Abstract
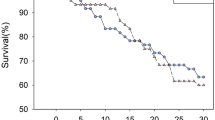
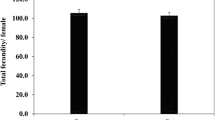
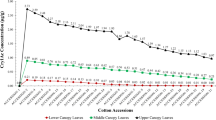
Transgenic cotton has been released for cultivation in several parts of the world to increase crop productivity. However, concerns have been raised regarding the possible undesirable effects of genetically modified crops on non-target organisms in the eco-system. Therefore, we studied the effects of transgenic cottons with cry1Ac gene from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner (Bt) on the natural enemies of cotton bollworm/legume pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under field and laboratory conditions. There was no apparent effect of transgenic cotton on the relative abundance of predatory spiders (Clubiona sp. and Neoscona sp.), coccinellid (Cheilomenes sexmaculatus Fab.), and the chrysopid (Chrysoperla carnea Stephens). However, the abundance of spiders, coccinellids, and chrysopids was quite low in insecticide protected plots towards end of the cropping season. There was a significant reduction in cocoon formation and adult emergence of the ichneumonid parasitoid, Campoletis chlorideae Uchnida reared on H. armigera larvae fed on the leaves of transgenic cottons before and after parasitization. However, no Bt toxins were detected in H. armigera larvae and the parasitoid cocoons with enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Reduction in cocoon formation was because of early mortality of the H. armigera larvae due to Bt toxins in the leaves of transgenic cotton. There was a slight reduction in adult weight and fecundity, and prolongation of the larval period when the parasitoid was raised on H. armigera larvae fed on the leaves of transgenic cotton before and after parasitization. Survival and development of C. chlorideae was also poor when H. armigera larvae were fed on the leaves of cotton hybrid Mech 184. The adverse effects of transgenic cotton on survival and development of C. chlorideae were largely due to early mortality, and possibly poor nutritional quality of H. armigera larvae due to toxic effects of the transgene.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armes N.J., Bond G.S., Cooters R.J. (1992) The Laboratory Culture and Development of Helicoverpa armigera. Natural Resources Institute Bulletin No. 57. Natural Resources Institute, Chatham, UK
Benedict J.H., Sachs E.S., Altman D.W., Deaton D.R., Kohel R.J., Ring D.R., Berberich B.A. (1996) Field performance of cotton expressing CryIA insecticidal crystal protein for resistance to Heliothis virescens and Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctiudae). J. Econ. Entomol. 89:230–238
Brickle, D.S., S.G. Turnipseed, M.J. Sullivan and P. Dugger, 1999. The efficacy of different insecticides and rates against bollworms (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in B.T. and conventional cotton. In: D. Richter (ed.), The Proceedings, Beltwide Cotton Production and Research Conference, 3–7 Jan 1999, Orlando, Florida, USA. Volume 2, National Cotton Council, Memphis, USA. pp. 934–936
Cui J.J., Xia J.Y. (1997) The effect of Bt transgenic cotton on the feeding function of major predators. China Cottons 24:19
Cui J.J., Xia J.Y. (1998) Effects of early seasonal strain of Bt transgenic cotton on population dynamics of main pests and their natural enemies. Acta Gossypii Sin. 10:255–262
Cui J.J., Xia J.Y. (1999) Effects of transgenic Bt cotton on development and reproduction of cotton bollworm. Acta Agric. Univ. Henan 33:20–24
Daly T., Buntin G.D. (2005) Effect of Bacillus thuringiensis transgenic corn for Lepidopteran control of nontarget arthropods. Environ. Entomol. 34:1292–1301
Dutton A., Klein H., Romeis J., Bigler F. (2002) Uptake of Bt toxin by herbivores feeding on transgenic maize and consequences for the predator, Chrysoperla carnea. Ecol. Entomol. 27:441–447
Dutton A., Klein H., Romeis J., Bigler F. (2003) Prey mediated effects of Bacillus thuringiensis spray on the predator Chrysoperla carnea in maize. Biol. Control 26:209–215
Fitt G.P. (2003) Deployment and impact of transgenic Bt cottons in Australia. In: Kalaitzandonakes N.G. (ed). The Economic and Environmental Impacts of Agbiotech: A Global Perspective. Kluwer Press, New York, USA, pp 141–164
