Abstract
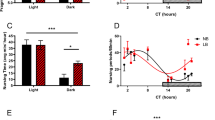
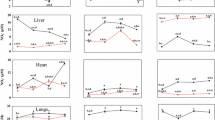
Circadian system has direct relevance to the problems of modern lifestyle, shift workers, jet lag etc. To understand non-photic regulation of biological clock, the effects of restricted feeding (RF) on locomotor activity and daily leptin immunoreactivity (ir) rhythms in three age groups [3, 12 and 24 months (m)] of male Wistar rats maintained in light:dark (LD) 12:12 h conditions were studied. Leptin-ir was examined in the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), the medial preoptic area (MPOA) and organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis (OVLT). Reversal of feeding time due to restricted food availability during daytime resulted in switching of the animals from nocturnality to diurnality with significant increase in day time activity and decrease in night time activity. The RF resulted in % diurnality of approximately 32, 29 and 73 from % nocturnality of 82, 92 and 89 in control rats of 3, 12 and 24 m age, respectively. The increase in such switching from nocturnality to diurnality with restricted feeding was found to be robust in 24 m rats. The OVLT region showed daily leptin-ir rhythms with leptin-ir maximum at ZT-0 in all the three age groups. However leptin-ir levels were minimum at ZT-12 in 3 and 12 m though at ZT-18 in 24 m. In addition the mean leptin-ir levels decreased with increase in food intake and body weight significantly in RF aged rats. Thus we report here differential effects of food entrained regulation in switching nocturnality to diurnality and daily leptin-ir rhythms in OVLT in aged rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arble DM, Bass J, Laposky AD, Vitaterna MH, Turek FW (2009) Circadian timing of food intake contributes to weight gain. Obesity 17:2100–2102
Barclay JL, Husse J, Bode B, Naujokat N, Meyer-Kovac J, Schmid SM, Lehnert H, Oster H (2012) Circadian desynchrony promotes metabolic disruption in a mouse model of shift work. PLoS ONE 7:e37150
Bechtold D, Loudon A (2013) Hypothalamic clocks and rhythms in feeding behaviour. Trends Neurosci 36:74–82
Boden G, Chen X, Mozzoli M, Ryan I (1996) Effect of fasting on serum leptin in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:3419–3423
Bodosi B, Gardi J, Hajdu I, Szentirmai E, Obal F Jr, Krueger JM (2004) Rhythms of ghrelin, leptin, and sleep in rats: effects of the normal diurnal cycle, restricted feeding, and sleep deprivation. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 287:R1071–R1079
Bosler O, Descarries L (1988) Monoamine innervation of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis (OVLT): a high resolution radioautographic study in the rat. J Comp Neurol 272:545–561
Boulos Z, Terman M (1980) Food availability and daily biological rhythms. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 4:119–131
Caba M, Tovar A, Silver R, Mogado E, Meza E, Zavaleta Y, Juárez C (2008) Nature’s food anticipatory experiment: entrainment of locomotor behavior, suprachiasmatic and dorsomedial hypothalamic nuclei by suckling in rabbit pups. Eur J Neurosci 27:432–443
Carneiro BTS, Araujo JF (2011) Influence of scheduled restricted feeding on reentrainment of motor activity rhythm after a 6-h light-dark advance in rats. Psychol Neurosci 4:317–322
Chabot CC, Connolly DM, Waring BB (2012) The effects of lighting conditions and food restriction paradigms on locomotor activity of common spiny mice, Acomys cahirinus. J Circadian Rhythm 10:1–7
Challet E (2010) Interactions between light, mealtime and calorie restriction to control daily timing in mammals. J Comp Physiol B 180:631–644
Choi SJ, Wong LS, Yamat C, Dallman MF (1998) Hypothalamic ventromedial nuclei amplify circadian rhythms: do they contain a food-entrained endogenous oscillator? J Neurosci 18:3843–3852
Clark KA, MohanKumar SM, Kasturi BS, MohanKumar PS (2006) Effects of central and systemic administration of leptin on neurotransmitter concentrations in specific areas of the hypothalamus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 290:R306–R312
Cohen IR, Wise PM (1988) Age related changes in the diurnal rhythms of serotonin turnover in microdissected brain area of estradiol-treated ovariectomized rats. Endocrinology 88:2626–2633
Dallongeville J, Hecquet B, Lebel P, Edme JL, Le Fur C, Fruchart JC, Auwerx J, Romon M (1998) Short term response of circulating leptin to feeding and fasting in man: influence of circadian cycle. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22:728–733
Damiola F, Minh NL, Preitner N, Kornmann B, Fleury-Olela F, Schibler U (2000) Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev 14:2950–2961
