3323
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Thorgeirsdotteir S, Sigurdarson S, Thorisson HM, Georgsson G, Palsdottir A (1999) PrP gene polymorphism and natural scrapie in Icelandic sheep. J Gen Virol 80:2527–2534
Tranulis MA (2002) Influence of the prion protein gene, Prnp, on scrapie susceptibility in sheep. APMIS 110:33–43
Tsunoda K, Chang H, Sun W, Hasnath MA, Nyunt MM, Rajbhandary HB, Tashi D, Tumennasan H, Sato K (2006) Phylogenetic relationships among indigenous sheep populations in East Asia based on five informative blood protein and nonprotein polymorphisms. Biochem Genet 44:287–306
Van Keulen LJ, Schreuder BE, Meloen RH, Mooij-Harkes G, Vromans ME, Langeveld JP (1996) Immunohistochemical detection of prion protein in lymphoid tissues of sheep with natural scrapie. J Clinic Microbiol 34:1228–1231
Wang L, Hirayasu K, Isizawa M, Kobayashi Y (1994) Purification of genomic DNA from human whole blood by isopropanol-fractionation with concentrated NaI and SDS. Nucleic Acids Res 22:1774–1775
Westaway D, Zuliani V, Mirenda Cooper C, Da Costa M, Neuman S, Jenny AL, Detwiler L, Prusiner SB (1994) Homozygosity for prion protein alleles encoding glutamine 171 renders sheep susceptible to natural scrapie. Genes Dev 8:959–969
Zheng L, Li N, Fan B, Fang M, Xu W (2004) PRNP polymorphisms in Chinese ovine, caprine and bovine breeds. Anim Genet 35:457–461
Acknowledgments
We deeply thank many Japanese members of the Society for Research on Native Livestock and the many people concerned in different countries for their kind cooperation and assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsunoda, K., Namikawa, T., Sato, K. et al. Prion Protein Polymorphisms and Estimation of Risk of Scrapie in East Asian Sheep. Biochem Genet 48, 13–25 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-009-9287-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-009-9287-6