Abstract
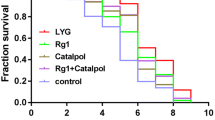
There is considerable interest in using traditional Chinese medicine formulas (TCMF) to delay aging or treat age-related diseases. Due to cost and duration, the beneficial effects of TCMF on prolongation are mainly extrapolated from vitro studies or physiological indexes. Little is known about whether TCMF are beneficial in whole level, particularly with respect to lifespan. To address this issue, we selected eight formulas with anti-oxidative activity and examined their effects on the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. The results showed that seven of the eight formulas could prolong lifespan of TK22 mutant significantly and five of the eight formulas could obviously extend lifespan of N2 wild-type. To further characterize the prolongation effects, oxidative stress, thermal stress and reproduction test were assayed. We found that the formulas that extended lifespan of TK22 could also protect it from oxidative stress, without reducing the reproductive capacity. Meanwhile, the formulas that prolonged lifespan of N2 wild-type could also enhance its resistance against thermal stress, with damaging the reproductive fitness. These observations indicate that TCMF used in our experiment could be potential therapeutics for anti-aging.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler MI, Cassidy EJ, Fricke C et al (2013) The lifespan-reproduction trade-off under dietary restriction is sex-specific and context-dependent. Exp Gerontol 48(6):539–548
Balaban RS, Nemoto S, Finkel T (2005) Mitochondria, oxidants, and aging. Cell 120(4):483–495
Bass TM, Weinkove D, Houthoofd K et al (2007) Effects of resveratrol on lifespan in Drosophila melanogaster and Caenorhabditis elegans. Mech Ageing Dev 128(10):546–552
Blagosklonny MV (2009) Validation of anti-aging drugs by treating age-related diseases. Aging 1(3):281–288
Cai YZ, Luo Q, Sun M et al (2004) Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds of 112 traditional Chinese medicinal plants associated with anticancer. Life Sci 74(17):2157–2184
Chen YF, Wu CY, Kao CH et al (2010) Longevity and lifespan control in mammals: lessons from the mouse. Ageing res rev 9:S28–S35
Collins JJ, Evason K, Kornfeld K (2006) Pharmacology of delayed aging and extended lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans. Exp Gerontol 41(10):1032–1039
Committee CP (2010) Pharmacopoeia of the people’s Republic of China. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing
Du X, Yang RX, Chen XQ (1992) Effect on anti-aging and treating yang deficiency of kidney with huanshao dan capsules: a clinical report of 309 cases. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med (in Chinese) 12(1):20–22
Feng P, Wang XJ (2006) Antioxidation and scavenging effects of shengmaisan. Pharmacol Clin Chin mater med (in Chinese) 22(3):18–20
Gruber J, Tang SY, Halliwell AB (2007) Evidence for a trade-off between survival and fitness caused by resveratrol treatment of Caenorhabditis elegans. Ann NY Acad Sci 1100(1):530–542
Halliwell and Barry (1999) Establishing the significance and optimal intake of dietary antioxidants: the biomarker concept. Nutr Rev 57(4):104–113
Harman D (1972) Free radical theory of aging: dietary implications. Am J Clin nutr 25(8):839–843
Harman D (2009) Origin and evolution of the free radical theory of aging: a brief personal history, 1954–2009. Biogerontology 10(6):773–781
He GX (2010) Clinical new uses of Shiquan dabu pill. J Benef Read Drug Inf Med Adv (in Chinese) 003:50–51
Ho YS, So KF, C-C Chang R (2010) Anti-aging herbal medicine—How and why can they be used in aging-associated neurodegenerative diseases? Ageing Res Rev 9(3):354–362
Ishii N, Senoo-Matsuda N, Miyake K (2004) Coenzyme Q10 can prolong C. elegans lifespan by lowering oxidative stress. Mech Ageing Dev 125(1):41–46
Jiang KM (1987) Anti-aging traditional Chinese medicine formulas dictionary. Shanghai College of Traditional Chinese Medicine Press, Beijing
Jiang WY (2005) Therapeutic wisdom in traditional Chinese medicine: a perspective from b modern science. Trends Pharmacol Sci 26(11):558–563
Leung PC (2010) Healthy aging. World Scientific Publishing Co. Pte. Ltd., Jurong East
Li CZ, Zeng CC, Li JP et al (2003) Effects of Qibao Meiran Pellet on free radicals and immune indexes in aging rats. J Guangzhou Univ of Tradit Chin Med 20(1):66–68