Flint H.M., Henneberry T.J., Wilson F.D., Holguin E., Parks N., Buehler R.E. (1995) The effects of transgenic cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L.; containing Bacillus thuringiensis toxin genes for the control of the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossipiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera, Gelechiidae) and other arthropods. Southwest Entomol. 20:281–292
Greenplate J.T. (1999) Quantification of Bacillus thuringiensis insect control protein Cry1A(c) over time in Bollgard cotton fruit and terminals. J. Econ. Entomol. 92:1377–1383
Guo S.D., Cui H.Z., Xia L.Q., Wu D.L., Ni W.C., Zhang Z.L., Zhang B.L., Xu Y.J. (1999) Development of bivalent insect-resistant transgenic cotton plants. Sci. Agric. Sin. 32:1–7
Hagerty A.M., Kilpatrick A.L., Turnipseed S.G., Sullivan M.J., Bridges W.C. (2005) Predaceous arthropods and lepidopteran pests on conventional Bollgard and Bollgard II cotton under untreated and disrupted conditions. Environ. Entomol. 34:105–114
Harwood J.K., Wallin W.G., Obrycki J.J. (2005) Uptake of Bt endotoxins by nontarget herbivores and higher arthropod predators: molecular evidence from a transgenic corn agroecosystem. Mol. Ecol. 14:2815–2823
Head G., Moar W., Eubanks M., Freeman B., Ruberson J., Hagerty A., Turnipseed S. (2005) A multiyear, large-scale comparison of arthropod populations on commercially managed Bt and non-Bt cotton fields. Environ. Entomol. 34:1257–1266
Hilbeck A., Baumgartner M., Fried P.M., Bigler F. (1998a) Effects of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis corn-fed prey on mortality and development time of immature Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Environ. Entomol. 27:480–487
Hilbeck A., Moar W.J., Pusztai C.M., Filippini A., Bigler F. (1998b) Toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis Cry1Ab toxin to the predator, Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Environ. Entomol. 27:1255–1263
Hilbeck A., Moar W.J., Puzstai C.M., Filippini A., Bigler F. (1999) Prey mediated effects of Cry1Ab toxin and protoxin on the predator, Chrysoperla carnea. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 91:305–316
Hilder V.A., Boulter D. (1999) Genetic engineering of crop plants for insect resistance – a critical review. Crop Prot. 18:177–191
Hoffmann M.P., Zalom F.G., Wilson L.T., Smilanick J.M., Malyj L.D., Kiser J., Hilder V.A., Barnes W.M. (1992) Field evaluation of transgenic tobacco containing genes encoding Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin or cowpea trypsin inhibitor: efficacy against Helicoverpa zea (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 85:2516–2522
James, C. 2003. Preview: Global Status of Commercialized Transgenic Crops: 2003. ISAAA Briefs No. 30. International Service for Acquisition of Agri-Biotech Applications (ISAAA), Ithaca, New York, USA. http://www.isaaa.org/Publications/briefs_26.htm
Johnson M.T. (1997) Interaction of resistant plants and wasp parasitoids of tobacco budworm (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Environ. Entomol. 26:207–214
Johnson M.T., Gould R. (1992) Interaction of genetically engineered host plant resistance and natural enemies of Heliothis virescens (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in tobacco. Environ. Entomol. 21:586–597
Johnson M.T., Gould F., Kennedy G.G. (1997) Effects of natural enemies on relative fitness of Heliothis virescens genotypes adapted and not adapted to resistant host plants. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 82:219–230
Liu Z.C., Ye G.Y., Fu Q., Zhang Z.T., Hu C. (2003) Indirect impact assessment of transgenic rice with cry1Ab gene on predations by the wolf spider, Pirata subpiraticus. Chinese J. Rice Sci. 17:175–178
Lu R., Zhong Y.Y., Xuan L., Lin M., Shu Y.Y., QiLian Q. (2004) Impact of transgenic Cry1A plus CpTI cotton on Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and its two endoparasitoid wasps Microplitis mediator (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and Campoletis chlorideae (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Acta Entomol. Sin. 47:1–7
