Abstract
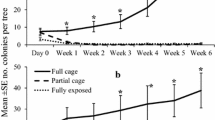
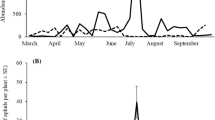
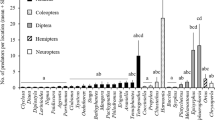
Three species of hover fly commonly prey on woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum, in Virginia, USA apple orchards. Larvae of Heringia calcarata are specialized predators of this pest, while Eupeodes americanus and Syrphus rectus are generalist aphid predators. The developmental duration of the immature stages of H. calcarata was determined under laboratory conditions, revealing a generation time of 19–20 d at 25°C. Descriptions of the larval, pupal and adult stages of H. calcarata are reported. Potted apple trees infested with arboreal colonies of woolly apple aphid and deployed in an orchard in Virginia were used as sentinels to measure seasonal changes in the relative abundance of the three syrphid species, based on the number of unhatched eggs deposited during weekly, 48-h exposure intervals from April to October, 2003–2005. Similar trends in the relative abundance of each species were recorded across all years. Eupeodes americanus was recorded first, showing a pronounced peak between mid-April and mid-May, followed by a prolonged period during which it was absent or present in very low numbers and then a much smaller peak in September and October. First records of H. calcarata occurred slightly later than for E. americanus. Early peaks of H. calcarata abundance typically occurred in May and June and tended to be smaller than those of E. americanus. Heringia calcarata eggs were recovered throughout most of each season. The potential role of predation by aphidophagous hover flies on the suppression of woolly apple aphid outbreaks in eastern apple orchards is discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfieri E (1920) A probably new species of gallicolous aphid of the elm and its symbionts. Boll Lab Zool Gen Agrar R Scuola Sup Agric, Portici 14:18–32
Asante SK (1997) Natural enemies of the woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) (Hemiptera: Aphididae): a review of the world literature. Plant Prot Quart 12:166–172
Asante SK, Danthanarayana W (1992) Development of Aphelinus mali an endoparasitoid of woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum at different temperatures. Entomol Exp Appl 65:31–37
Baker AC (1915) The woolly apple aphis. USDA Rept. No. 101, 56 pp
Bhatia ML (1939) Biology, morphology and anatomy of aphidophagous syrphid larvae. Parasitology 31:78–129
Bergh JC, Louque RL (2000) Heringia (Neocnemodon) calcarata: A specialist predator of the woolly apple aphid? Proc 76th Cumberland-Shenandoah Fruit Workers Conf. Winchester, VA
Bodenheimer FS (1947) Studies on the physical ecology of the woolly apple aphis (Eriosoma lanigerum) and its parasite Aphelinus mali in Palestine. Bull. Rehovot. Agric. Res. Stn. No. 43, 20 pp
Brodeur J, Rosenheim JA (2000) Intraguild interactions in aphid parasitoids. Entomol Exp Appl 97:93–108
Brown MW, Schmitt JJ (1990) Growth reduction in nonbearing apple trees by woolly apple aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) on roots. J Econ Entomol 83:1526–1530
Brown MW, Schmitt JJ (1994) Population dynamics of woolly apple aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) in West Virginia apple orchards. Environ Entomol 23:1182–1188
Brown MW, Glenn DM, Wisniewski ME (1991) Functional and anatomical disruption of apple roots by the woolly apple aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae). J Econ Entomol 84:1823–1826
Brown MW, Schmitt JJ, Range S, Hogmire HW (1995) Yield reduction in apple by edaphic woolly apple aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations. J Econ Entomol 88:127–133
Cohen H, Horowitz AR, Nestel D, Rosen D (1996) Susceptibility of the woolly apple aphid parasitoid, Aphelinus mali (Hym.: Aphelinidae), to common pesticides used in apple orchards in Israel. Entomophaga 41:225–233
Cornelius M, Barlow CA (1980) Effect of aphid consumption by larvae on development and reproductive efficiency of a flower fly, Syrphus corollae (Diptera: Syrphidae). Can Entomol 112:989–992
DeBach P (1964) Biological control of insect pests and weeds. Chapman Hall, London, pp 844
Dumbleton LJ, Jeffreys FJ (1938) The control of the woolly aphis by Aphelinus mali. N Z J Sci Technol 20:183–192
Evenhuis HH (1959) Cnemodon vitripennis (Meig.) as a predator of the woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausm.). Entomol Ber 19:238–240
Evenhuis HH (1961) Some notes on the Dipterous enemies of aphids harmful for apple growing in Nova Scotia. Can Entomol 93:1020–1021
Evenhuis HH (1966) Syrphid predators of apple aphids and their parasites, pp. 191–193. Proc. Symp. on Ecology of Aphidophagous Insects, Liblice near Prague, 1965
Gladis T (1994) Establishment and utilization of a mass rearing of Eristalis tenax (Diptera, Syrphidae) in the Gatersleben genebank. Insecta 1:287–294
Gruys P (1982) Hits and misses. The ecological approach to pest control in orchards. Ent Exp Appl 31:70–87
Hagen KS, van den Bosch R (1968) Impact of pathogens, parasites and predators on aphids. Annu Rev Entomol 13:325–338
Heeger VE (1858) Neue metamorphosen einiger dipteren. Sitzungsber Akad Wiss Wien Nat Kl 31:295–309
Heiss EM (1938) A classification of the larvae and puparia of the Syrphidae of Illinois exclusive of aquatic forms. Ill Biol Monogr 4:1–142
