Abstract
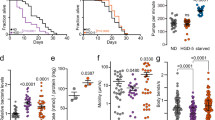
Aging is associated with accumulation of toxic intracellular and extracellular protein aggregates. Cells manage “aged” proteins by mobilizing their molecular chaperones or heat shock proteins that are also considered as determinants of lifespan in diverse species. In this study, we tested whether an exogenous addition of the non-toxic chemical chaperone ‘glycerol’ could elicit stress and geronto-protective activities. We found that glycerol enhanced chaperoning of heat-denatured proteins. In addition to stimulating proteasome activity, glycerol led to an increased expression of the stress chaperone ‘mortalin’ and decreased p53 function in human cells. Glycerol-fed worms exhibited thermo-tolerance and lower level of age-associated auto-fluorescence. Through the combined stimulation of the proteasome and chaperoning activities of mortalin, in particular, glycerol treatment resulted in increased survival and fitness against oxidative- and heat-stress. These results may have significant implications in the use of glycerol as a candidate geronto-modulator in development of practical interventions for “healthy aging”.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai C, Biwersi J, Verkman AS, Matthay MA (1998) A mouse model to test the in vivo efficacy of chemical chaperones. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 40:39–45
Ballinger CA, Connell P, Wu Y, Hu Z, Thompson LJ, Yin LY, Patterson C (1999) Identification of CHIP, a novel tetratricopeptide repeat-containing protein that interacts with heat shock proteins and negatively regulates chaperone functions. Mol Cell Biol 19:4535–4545
Bayer AJ, Pathy MS, Newcombe R (1987) Double-blind randomised trial of intravenous glycerol in acute stroke. Lancet 1:405–408
Benaroudj N, Lee DH, Goldberg AL (2001) Trehalose accumulation during cellular stress protects cells and cellular proteins from damage by oxygen radicals. J Biol Chem 276:24261–24267
Berger C, Sakowitz OW, Kiening KL, Schwab S (2005) Neurochemical monitoring of glycerol therapy in patients with ischemic brain edema. Stroke 36:e4–e6
Brown CR, Hong-Brown LQ, Biwersi J, Verkman AS, Welch WJ (1996) Chemical chaperones correct the mutant phenotype of the delta F508 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein. Cell Stress Chaperones 1:117–125
Campisi J (2005) Senescent cells, tumor suppression, and organismal aging: good citizens, bad neighbors. Cell 120:513–522
Chavez Zobel AT, Loranger A, Marceau N, Theriault JR, Lambert H, Landry J (2003) Distinct chaperone mechanisms can delay the formation of aggresomes by the myopathy-causing R120G alphaB-crystallin mutant. Hum Mol Genet 12:1609–1620
Chondrogianni N, Gonos ES (2005) Proteasome dysfunction in mammalian aging: steps and factors involved. Exp Gerontol 40:931–938
Chou TC, Motzer RJ, Tong Y, Bosl GJ (1994) Computerized quantitation of synergism and antagonism of taxol, topotecan, and cisplatin against human teratocarcinoma cell growth: a rational approach to clinical protocol design. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:1517–1524
Conconi M, Friguet B (1997) Proteasome inactivation upon aging and on oxidation-effect of HSP 90. Mol Biol Rep 24:45–50
Dahlmann B, Becher B, Sobek A, Ehlers C, Kopp F, Kuehn L (1993) In vitro activation of the 20S proteasome. Enzyme Protein 47:274–284
de Jong JC, Willems PH, Goossens M, Vandewalle A, van den Heuvel LP, Knoers N. V, Bindels RJ (2004) Effects of chemical chaperones on partially retarded NaCl cotransporter mutants associated with Gitelman’s syndrome in a mouse cortical collecting duct cell line. Nephol Dial Transplant 19:1069–1076
Deocaris CC, Shrestha BG, Kraft DC, Yamasaki K, Kaul SC, Rattan SI, Wadhwa R (2006) Geroprotection by glycerol: insights to its mechanisms and clinical potentials. Ann NY Acad Sci 1067:488–492
Diamant S, Eliahu N, Rosenthal D, Goloubinoff P (2001) Chemical chaperones regulate molecular chaperones in vitro and in cells under combined salt and heat stresses. J Biol Chem 276:39586–39591
Ehenfried JA, Evers BM, Chu KU, Townsend CM Jr, Thompson JC (1996) Caloric restriction increases the expression of heat shock protein in the gut. Ann Surg 223:592–597
Fisher AL, Lithgow GJ (2006) The nuclear hormone receptor DAF-12 has opposing effects on Caenorhabditis elegans lifespan and regulates genes repressed in multiple long-lived worms. Aging Cell 5:127–138
Frigeri A, Gropper MA, Umenishi F, Kawashima M, Brown D, Verkman AS (1995) Localization of MIWC and GLIP water channel homologs in neuromuscular, epithelial and glandular tissues. J Cell Sci 108:2993–3002
Gu Y, Singh N (2004) Doxycycline and protein folding agents rescue the abnormal phenotype of familial CJD H187R in a cell model. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 123:37–44