Luttrell, R.G., V.J. Mascarenhas, J.C. Schneider, C.D. Parker and P.D. Bullock, 1995. Effect of transgenic cotton expressing endotoxin protein on arthropod population in Mississippi cotton. In: Proceedings, Beltwide Cotton Production Research Conference. National Cotton Council of America, Memphis, Tennesse, USA. pp. 760–763
Men X.Y., Ge F., Liu X.H., Yardim E.N. (2003) Diversity of arthropod communities in transgenic Bt cotton and nontransgenic cotton agroecosystems. Environ. Entomol. 32:270–275
Naranjo S.E. (2005) Long-term assessment of the effects of transgenic Bt cotton on the abundance of nontarget arthropod natural enemies. Environ. Entomol. 34:1193–1210
Ni W.C., Huang J.Q., Guo S.D., Shu C.G., Wu J.Y., Wang W.G., Zhang A.L., Chen S., Mao L.Q., Wang Y., Xu Y.J., Gu L.M., Zhou B.L., Shen X.L., Xiao S.H. (1996) Transgenic bollworm-resistant cotton plants containing the synthetic gene coding Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal protein. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 12:1–6
Orr D.B., Landis D.A. (1997) Oviposition of European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and impact of natural enemy populations in transgenic versus isogenic corn. J. Econ. Entomol. 90:905–909
Pilcher C.D., Rice M.E., Obrycki J.J. (2005) Impact of transgenic Bacillus thuringiensis corn and crop phenology on five nontarget arthropods. Environ. Entomol. 34:1302–1316
Qaim M., Zilberman D. (2003) Yield effects of genetically modified crops in developing countries. Science 299:900–902
Romeis J., Dutton A., Bigler F. (2004) Bacillus thuringiensis toxin (CryA1b) has no direct effect on the green lacewing Chrysoperla carnea (Stephens) (Neuroptera; Chrysopidae). J. Insect Physiol. 50:175–183
Sharma H.C., Ortiz R. (2000) Transgenics, pest management, and the environment. Curr. Sci. 79:421–437
Sharma H.C., Pampapathy G., Dhillon M.K., Ridsdill-Smith T.J. (2005) Detached leaf assay to screen for host plant resistance to Helicoverpa armigera. J. Econ. Entomol. 98:568–576
Sharma, H.C., K.K. Sharma, N. Seetharama and R. Ortiz, 2000. Prospects for using transgenic resistance to insects in crop improvement. Electronic J. Biotechnol. 3(2). http://www.ejb.org/content/vol3/issue 2/full/20
Sharma H.C., Sharma K.K., Seetharama N., Crouch J.H. (2004) Genetic engineering of crops for insect control: Effectiveness and strategies for gene deployment. CRC Critical Rev. Plant Sci. 23:47–72
Shelton A.M., Zhao J.Z., Roush R.T. (2002) Economic, ecological, food safety, and social consequences of the deployment of Bt transgenic plants. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 47:845–881
Sims S.R. (1995) Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki CryIA (c) protein expressed in transgenic cotton: effects on beneficial and other non-target insects. Southwest Entomol. 20:493–500
Torres J.B., Ruberson J.R. (2005) Canopy- and ground-dwelling predatory arthropods in commercial Bt and non-Bt cotton fields: patterns and mechanisms. Environ. Entomol. 34:1242–1256
Wang C.Y., Xia J.Y. (1997) Differences of population dynamics of bollworms and of population dynamics of major natural enemies between Bt transgenic cotton and conventional cotton. China Cottons 24:13–15
Wilson W.D., Flint H.M., Deaton R.W., Fischhoff D.A., Perlak F.J., Armstrong T.A., Fuchs R.L., Berberich S.A., Parks N.J., Stapp B.R. (1992) Resistance of cotton lines containing a Bacillus thuringiensis toxin to pink bollworm (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) and other insects. J. Econ. Entomol. 85:1516–1521
Xin C.H., Di L.W., Ming W.K., Quing F.H., Guang X., Yuan G.Y. (2004) Effect of transgenic cotton carrying CryA + CpTI + cry1Ac genes on diversity of arthropod communities in cotton field in North China. Chinese J. Agric. Biotech. 1:17–21
Zwahlen C., Andow D.A. (2005) Field evidence for the exposure of ground beetles to Cry 1Ab from trangenic corn. Environ. Biosafety Res. 4:113–117
Acknowledgements
We thank S.V. Narayanchandra, K. Hareendranath, Madhusudhan Reddy, J. Raja Rao and V. Venkateswara Rao for their help in these studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, H.C., Arora, R. & Pampapathy, G. Influence of transgenic cottons with Bacillus thuringiensis cry1Ac gene on the natural enemies of Helicoverpa armigera . BioControl 52, 469–489 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-006-9032-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-006-9032-6