Díaz-Muñoz M, Vázquez-Martínez O, Aguilar-Roblero R, Escobar C (2000) Anticipatory changes in liver metabolism and entrainment of insulin, glucagon, and corticosterone in food-restricted rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R2048–R2056
Doi M, Ishida A, Miyake A, Sato M, Komatsu R, Yamazaki F, Kimura I, Tsuchiya S, Kori H, Seo K, Yamaguchi Y, Matsuo M, Fustin JM, Tanaka R, Santo Y, Yamada H, Takahashi Y, Araki M, Nakao K, Aizawa S, Kobayashi M, Obrietan K, Tsujimoto G, Okamura H (2011) Circadian regulation of intracellular G-protein signalling mediates intercellular synchrony and rhythmicity in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Nat Commun 2:327–336
Doyle SE, Yoshikawa T, Hillson H, Menaker M (2008) Retinal pathways influence temporal niche. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13133–13138
Froy O (2010) Metabolism and circadian rhythms—implications for body weight. Open Neuroendocrinol J 3:28–37
Jagota A (2005) Aging and sleep disorders. Indian J Gerontol 19:415–424
Jagota A (2006) Suprachiasmatic nucleus: center for circadian timing system in mammals. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad B 71:285–300
Jagota A (2012) Age induced alterations in biological clock: therapeutic effects of melatonin. In: Thakur MK, Rattan SI (eds) Brain aging and therapeutic interventions. Springer Netherlands, London, pp 111–129
Jagota A, Kalyani D (2008) Daily serotonin rhythms in rat brain during postnatal development and aging. Biogerontology 9:229–234
Jagota A, Kalyani D (2010) Effect of melatonin on age induced changes in daily serotonin rhythms in suprachiasmatic nucleus of male wistar rat. Biogerontology 11:299–308
Jagota A, Reddy MY (2007) The effect of curcumin on ethanol induced changes in suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and pineal. Cell Mol Neurobiol 27:997–1006
Jagota A, de la Iglesia HO, Schwartz WJ (2000) Morning and evening circadian oscillations in the suprachiasmatic nucleus in vitro. Nat Neurosci 3:372–376
Jiang ZG, Teshima K, Yang Y, Yoshioka T, Allen CN (2000) Pre- and postsynaptic actions of serotonin on rat suprachiasmatic nucleus neurons. Brain Res 866:247–256
Johnson AK, Loewy AD (1990) Circumventricular organs and their role in visceral functions. In: Loewy AD, Spyer KM (eds) Central regulation of autonomic function. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 247–267
Kalsbeek A, Scheer FA, Perreau-Lenz S, La Fleur SE, Yi CX, Fliers E, Buijs RM (2011) Circadian disruption and SCN control of energy metabolism. FEBS Lett 585:1412–1426
Karakas A, Serin E, Gunduz B (2006) Food restriction affects locomotor activity in Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). Turkish J Biol 30:23–28
Korkmaz A, Topal T, Tan DX, Reiter RJ (2009) Role of melatonin in metabolic regulation. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 10:261–270
Krajnak K, Rosewell KL, Duncan MJ, Wise PM (2003) Aging, estradiol and time of day differentially affect serotonin transporter binding in the central nervous system of the female rats. Brain Res 990:87–94
Krieger DT (1974) Food and water restriction shifts corticosterone, temperature, activity and brain amine periodicity. Endocrinology 95:1195–1201
Laposky AD, Bass J, Kohsaka A, Turek FW (2008) Sleep and circadian rhythms: key components in the regulation of energy metabolism. FEBS Lett 582:142–151
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM (1996) Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 379:632–635
Lee SJ, Verma S, Simonds SE, Kirigiti MA, Kievit P, Lindsley SR, Loche A, Smith MS, Cowley MA, Grove KL (2013) Leptin stimulates neuropeptide y and cocaine amphetamine-regulated transcript coexpressing neuronal activity in the dorsomedial hypothalamus in diet-induced obese mice. J Neurosci 33:15306–15317
Lévi F, Okyar A, Dulong S, Innominato PF, Clairambault J (2010) Circadian timing in cancer treatments. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:377–421
Mammen AP, Jagota A (2011) Immunocytochemical evidence for different patterns in daily rhythms of VIP and AVP peptides in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of diurnal Funambulus palmarum. Brain Res 1373:39–47
Manikonda PK, Jagota A (2012) Melatonin administration differentially affects age-induced alterations in daily rhythms of lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzymes in male rat liver. Biogerontology 13:511–524
Marie M, Findlay PA, Thomas L, Adam CL (2001) Daily patterns of plasma leptin in sheep: effects of photoperiod and food intake. J Endocrinol 170:277–286