Holdsworth RP (1970) Aphids and aphid enemies: Effect of integrated control in an Ohio apple orchard. J Econ Entomol 63:530–535
Howard LO (1929) Aphelinus mali and its travels. Ann Entomol Soc Am 22:341–368
Kan E (1988) Assessment of aphid colonies by hoverflies. II Pea aphids and 3 syrphid species; Betasyrphus serarius (Wiedemann), Metasyrphus frequens Matsumura and Syrphus vitripennis (Meigen) (Diptera: Syrphidae). J Ethol 6:135–142
Lakhanpal GC, Raj D (1998) Predation potential of coccinellid and syrphid on important aphid species infesting rapeseed in Himachal Pradesh. J Entomol Res 2:181–190
Maier CT, Waldbauer GP (1979) Diurnal activity patterns of flower flies (Diptera: Syrphidae) in an Illinois sand area. Ann Entomol Soc Am 72:237–245
Metcalf CL (1916) Syrphidae of Maine. ME Agric Exp Stn Bull 253:193–264
Michaud JP, Belliure B (2001) Impact of syrphid predation on production of migrants in colonies of the brown citrus aphid, Toxoptera citricida (Homoptera: Aphididae). Biol Control 1:91–95
Mols PJM, Boers JM (2001) Comparison of a Canadian and a Dutch strain of the parasitoid Aphelinus mali (Hald.) (Hym., Aphelinidae) for control of woolly apple aphid Eriosoma lanigerum (Haussmann) (Hom., Aphididae) in the Netherlands: a simulation approach. J Appl Entomol 125:255–262
Mueller IE, Blommers LHM, Mols PJM (1988) Earwig (Forficula auricularis) predation on the woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum. Entomol Exp Appl 47:145–152
Nicholas AH, Spooner-Hart RN, Vickers RA (2005) Abundance and natural control of the woolly aphid Eriosoma lanigerum in an Australian apple orchard IPM program. BioControl 50:271–291
Penman DR, Chapman RB (1980) Woolly apple aphid outbreak following use of fenvalerate in apples in Canterbury, New Zealand. J Econ Entomol 73:49–51
Rojo S, Marcos-García MA (1997) Syrphid predators (Dipt.: Syrphidae) of gall forming aphids (Hom.: Aphididae) in Mediterranean areas: Implications for biological control of fruit trees pests. Entomophaga 42:269–276
Rojo S, Gilbert FS, Marcos-Garcia MA, Nieto JM, Mier MP (2003) A world review of predatory hoverflies (Diptera, Syrphidae: Syrphinae) and their prey. CIBIO ediciones, Alicante, Spain, 319 pp
Rosenheim JA (1998) Higher-order predators and the regulation of insect herbivore populations. Annu Rev Entomol 43:421–447
Rüzička Z (1975) The effects of various aphids as larval prey on the development of Metasyrphus corollae (Dipt.: Syrphidae). Entomophaga 20:393–402
Sadeghi H, Gilbert F (2000) Aphid suitability and its relationship to oviposition preference in predatory hoverflies. J Animal Ecol 69:771–784
Schoene WJ, Underhill GW (1935) Life history and migration of the apple woolly aphis. Va. Exp. Stn. Tech. Bull. No. 57. 31 pp
Short BD (2003) Inaugural studies of the life history and predator/prey associations of Heringia calcarata (Loew) (Diptera: Syrphidae), a specialist predator of the woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann) (Homoptera: Eriosomatidae). M.Sc. thesis, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA
Short BD, Bergh JC (2004) Feeding and egg distribution studies of Heringia calcarata (Loew) (Diptera: Syrphidae), a specialized predator of the woolly apple aphid (Homoptera: Eriosomatidae) in Virginia apple orchards. J Econ Entomol 97:813–819
Short BD, Bergh JC (2005) Separation of three common hover fly predators of woolly apple aphid based on the exochorionic sculpturing of eggs. Can Entomol 137:67–70
Soleyman-Nezhadiyan E, Laughlin R (1998) Voracity of larvae, rate of development in eggs, larvae and pupae, and flight seasons of adults of the hoverflies Melangyna viridiceps Macquart and Symosyrphus grandicornis Macquart (Diptera: Syrphidae). Aust J Entomol 37:243–248
Vockeroth JR (1992) The flower flies of the subfamily Syrphinae of Canada, Alaska and Greenland. Diptera: Syrphidae. The insects and arachnids of Canada, Part 18. Agriculture Canada publication 1867, 456 pp
Walker JTS (1985) The influence of temperature and natural enemies on population development of woolly apple aphid, Eriosoma lanigerum (Hausmann). Ph.D. dissertation, Washington State University, Pullman, WA, 88 pp
Walsh BD, Riley CV (1869) The apple-root plant-louse. Am Entomol 5:81–84
Weber DC, Brown MW (1988) Impact on woolly apple aphid (Homoptera: Aphididae) on the growth of potted apple trees. J Econ Entomol 81:1170–1177
Wirth WW, Sedman YS, Weems Jr HV (1965) Family Syrphidae. In: Stone A, Sabrosky C, Wirth W, Foote R, Coulson J (eds) A Catalog of the Diptera of America North of Mexico. United States Department of Agriculture Handbook Number, 276 pp. 557–625
Yothers MA (1953) An annotated bibliography on Aphelinus mali (Hald.) a parasite of the woolly apple aphid 1851–1950. USDA
Acknowledgments
We thank B. Mackintosh for donating sentinel apple trees, C. Thompson and M. Brown for valuable insights and consultation, J. Engleman for assistance with data collection, A. Zhang for photographs of H. calcarata and the Virginia Apple Research Program for partial support of this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergh, J.C., Short, B.D. Ecological and life-history notes on syrphid predators of woolly apple aphid in Virginia, with emphasis on Heringia calcarata . BioControl 53, 773–786 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-007-9114-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-007-9114-0