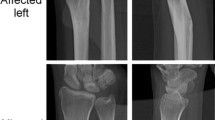
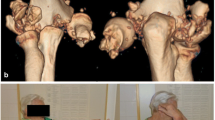
A mobilization hub inserted into an external fixator was developed for the treatment of fractures of the distal epimetaphysis of the radius bone. The hub was designed in a three-dimensional solid-body modeling system. Experimental prototypes were made of ABS plastic by 3D printing. Cadaver experiments showed that with the device carrying the mobilization hub, the range of movements was not statistically significantly different from the range of passive movements in the intact joint. The X-ray-transparent material used for the hub provides unimpeded visualization of the fracture site and wrist joint. Single use of the hub is proposed, as it can be made using inexpensive plastic and 3D printing, while batch production is by pressure casting.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Traumatology: National Guidelines [in Russian], G. P. Kotel’nikov and S. P. Mironov (eds.), GEOTAR-Media, Moscow (1980).
Sharma, H. et al., “Outcomes and complications of fractures of distal radius (AO type B and C): Volar plating versus nonoperative treatment,” J. Orthop. Sci., 19, No. 4, 537-544 (2014).
Wulf, C. A., Ackerman, D. B., and Rizzo, M., “Contemporary evaluation and treatment of distal radius fractures,” Hand Clin., 23, No. 2, 209-226 (2007).
Franko, O. I., Zurakowski D., and Day C. S., “Functional disability of the wrist: Direct correlation with decreased wrist motion,” J. Hand Surg. Am., 33, No. 4, 485-492 (2008).
Kapandzhi, A. I., “The upper limb,” in: Joint Physiology [in Russian], Abelev, G. and Kishinevskii, E. (eds.), Eksmo, Moscow (2017).
An, K.-N., Berger, R. A., and Cooney, W. P., Biomechanics of the Wrist Joint, An, K.-N., Berger, R. A., and Cooney, W. P. (eds.), Springer, New York (1991).
Berger, R. A., “The anatomy and basic biomechanics of the wrist joint,” J. Hand Ther., 9, 84-93 (1996).
The KUD-SAI-01 Rod Compression−Distraction Apparatus for Fixation of Small Tubular Bones [in Russian], http://cito-pro.ru/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=170:kud-sai-01&catid=31:apparat&Itemid=55 (accessed: January 11, 2016).
Golubev, G. Sh. and Petrov, K. V., An Apparatus for the Treatment of Distal Radius Metaepiphyseal Fractures: RF Patent No. 17278 U1 [in Russian], Byul. 21.
Palmer, A. K. and Werner, F. W., “Biomechanics of the distal radioulnar joint,” Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res., No. 187, 26-35 (1984).
Agee, J. M. and King, F. C. Articulated Colles’ Fracture Splint: USA Patent No. 4611586 (1986).
Drobetz, H. et al., “Volar locking distal radius plates show better short-term results than other treatment options: A prospective randomised controlled trial,” World J. Orthop., 7, No. 10, 687-694 (2016).
Song, J., Yu, A.-X., and Li, Z.-H., “Comparison of conservative and operative treatment for distal radius fracture: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials,” Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med., 8, No. 10, 17,023-17,035 (2015).
Navarro, C. M., Pettersson, H. J., and Enocson, A., “Complications after distal radius fracture surgery,” J. Orthop. Trauma, 29, No. 2, e36-e42 (2015).
Satake, H. et al., “Complications of distal radius fractures treated by volar locking plate fixation,” Orthopedics, 39, No. 5, e893-e896 (2016).
Thorninger, R. et al., “Complications of volar locking plating of distal radius fractures in 576 patients with 3.2 years follow-up,” Injury, 48, No. 6, 1104-1109 (2017).
Shukla, R. et al., “External fixation versus volar locking plate for displaced intra-articular distal radius fractures: A prospective randomized comparative study of the functional outcomes,” J. Orthop. Traumatol., 15, No. 4, 265-270 (2014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Meditsinskaya Tekhnika, Vol. 52, No. 5, Sep.-Oct., 2018, pp. 24-27.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golubev, G.S., Petrov, K.V. The Hub of an External Fixation Device for Early Mobilization of the Wrist in the Treatment of Distal Radial Epimetaphyseal Fractures. Biomed Eng 52, 326–330 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-019-09840-0
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10527-019-09840-0