Abstract
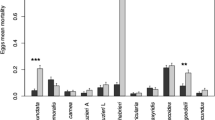
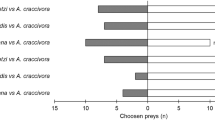
A semi-field experiment was carried out in two peach orchards in northern Italy to assess mortality due to predators and parasitoids on the exotic coccinellid Harmonia axyridis (Pallas) (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in comparison with the native coccinellid Adalia bipunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). The experiments were conducted in cages to avoid the possible escape of the exotic ladybird (not yet established in Italy). Two kinds of cage experiments were included: ‘exclusion cages’ (access by walking predators impeded) and ‘free cages’ (walking predators free to enter). The cages, containing all the stages of the two ladybird species, were placed in two localities and left for 24 h. All ladybird stages used for the semi-field experiments came from a laboratory rearing. The eggs of H. axyridis experienced less mortality than those of A. bipunctata. The ant workers were the most frequent predators in ‘free cages’ but A. bipunctata cannibalism on eggs was also detected. Larvae of both coccinellid species were predated equally but larval predation of L1 and L2 was higher in comparison to predation of L3 and L4. Pupae and adults of both exotic and native ladybirds were never attacked by predators. Predation on younger larval stages was higher in the ‘free cages’ in comparison with ‘exclusion cages’. No ladybird parasitisation was observed. The ‘free cage’ technique seems to provide a standardised and realistic estimation of predation impact but more studies are needed to evaluate ladybird parasitisation in semi-field conditions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agarwala BK, Dixon AFG (1992) Laboratory study of cannibalism and interspecific predation in ladybirds. Ecol Entomol 17:303–309
Bazzocchi GG, Lanzoni A, Accinelli G, Burgio G (2004) Overwintering, phenology and fecundity of Harmonia axyridis in comparison with native coccinellid species in Italy. BioControl 49:245–260
Brown MW, Miller SS (1998) Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) in apple orchards of eastern West Virginia and their impact of invasion by Harmonia axyridis. Ent News 109(2):136–142
Brown PMJ, Adriaens T, Bathon H, Cuppen J, Goldarazena A, Hägg T, Kenis M, Klausnitzer BEM, Kovář I, Loomans AJM, Majerus MEN, Nedved O, Pedersen J, Rabitsch W, Roy HE, Ternois V, Zakharov IA, Roy DB (2007) Harmonia axyridis in Europe: spread and distribution of a non-native coccinellid. BioControl (this issuse). doi:10.1007/s10526-007-9132-y
Burgio G, Santi F, Maini S (2002) On intraguild predation and cannibalism in Harmonia axyridis Pallas and Adalia bipunctata L. (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Biol Control 24:110–116
Burgio G, Ferrari R, Pozzati M, Boriani L (2004) The role of ecological compensation areas on predator populations: an analysis on biodiversity and phenology of Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) on non-crop plants within hedgerows in Northern Italy. Bull Insectology 57:1–10
Burgio G, Ferrari R, Boriani L, Pozzati M, van Lenteren J (2006) The role of ecological infrastructures on Coccinellidae (Coleoptera) and other predators in weedy field margins within northern Italy agroecosystems. Bull Insectology 59:5–67
Cartwright B, Eikenbary RD, Angalet GW (1982) Parasitism by Perilitus coccinellae (Hym.: Braconidae) of indigenous coccinellids hosts and the introduced Coccinella septempunctata (Col.: Coccinellidae), with notes on winter mortality. Entomophaga 27:237–244
Colunga-Garcia M, Gage SH (1998) Arrival, establishment, and habitat use of the multicolor Asian lady beetle (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in a Michigan landscape. Environ Entomol 27:1574–1580
Cottrell TE (2005) Predation and cannibalism of lady beetle eggs by adult lady beetles. Biol Control 34:159–164
Cottrell TE, Yeargan KV (1998a) Influence of a native weed, Acalypha ostryaefolia (Euphorbiaceae), on Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) population density, predation, and cannibalism in sweet corn. Environ Entomol 27:1375–1385
Cottrell TE, Yeargan KV (1998b) Effect of pollen on Coleomegilla maculata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) population density, predation, and cannibalism in sweet corn. Environ Entomol 27:1402–1410
Dixon AFG (2000) Insect predator–prey dynamic: ladybird, beetles and biological control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Elliott N, Kieckhefer R, Kauffman W (1996) Effects on an invading coccinellid on native coccinellids in an agricultural landscape. Oecologia 105:537–544
Gardiner MM, Landis DA (2007) Impact of intraguild predation by adult Harmonia axyridis (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on Aphis glycines (Hemiptea: Aphididae) biological control in cage studies. Biol Control 40:386–395
