Abstract
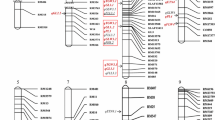
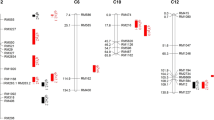
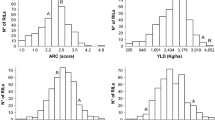
Phenolic acids are secondary metabolic organic compounds produced by plants and often are mentioned as allelochemicals. This study was conducted to determine the genetic basis controlling the ferulic acid content of rice straw in a recombinant inbred (RI) population derived from a cross between a japonica variety, Asominori, with a higher content of ferulic acid, and an indica variety, IR24, with a lower content, using 289 RFLP markers. Continuous distributions and transgressive segregations of ferulic acid content were observed in the RI population, which showed that ferulic acid content in rice straw was quantitatively inherited. Single marker analysis and composite interval mapping identified three quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for ferulic acid content with LOD values of 2.03 (chromosome 3), 3.16 (chromosome 6), and 3.06 (chromosome 7); all three had increased additive effects (13.5, 18.3, and 18.1 μg g −1) from the Asominori parent and accounted for 5.5, 16.9, and 12.8% of total phenotypic variation, respectively. This is the first report on the identification of QTLs associated with ferulic acid and their chromosomal localization on the molecular map of rice. The tightly linked molecular markers that flank the QTLs might be useful in breeding and selection of varieties with higher phenolic acid content.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Rahman, A., and Habig, S. A. (1989). Allelopathic effects of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) on bladygrass (Imperata cylindrica). J. Chem. Ecol. 15:2289–2300.
Blum, U., Wentworth, T. R., Klein, K., Worsham, A. D., King, L. D., Gerig, T. M., and Lyu, S. W. (1991). Phenolic acid content of soil from wheat-no till, wheat-conventional till, and fallow-conventional till soybean cropping systems. J. Chem. Ecol. 17:1045–1068.
Chou, C. H., and Chung, Y. T. (1974). The allelopathic potential of Miscanthus floridulus. Bot. Bull. Acad. Sin. 15:14–17.
Chung, I. M., Ahn, J. K., and Yun, S. J. (2001). Identification of allelopathic compounds from rice (Oryza sativa L.) straw and their biological activity. Can. J. Plant Sci. 81:815–819.
Chung, I. M., Kim, K. H., Ahn, J. K., Chun, S. C., Kim, C. S., Kim, J. T., and Kim, S. H. (2002). Screening of allelochemicals on barnyardgrass (Echinochloa crus-galli) and identification of potentially allelopathic compounds from rice (Oryza sativa) variety hull extracts. Crop Prot. 21:913–920.
Dalton, B. R. (1999). The occurrence and behavior of plant phenolic acids in soil environments and their potential involvement in allelochemical interference interactions: Methodological limitations in establishing conclusive proof of allelopathy. In Inderjit, Dakshini, K. M. M., and Foy, C. L. (eds.), Principles and Practices in Plant Ecology, Allelochemical Interactions, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 57–74.
Dong, Y., Tsuzuki, E., Kamiunten, H., Terao, H., and Lin, D (2003a). Mapping of QTL for embryo size in rice. Crop Sci. 43:1068–1071.
Dong, Y., Tsuzuki, E., Kamiunten, H., Terao, H., Lin, D., Matsuo, M., and Zheng, Y. (2003b). Identification of quantitative trait loci associated with pre-harvest sprouting resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) Field Crops Res. 81:133–139.
Dong, Y., Zheng, Y., Tsuzuki, E., and Terao, H. (2002). Quantitative trait loci controlling steamed-rice shape in a recombinant inbred population. Int. Rice Res. (Note) 27:19–20.
Ebana, K., Yan, G. W., Dilday, R. H., Namai, H., and Okuno, K. (2001). Analysis of QTLs associated with the allelopathic effect of rice using water soluble extracts. Breeding Sci. 51:47–51.
Fujii, Y. (1992). The allelopathic effects of some rice varieties. In Proceedings of the Internation Symposium on Biological Control and Integrated Management of Paddy and Aquatic Weeds in Asia, National Agricultural Research Center, Tsukuba, Japan, Oct. 20–23, 1992, pp. 1–6.
Fujii, Y., Shibuya, T., Yasuda, T., Ootani, T., and Furukawa, M. (1991). Analysis of phenolic acids from soil and plants by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Jpn. J. Soil Fertilizer 62:529–532 (in Japanese).
Harborne, J. B. (1985). Phenolics and plant defence. In Sumere, C. F., and Lea, P. L. (eds.), Biochemistry: Volume 1 Plant Phenolis, Academic Press, London, pp. 393–408.
Harborne, J. B. (1993). Introduction to Ecological Biochemistry, 4th edn., Academic Press, London.
Hartley, R. D., and White, D. C. (1985). Phenolic acids in soils and their influence on plant growth and soil microbial processes. In Vaughan, D., and Malcolm, R. E. (eds.), Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity. Developments in Plant and Soil Sciences, Vol. 16., Martinus Nijhoff/Dr W. Junk Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands, pp. 109–262.