Liang GY (2008) Anti-aging research overview of traditional Chinese medicine. Clin J Tradit Chin Med (in Chinese) 20(2):208–209
Lithgow GJ, Walker GA (2002) Stress resistance as a determinate of C. elegans lifespan. Mech Ageing Dev 123(7):765–771
Liu YY, He SQ, Zhang XT et al (2003) Experimental study of the Erchen decoction on subacute aging mice. J Liaoning coll TCM 5(4):373–375
Liu QL, Zhang YJ, Hu M et al (2005) Ability of eliminating active oxygen and the changes of DNA telomere length in aging mice and the interventional effects of huanshao dan. Chin J Clin Rehabil 9(19):146–147
Mattson MP (2008) Hormesis defined. Ageing Res Rev 7:1–7
Muller FL, Lustgarten MS, Jang Y et al (2007) Trends in oxidative aging theories. Free Radic Biol Med 43:477–503
Muñoz MJ, Riddle DL (2003) Positive selection of Caenorhabditis elegans mutants with increased stress resistance and longevity. Genetics 163(1):171–180
Olsen A, Vantipalli MC, Lithgow GJ (2006) Using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model for aging and age-related diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1067(1):120–128
Pun PBL, Gruber J, Tang SY et al (2010) Ageing in nematodes: do antioxidants extend lifespan in Caenorhabditis elegans? Biogerontology 11(1):17–30
Ran QT, Liang HY, Ikeno YJ et al (2007) Reduction in glutathione peroxidase 4 increases life span through increased sensitivity to apoptosis. J Gerontol A 62(9):932–942
Silverman GA, Luke CJ, Bhatia SR et al (2009) Modeling molecular and cellular aspects of human disease using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. Pediatr Res 65(1):10–18
Stiernagle T (2006). Maintenance of C.elegans. The C.elegans Research Community, WormBook, USA
Stroustrup N, Ulmschneider BE, Nash ZM et al (2013) The Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan machine. Nat Methods 10:665–670
Sulston JE, Brenner S (1974) The DNA of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 77:95–105
Tang SY, Whiteman M, Peng ZF et al (2004) Characterization of antioxidant and antiglycation properties and isolation of active ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines. Free Radic Biol Med 36(12):1575–1587
Wang XY, Cheng WL, Kuang SS (2009). The study on learning memory and antioxidantion of Shi quandabu decoction to the d-galactose model of mouse. China Prac. Med. 8, 4(23): 52–54
Wang XJ, Zhang AH, Sun H (2012) Future perspectives of chinese medical formulae: chinmedomics as an effector. OMICS J Integr Biol 16(7–8):414–421
Wiegant FAC, Surinova S, Ytsma E et al (2009) Plant adaptogens increase lifespan and stress resistance in C.elegans. Biogerontology 10(1):27–42
Wilson MA, Shukitt-Hale B, Kalt W et al (2006) Blueberry polyphenols increase lifespan and thermotolerance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 5:59–68
Wood JG, Rogina B, Lavu S et al (2004) Sirtuin activators mimic caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature 430:686–689
Wu SX, Guo NR (2005) Analysis anti-aging effects of traditional chinese medicine from free radical theory. Chin J Dermatovenerol of Integr Tradit West Med (in Chinese) 4(1):52–53
Xie XY, Chao YM, Du Z et al (2010) Effects of polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata B1 on anti-aging of aging mice. Pharma J Chin people’s Lib Army (in Chinese) 26(3):206–209
You JS, Huang HF, Lee YS (2006) Sheng-mai-san reduces adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Am J Chin Med 34(02):295–305
Zhou HS (2006) Mechanism of anti-aging activity in Liuwei dihuang Pill. Guangming J Chin Med (in Chinese) 21(10):45–46
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the special international cooperation project of MOST (2012DFA30480); the key project of Gansu Province science and technology (1002WKDE55); Gansu Province International Science and Technology Cooperation Project (090WCGA900); the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities of China (lzujbky-2013-71, lzujbky-2013-75, lzujbky-2014-147, lzujbky-2014-149, and lzujbky-2014-150).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, F., Zhi, D., Liu, D. et al. Lifespan extension in Caenorhabiditis elegans by several traditional Chinese medicine formulas. Biogerontology 15, 377–387 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9508-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9508-1