Abstract
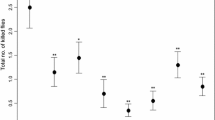
The impact of five selective insecticides on the functional response of a potential biological control agent, the spider Philodromus cespitum (Walckenaer) (Araneae: Philodromidae), was studied in the laboratory. This spider is the most abundant beneficial arthropod on trees in commercial orchards in central Europe. We expected that selective insecticides applied at the recommended doses would have no effect or a negligible effect on the spiders’ performance. Our results showed that the mortality of spiders resulting from residual uptake of the chemicals differed among insecticides. Dimilin, NeemAzal, Mospilan, and Integro caused mortality of less than 10%, while SpinTor caused mortality of 17%. All five preparations can be considered harmless in terms of mortality in comparison with Decis, which caused 80% mortality. Exposure to residues of NeemAzal, SpinTor, and Dimilin resulted in a significantly lower predation rate than the control. The lowest predation rate was observed in spiders treated with SpinTor. These results imply that the natural pest control provided by P. cespitum spiders can be weakened by the application of SpinTor, NeemAzal, and Dimilin. On the other hand, the functional response was not significantly affected by the application of Integro and Mospilan. Therefore, these two insecticides are recommended for use in the integrated pest management (IPM) of orchards.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert R, Bogenschütz H (1984) Prüfung der Wirkung von Pflanzenbehandlungsmitteln auf die Nutzarthropode Coelotes terrestris (Wider) (Araneida, Agelenidae) mit Hilfe eines Glasplattentests. Anz Schädlingskd Pfl 57:111–117
Ambrose DP, Rajan SJ, Kumar AG (2008) Impact of insecticide Synergy-505 on the functional response of a non-target reduviid predator Rhynocoris marginatus (Fabricius) (Heteroptera: Reduviidae) feeding on Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Biol Control 22:283–290
Anonymous (2008) [List of plant protection products]. State Phytosanitary Administration, Czech Republic (in Czech)
Basedow T, Rzehak H, Voß K (1985) Studies on the effect of deltamethrin sprays on the numbers of epigeal predatory arthropods occurring in arable fields. Pestic Sci 16:325–331
Beltramin da Fonseca PR, Bertoncello TF, Ribeiro JF, Fernandes MG, Degrande PE (2008) Selectivity of insecticides to natural enemies on soil cultivated with cotton. Pesqui Agropecu Trop 38:304–309
Bogya S, Markó V, Szinetár CS (1999) Comparison of pome fruit orchard inhabiting spider assemblages at different geographical scales. Agr For Entomol 1:261–269
Casas J, Hulliger B (1994) Statistical analysis of functional response experiments. Biocontrol Sci Technol 4:133–145
Cisneros J, Goulson D, Derwent LC, Penagos DI, Hernández O, Williams T (2002) Toxic effects of spinosad on predatory insects. Biol Control 23:156–163
Claver MA, Ravichandran B, Khan MM, Ambrose DP (2003) Impact of cypermethrin on the functional response, predatory and mating behaviour of a non-target potential biological control agent Acanthaspis pedestris (Stål) (Het., Reduviidae). J Appl Entomol 127:18–22
De Clercq P, De Cock A, Tirry L, Viñuela E, Degheele D (1995) Toxicity of diflubenzuron and pyriproxyfen to the predatory bug Podisus maculiventris. Entomol Exp Appl 74:17–22
Delbeke P, Vercruysse L, Tirry L, De Clercq P, Degheele D (1997) Toxicity of diflubenzuron, pyriproxyfen, imidacloprid and diafenthiuron to the predatory bug Orius laevigatus (Het.: Anthocoridae). Entomophaga 42:349–358
Deng L, Dai J, Cao H, Xu M (2007) Effects of methamidophos on the predating behavior of Hylyphantes graminicola (Sundevall) (Araneae: Linyphiidae). Environ Toxicol Chem 26:478–482
Dhadialla TS, Jansson RK (1999) Non-steroidal ecdysone agonists: new tools for IPM and insect resistance management. Pestic Sci 55:357–359
Everts JW, Aukema B, Mullié WC, van Gemerden A, Rottier A, van Katz R, van Gestel CAM (1991) Exposure of the ground dwelling spider Oedothorax apicatus (Blackwall) (Erigonidae) to spray and residues of deltamethrin. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 20:13–19
Foelix RF (1996) Biology of spiders, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Gu DJ (1991) Influence of sublethal dose of insecticides on the foraging behavior of Diaeretiella rapae. Acta Ecol Sin 11:324–329
Hardman JM, Turnbull AL (1974) The interaction of spatial heterogeneity, predator competition and the functional response to prey density in a laboratory system of wolf spiders (Araneae: Lycosidae) and fruit flies (Diptera: Drosophilidae). J Anim Ecol 43:155–171