Inderjit (1996). Plant phenolic in allelopathy. Bot. Rev. 62:186–202.
Jensen, L. B., Courtois, B., Shen, L., Li, Z., Olofsdotter, M., and Manuleon, R. P. (2001). Locating genes controlling allelopathic effects against barnyardgrass in upland rice. Agronomy J. 93:21–26.
Kubo, T., and Yoshimura, A. (2002). Genetic basis of hybrid breakdown in a Japonica/Indica cross of rice, Oryza sativa L. Theor. Appl. Genet. 105:906–911.
Kuiters, A. T. (1990). Role of phenolic substances from decomposing forest litter in plant–soil interactions. Acta Bot. Neerl. 39:329–348.
Kuiters, A. T., and Denneman, C. A. (1987). Water-soluble phenolic substances in soils under several coniferous and deciduous tree species. Soil Biol. Biochem. 19:765–769.
Matsui, H., Matsushita, Y., Sugamoto, K., and Hidaka, K. (2002). Influence of moisture content of Sugi (Cryptomeria japonica D.) wood on yields of carbonization products and constituents of wood vinegar. Memoirs Fac. Eng., Miyazaki Univ. 31:69–74 (in Japanese).
Matsuo, M. (2001). Studies on Allelopathy in Rice and Its Bioassay Methods. PhD dissertation, Kagoshima University, Japan, pp. 111–130 (in Japanese).
McCouch, S. R., Cho, Y. G., Yano, M., Paul, E., and Blinstrub, M. (1997). Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet. Newsl. 14:11–13.
Miller, D. A. (1996). Allelopathy in forage and crop system. Agronomy J. 88:854–859.
Olofsdotter, M., Rebulanan, M., Madrid, A., Dali, W., Navarez, D., and Olk, D. C. (2002). Why phenolic acids are unlikely primary allelochemicals in rice. J. Chem. Ecol. 22:2292–2242.
Sasahara, H., Fukuta, Y., and Fukuyama, Y. (1999). Mapping of QTLs for vascular bundle system and spike morphology in rice, Oryza sativa L. Breeding Sci. 49:75–81.
Siqueira, J. O., Nair, M. G., Hammerschmidt, R., and Safir, G. R. (1991). Significance of phenolic compounds in plant–soil–microbial systems. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 10:63–121.
Tang, C. S. (1986). Continuous trapping techniques for the study of allelochemicals from higher plants. In Putnam, A. R., and Tang, C. S. (eds.), The Science of Allelopathy, Wiley-Interscience, New York, pp. 113–131.
Tang, C. S., and Young, C. C. (1982). Collection and identification of allelopathic compounds from undisturbed root systems of Bigalta Limpograss (Hermarthria altissima). Plant Physiol. 69:155–160.
Tinnin, R. O., and Muller, C. H., (1971). The allelopathic potential of Avenai fatua: Influence on herb distribution. Bull. Torrey Bot. Club 98:243–250.
Tsunematsu, H., Yoshimura, A., Harushima, Y., Nagamura, Y., Kurata, N., Yano, M., and Iwata, N. (1996). RFLP framework map using recombinant inbred lines in rice. Breeding Sci. 46:279–284.
Tsuzuki, E., and Yamamoto, Y. (1987). Isolation and identification of phenolic substances from wild perennial buckwheat (F. cymosum M.). Bull. Fac. Agric., Miyazaki Univ. 34:289–295.
Wang, S. C., Zeng, B. Z., and Basten, C. J. (1999). QTL cartographer windows version 1.13g copyright (Programed, 1999). http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/cartographer.hml (Verified, Aug. 15, 2001).
Whitehead, D. C., Dibb, H., and Hartley, R. D. (1982). Phenolic compounds in soil as influenced by the growth of different plant species. J. Appl. Ecol. 19:579–588.
Yamazaki, M., Tsunematstu, H., Yoshimura, A., Iwata, N., and Yasui, H. (1999). Quantitative trait locus mapping of ovicidal response in rice(Oryza sativa L.) against whitebacked planthopper (Sogatella furcifera Horvath). Crop Sci. 39:1178–1183.
Yamazaki, M., Yoshimura, A., and Yasui, H. (2000). Mapping of quantitative trait loci of ovicidal response to brown planthopper (Nilaparvata lugen Stal) in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Breeding Sci. 50:291–296.
Yoshimura, A., Okamoto, M., Nagamine, T., and Tsunematsu, H. (1998). Rice QTL analysis for days to heading-under the cultivation of Ishigaki island. Breeding Sci. 48(Suppl. 1):73.
Zeng, B. Z. (1994). Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468.
Zheng, Y., Dong, Y., Matsui, A., Udatsu, T., and Fujiwara, H. (2003). Molecular genetic basis of determining subspecies of ancient rice using the shape of phytoliths. J. Archaeol. Sci. 30:1215–1221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Tsuzuki, E., Kamiunten, H. et al. Molecular Genetic Analysis of QTLs for Ferulic Acid Content in Dried Straw of Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biochem Genet 43, 25–34 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-005-1064-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-005-1064-6