Geoghegan IE, Majerus TMO, Majerus MEN (1998) Differential parasitization of adult and pre-imaginal Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) by Dinocampus coccinellae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Eur J Entomol 95:571–579
Hemptinne JL, Lognay G, Gauthier C, Dixon FG (2000) Role of surface chemical signals in egg cannibalism and intraguild predation in ladybirds (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Chemoecology 10:123–128
Hironori Y, Katsuhino S (1997) Cannibalism and interspecific predation in two predatory ladybirds in relation to prey abundance in the field. Entomophaga 42:153–163
Hodek I, Honék A (1996) Ecology of coccinellidae. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Iperti G (1964) Les parasites des coccinelles aphidiphages dans les Alpes-Maritimes et les Basses-Alpes. Entomophaga 9:153–180
Kajita H, Takano F, Yasuda H, Agarwala BK (2000) Effects of indigenous ladybird species (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on survival of an exotic species in relation to prey abundance. Appl Entomol Zool 35(4):473–479
Kenis M, Roy HE, Zindel R, Majerus MEN (2007) Current and potential management strategies against Harmonia axyridis. BioControl (this issuse). doi:10.1007/s10526-007-9136-7
Lanzoni A, Accinelli G, Bazzocchi GG, Burgio G (2004) Biological traits and life table of the exotic Harmonia axyridis compared with Hippodamia variegata, and Adalia bipunctata (Col., Coccinellidae). J Appl Entomol 128:298–306
Lucas E (2005) Intraguild predation among aphidophagous predators. Eur J Entomol 102:351–364
Obrycki JJ (1989) Parasitization of native and exotic Coccinellids by Dinocampus coccinellae (Schrank) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). J Kans Entomol Soc 32:211–218
Obrycki JJ, Tauber MJ, Tauber CA (1985) Perilitus coccinellae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae): parasitization and development in relation to host-stage attacked. Ann Entomol Soc Am 78:852–854
Obrycki JJ, Giles KL, Ormord AM (1998a) Experimental assessment of interactions between larval Coleomegilla maculata and Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) in field cages. Environ Entomol 27:1280–1288
Obrycki JJ, Giles KL, Ormord AM (1998b) Interactions between an introduced and indigenous coccinellid species at different prey densities. Oecologia 117:279–285
Okuda T, Ceryngier P (2000) Host discrimination in Dinocampus coccinellae (Hymenoptera: Braconidae). Appl Entomol Zool 35:595–539
Pasteels JM, Deroe C, Tursch B, Braekman JC, Daloze D, Hootele C (1973) Distribution et activites des alcaloides defensifs des Coccinellidae. J Insect Physiol 19:1771–1784
Pervez A, Omkar GM (2006) Ecology and biological control application of multicoloured Asian ladybird, Harmonia axyridis: a review. Biocontrol Sci Technol 16:111–128
Rosenheim JA, Kaya HK, Ehler LE, Marois JJ, Jaffee BAJ (1995) Intraguild predation among biological-control agents: theory and evidence. Biol Control 5:303–335
Roy HE, Brown PMJ, Rothery P, Ware RL, Majerus MEN (2007) Interactions between the fungal pathogen Beauveria bassiana and three species of coccinellid: Harmonia axyridis, Coccinella septempunctata and Adalia bipunctata. BioControl (this issuse). doi:10.1007/s10526-007-9122-0
Santi F, Maini S (2006) Predation upon Adalia bipunctata and Harmonia axyridis eggs by Chrysoperla carnea larvae and Orius laevigatus adults. Bull Insectology 59:53–58
Toda Y, Sakuratani Y (2006) Expansion of the geographical distribution of an exotic ladybird beetle, Adalia bipunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), and its interspecific relationships with native ladybird beetles in Japan. Ecol Res 21:292–300
Ware RL, Majerus MEN (2007) Intraguild predation of immature stages of British and Japanese coccinellids by the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. BioControl (this issuse). doi:10.1007/s10526-007-9135-8
Ware RL, Ramon-Portugal F, Magro A, Ducamp C, Hemptinne J-L, Majerus MEN (2007) Chemical protection of Calvia quatuordecimguttata eggs against intraguild predation by the invasive ladybird Harmonia axyridis. BioControl (this issuse). doi:10.1007/s10526-007-9129-6
Zar JH (1984) Biostatistical analysis, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Michele Ruzza for technical assistance during the experiments. This research was funded by ERBIC (Evaluating Risks of Biological Control Introductions into Europe) FAIR5-CT97-3489. A special thank to Helen Roy for the English revision of the manuscript and for useful suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burgio, G., Lanzoni, A., Accinelli, G. et al. Estimation of mortality by entomophages on exotic Harmonia axyridis versus native Adalia bipunctata in semi-field conditions in northern Italy. BioControl 53, 277–287 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-007-9133-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-007-9133-x