Hassan SA, Albert R, Bigler F, Blaisinger P, Bogenschütz H, Boller E, Brun J, Chiverton P, Edwards P, Englert WD, Huang P, Inglesfield C, Naton E, Oomen PA, Overmeer WPJ, Rieckmann W, Samsøe-Petersen L, Stäubli A, Tuset JJ, Viggiani G, Vanwetswinkel G (1987) Results of the third joint pesticide testing programme by the IOBC/WPRS—working group “Pesticides and Beneficial Organisms”. Z Angew Entomol 103:92–107
Haynes DL, Sisojevic P (1966) Predatory behavior of Philodromus rufus Walckenaer (Araneae: Thomisidae). Can Entomol 98:113–133
Holling CS (1959) Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can Entomol 91:385–398
Holling CS (1965) The functional response of predators to prey density and its role in mimicry and population regulation. Mem Entomol Soc Can 45:1–60
Jebanesan A (1998) Sublethal effect of etofenprox (Trebon) on the predation of Culex quinquefasciatus (Say) by Diplonychus indicus (Venk. and Rao.). Indian J Environ Toxicol 8:33–34
Jiang Y, Zhang ZN, Niu CY, Deng JH, Lei CL (2002) Effects of avermectin on the suppression of the peach aphid, Myzus persicae, by Orius similis. Acta Entomol Sin 45:215–220
Kajak A (1978) An analysis of consumption by spiders under laboratory and field conditions. Ekol Pol 26:409–427
Kim DS, Brooks DJ, Riedl H (2006) Lethal and sublethal effects of abamectin, spinosad, methoxyfenozide and acetamiprid on the predaceous plant bug Deraeocoris brevis in the laboratory. BioControl 51:465–484
Li DX, Tian J, Shen ZR (2006) Effects of pesticides on the functional response of predatory thrips, Scolothrips takahashii to Tetranychus viennensis. J Appl Entomol 130:314–322
Luckey TD (1963) Antibiotic action in adaptation. Nature 198:263–265
Mahdian K, Van Leeuwen T, Tirry L, De Clercq P (2007) Susceptibility of the predatory stinkbug Picromerus bidens to selected insecticides. BioControl 52:765–774
Mansour F, Rosen D, Shulov A (1981) Disturbing effect of a spider on larval aggregations of Spodoptera littoralis. Entomol Exp Appl 29:234–237
Mansour F, Heimbach U, Wehling A (1992) Effects of pesticide residues on ground-dwelling lycosid and micryphantid spiders in laboratory tests. Phytoparasitica 20:195–202
Maupin JL, Riechert SE (2001) Superfluous killing in spiders: a consequence of adaptation to food-limited environments? Behav Ecol 12(5):569–576
Moura R, Garcia P, Cabral S, Soares AO (2006) Does pirimicarb affect the voracity of the euriphagous predator, Coccinella undecimpunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae)? Biol Control 38:363–368
Musser FR, Shelton AM (2003) Bt sweet corn and selective insecticides: impacts on pests and predators. J Econ Entomol 96:71–80
Myers L, Liburd OE, Arevalo HA (2006) Survival of Geocoris punctipes Say (Hemiptera: Lygaeidae) following exposure to selected reduced-risk insecticides. J Entomol Sci 41:57–64
Nentwig W (1989) Augmentation of beneficial arthropods by strip-management. II. Successional strips in a winter wheat field. J Plant Dis Prot 96:89–99
Nentwig W, Hänggi A, Kropf C, Blick T (2009) Spinnen Mitteleuropas/Central European Spiders—determination key. Version 8.12.2003. Available online at: http://www.araneae.unibe.ch
Nowak JT, McCravy KW, Fettig CJ, Berisford CW (2001) Susceptibility of adult hymenopteran parasitoids of the Nantucket pine tip moth (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) to broad-spectrum and biorational insecticides in a laboratory study. J Econ Entomol 94:1122–1127
Nyffeler M, Benz G (1987) Spiders in natural pest control: a review. J Appl Entomol 103:321–339
Nyffeler M, Breene RG (1990) Evidence of low daily food consumption by wolf spiders in meadowland and comparison with other cursorial hunters. J Appl Entomol 110:73–81
Oaten A, Murdoch WW (1975) Switching, functional response, and stability in predator–prey systems. Am Nat 109:299–318
Paul AVN, Thygarajan KS (1992) Toxicity of pesticides to natural enemies of crop pests in India. In: David BV (ed) Pest management and pesticides: Indian scenario. Narmrutha Publications, Madras, pp 158–176
Pekár S (1998) Effect of selective insecticides on the beneficial spider community of a pear orchard in the Czech Republic. In: Selden PA (ed) Proceedings of the 17th European colloquium of arachnology, Edinburgh, 14–18 July 1997, pp 337–342
Pekár S (1999) Effect of IPM practices and conventional spraying on spider population dynamics in an apple orchard. Agric Ecosyst Environ 73:155–166
Pekár S (2002) Susceptibility of the spider Theridion impressum to 17 pesticides. J Pest Sci 75:51–55
Pekár S, Beneš J (2008) Aged pesticide residues are detrimental to agrobiont spiders (Araneae). J Appl Entomol 132:614–622
Perry WB, Christiansen TA, Perry SA (1997) Response of soil and leaf litter microarthropods to forest application of diflubenzuron. Ecotoxicology 6:87–99