Martin SS, Qasim A, Reilly MP (2008) Leptin resistance: a possible interface of inflammation and metabolism in obesity-related cardiovascular disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 52:1201–1210
Mercer JG, Hoggard N, Williams LM, Lawrence CB, Hannah LT, Trayhurn P (1996) Localization of leptin receptor mRNA and the long form splice variant (Ob-Rb) in mouse hypothalamus and adjacent brain regions by in situ hybridization. FEBS Lett 387:113–116
Mistlberger RE, Kent BA, Chan S, Patton DF, Weinberg A, Parfyonov M (2012) Circadian clocks for all meal-times: anticipation of 2 daily meals in rats. PLoS ONE 7:e31772
Montoya A, López-Olmeda JF, Garayzar AB, Sánchez-Vázquez FJ (2010) Synchronization of daily rhythms of locomotor activity and plasma glucose, cortisoland thyroid hormones to feeding in Gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata) under a light–dark cycle. Physiol Behav 101:101–107
Partch CL, Green CB, Takahashi JS (2013) Molecular architecture of the mammalian circadian clock. Trends Cell Biol 24:90–99
Polston EK, Simerly RB (2006) Ontogeny of the projections from the anteroventral periventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in the female rat. J Comp Neurol 495:122–132
Prosser RA, Bergeron HE (2003) Leptin phase-advances the rat suprachiasmatic circadian clock in vitro. Neurosci Lett 336:139–142
Quennell JH, Mulligan AC, Tups A, Liu X, Phipps SJ, Kemp CJ, Herbison AE, Grattan DR, Anderson GM (2009) Leptin indirectly regulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuronal function. Endocrinology 150:2805–2812
Rattan SI (2012) Biogerontology: from here to where? The Lord Cohen Medal Lecture-2011. Biogerontology 13:83–91
Salgado-Delgado R, Tapia Osorio A, Saderi N, Escobar C (2011) Disruption of circadian rhythms: a crucial factor in the etiology of depression. Depress Res Treat 2011:839743
Scheer FA, Shea TJ, Hilton MF, Shea SA (2008) An endogenous circadian rhythm in sleep inertia results in greatest cognitive impairment upon awakening during the biological night. J Biol Rhythms 23:353–361
Schoeller DA, Cella LK, Sinha MK, Caro JF (1997) Entrainment of the diurnal rhythm of plasma leptin to meal timing. J Clin Invest 100:1882–1887
Schumann DM, Cooper HM, Hofmeyr MD, Bennett NC (2005) Circadian rhythm of locomotor activity in the four-striped field mouse, Rhabdomys pumilio: a diurnal African rodent. Physiol Behav 85:231–239
Smith RG, Betancourt L, Sun Y (2005) Molecular endocrinology and physiology of the ageing central nervous system. Endocrine Rev 26:203–250
Taheri S, Lin L, Austin D, Young T, Mignot E (2004) Short sleep duration is associated with reduced leptin, elevated ghrelin, and increased body mass index. PLoS Med 1:e62
Takeda H, Nakagawa K, Okubo N, Nishimura M, Muto S, Ohnishi S, Sakamoto N, Hosono H, Asaka M (2013) Pathophysiologic basis of anorexia: focus on the interaction between ghrelin dynamics and the serotonergic system. Biol Pharm Bull 36:1401–1405
Vujovic P, Lakic I, Laketa D, Jasnic N, Djurasevic SF, Cvijic G, Djordjevic J (2011) Time-dependent effects of starvation on serum, pituitary and hypothalamic leptin levels in rats. Physiol Res 60(Suppl 1):S165–S170
Welsh DK, Takahashi JS, Kay SA (2010) Suprachiasmatic nucleus: cell autonomy and network properties. Annu Rev Physiol 72:551–577
Yoon JA, Han DH, Noh JY, Kim MH, Son GH, Kim K, Kim CJ, Pak YK, Cho S (2012) Meal time shift disturbs circadian rhythmicity along with metabolic and behavioral alterations in mice. PLoS ONE 7:e44053
Yu EA, Weaver DR (2011) Disrupting the circadian clock: gene-specific effects on aging, cancer, and other phenotypes. Aging 3:479–493
Zhang G, Bai H, Zhang H, Dean C, Wu Q, Li J, Guariglia S, Meng Q, Cai D (2011) Neuropeptide exocytosis involving synaptotagmin-4 and oxytocin in hypothalamic programming of body weight and energy balance. Neuron 69:523–535
Zhao K, Ao Y, Harper RM, Go VL, Yang H (2013) Food-intake dysregulation in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats: hypothesized role of dysfunctional brainstem thyrotropin-releasing hormone and impaired vagal output. Neuroscience 247:43–54
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by ICMR (Ref. No. BMS/NTF/14/2006-2007, DST (Do No. SR/SO/AS-47/2004), UGC (ref: F.No. 32-613/2006/(SR) and UPE grants to AJ. VDK Reddy is thankful to ICMR for fellowship. Authors are thankful to Prof. W. J. Schwartz for critical reading and valuable suggestions during preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, V.D.K., Jagota, A. Effect of restricted feeding on nocturnality and daily leptin rhythms in OVLT in aged male Wistar rats. Biogerontology 15, 245–256 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9494-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-014-9494-3