Peveling R, Demba SA (1997) Virulence of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium flavoviride Gams and Rozsypal and toxicity of diflubenzuron, fenitrothion-esfenvalerate and profenofos-cypermethrin to nontarget arthropods in Mauritania. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 32:69–79
Poletti M, Maia AHN, Omoto C (2007) Toxicity of neonicotinoid insecticides to Neoseiulus californicus and Phytoseiulus macropilis (Acari: Phytoseiidae) and their impact on functional response to Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Biol Control 40:30–36
Qi B, Gordon G, Gimme W (2001) Effects of neem-fed prey on the predacious insects Harmonia conformis (Boisduval) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) and Mallada signatus (Schneider) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Biol Control 22:185–190
R Development Core Team (2009) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. http://www.R-project.org
Riechert SE, Bishop L (1990) Prey control by an assemblage of generalist predators: spiders in garden test systems. Ecology 71:1441–1450
Riechert SE, Harp JM (1987) Nutritional ecology of spiders. In: Slansky F Jr, Rodriguez JG (eds) Nutritional ecology of insects, mites, spiders, and related invertebrates. Wiley, New York, pp 645–672
Riechert SE, Lockley T (1984) Spiders as biological control agents. Annu Rev Entomol 29:299–320
Riechert SE, Luczak J (1982) Spider foraging: behavioral responses to prey. In: Witt PN, Rovner JS (eds) Spider communication: mechanisms and ecological significance. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 353–385
Smith RB, Wellington WG (1983) The functional response of a juvenile orb-weaving spider. In: Eberhard WG, Lubin YD, Robinson BC (eds) Proceedings of the 9th international congress of arachnology, Panama. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, pp 275–279
Stark JD, Jepson PC, Thomas CFG (1995) The effects of pesticides on spiders from the lab to the landscape. Rev Pestic Toxicol 3:83–110
Stebbing ARD (1982) Hormesis—the stimulation of growth by low levels of inhibitors. Sci Total Environ 22:213–234
Studebaker GE, Kring TJ (2003) Effects of insecticides on Orius insidiosus (Hemiptera: Anthocoridae), measured by field, greenhouse and Petri dish bioassays. Fla Entomol 86:178–185
Sunderland KD, Fraser AM, Dixon AFG (1986) Distribution of linyphiid spiders in relation to capture of prey in cereal fields. Pedobiologia 29:367–375
Tomlin CDS (2000) The pesticide manual, 12th edn. British Crop Protection Council, Farnham
Vargas RI, Peck SL, McQuate GT, Jackson CG, Stark JD, Armstrong JW (2001) Potential for areawide integrated management of Mediterranean fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae) with a braconid parasitoid and a novel bait spray. J Econ Entomol 94:817–825
Vickerman GP, Sunderland KD (1977) Some effects of dimethoate on arthropods in winter wheat. J Appl Ecol 14:767–777
Viñuela E, Adán A, Smagghe G, González M, Medina MP, Budia F, Vogt H, Del Estal P (2000) Laboratory effects of ingestion of azadirachtin by two pests (Ceratitis capitata and Spodoptera exigua) and three natural enemies (Chrysoperla carnea, Opius concolor and Podisus maculiventris). Biocontrol Sci Technol 10:165–177
Wang XY, Shen ZR (2002) Effects of sublethal doses of insecticides on predation of multicolored Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis (Pallas). Acta Ecol Sin 22:2278–2284
Wang Z, Song DX, Zhu MS (2006) Functional response and searching behavior to the brown planthopper, Nilaparvata lugens by the wolf spider, Pardosa pseudoannulata under low-dose chemical pesticides. Acta Entomol Sin 49:295–301
Wise DH (1975) Food limitation of the spider Linyphia marginata: experimental field studies. Ecology 56:637–646
Wise DH (1993) Spiders in ecological webs. Cambridge studies in ecology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Wise DH, Wagner JD (1992) Evidence of exploitative competition among young stages of the wolf spider Schizocosa ocreata. Oecologia 91:7–13
Acknowledgments
We thank Patrick De Clercq for his comments on the manuscript. This research was supported by grant no. 1G58081 of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Czech Republic. SP was also supported by project no. 0021622416 of the Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports of the Czech Republic.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Patrick De Clercq.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Řezáč, M., Pekár, S. & Stará, J. The negative effect of some selective insecticides on the functional response of a potential biological control agent, the spider Philodromus cespitum . BioControl 55, 503–510 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-010-9272-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-010-9272-3