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K (1989) Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods 119:203–210
Hatayama T, Fujimoto S, Sakai K (1997) Effect of hyperosmotic NaCl and glycerol stress on stress response of human HeLa cells. Biol Pharm Bull 20:605–612
Ishikawa M, Sekizuka E, Sato S, Yamaguchi N, Inamasu J, Kawase T (1999) Glycerol attenuates the adherence of leukocytes in rat pial venules after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Neurol Res 21:785–790
Kaul SC, Reddel RR, Sugihara T, Mitsui Y, Wadhwa R (2000) Inactivation of p53 and life span extension of human diploid fibroblasts by mot-2. FEBS Lett 474:159–164
Kaul SC, Taira K, Pereira-Smith OM, Wadhwa R (2002) Mortalin: present and prospective. Exp Gerontol 37:1157–1164
Kaul SC, Yaguchi T, Taira K, Reddel RR, Wadhwa R (2003) Overexpressed mortalin mot-2/mthsp70/GRP75 and hTERT cooperate to extend the in vitro lifespan of human fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 286:96–101
Kaul SC, Aida S, Yaguchi T, Kaur K, Wadhwa R (2005) Activation of wild type p53 function by its mortalin-binding, cytoplasmically localizing carboxyl terminus peptides. J Biol Chem 280:39373–39379
Khodagholi F, Yazdanparast R (2005) Artificial chaperone-assisted refolding of GuHCl-denatured alpha-amylase at low temperature: refolding versus aggregation. Protein J 24:303–313
Kim BE, Smith K, Meagher CK, Petris MJ (2002) A conditional mutation affecting localization of the Menkes disease copper ATPase. Suppression by copper supplementation. J Biol Chem 277:44079–44084
Kirita T, Ohnishi K, Ohnishi T (2001) A new strategy for cancer therapy based on a predictive indicator. Hum Cell 14:1–6
Kuckelkorn U, Knuehl C, Boes-Fabian B, Drung I, Kloetzel PM (2000) The effect of heat shock on 20S/26S proteasomes. Biol Chem 381:1017–1023
Lahiri DK, Chen DM, Lahiri P, Bondy S, Greig NH (2005) Amyloid, cholinesterase, melatonin, and metals and their roles in aging and neurodegenerative diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 1056:430–449
Levine AJ (1997) p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 88:323–331
Li D, Sun F, Wang K (2004) Protein profile of aging and its retardation by caloric restriction in neural retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:253–258
Lissin NM (1995) In vitro dissociation of self-assembly of three chaperonin 60s: the role of ATP. FEBS Lett 361:55–60
Liu M, Wang X, Yin C, Zhang Z, Lin Q, Zhen Y, Huang H (2006) One-step on-column purification and refolding of a single-chain variable fragment scFv antibody against tumour necrosis factor alpha. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 43:137–145
Masoro EJ (2005) Overview of caloric restriction and ageing. Mech Ageing Dev 126:913–922
Mendrysa SM, Perry ME (2006) Tumor suppression by p53 without accelerated aging: just enough of a good thing? Cell Cycle 5:714–717
Meng F, Park Y, Zhou H (2001) Role of proline, glycerol, and heparin as protein folding aids during refolding of rabbit muscle creatine kinase. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:701–709
Meriin AB, Sherman MY (2005) Role of molecular chaperones in neurodegenerative disorders. Int J Hyperthermia 21:403–419
Morello JP, Petaja-Repo UE, Bichet DG, Bouvier M (2000) Pharmacological chaperones: a new twist on receptor folding. Trends Pharmacol Sci 21:466–469
Nagao Y, Ishiguro H, Nukina N (2000) DMSO and glycerol reduce bacterial death induced by expression of truncated N-terminal huntingtin with expanded polyglutamine tracts. Biochim Biophys Acta 1502:247–256
Nath D, Rao M (2001) Artificial chaperone mediated refolding of xylanase from an alkalophilic thermophilic Bacillus sp. Implications for in vitro protein renaturation via a folding intermediate. Eur J Biochem 268:5471–5478
Nollen EA, Salomons FA, Brunsting JF, Want JJ, Sibon OC, Kampinga HH (2001) Dynamic changes in the localization of thermally unfolded nuclear proteins associated with chaperone-dependent protection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:12038–12043
Ohnishi K, Ohnishi T (2001) Heat-induced p53-dependent signal transduction and its role in hyperthermic cancer therapy. Int J Hyperthermia 17:415–427
Ohnishi T, Matsumoto H, Wang X, Takahashi A, Tamamoto T, Ohnishi K (1999) Restoration by glycerol of p53-dependent apoptosis in cells bearing the mutant p53 gene. Int J Radiat Biol 75:1095–1098
Ohnishi K, Ota I, Takahashi A, Ohnishi T (2000) Glycerol restores p53-dependent radiosensitivity of human head and neck cancer cells bearing mutant p53. Br J Cancer 83:1735–1739
Ohnishi K, Ota I, Yane K, Takahashi A, Yuki K, Emoto M, Hosoi H, Ohnishi T (2002a) Glycerol as a chemical chaperone enhances radiation-induced apoptosis in anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer 1:4
Ohnishi T, Ohnishi K, Takahashi A (2002b) Glycerol restores heat-induced p53-dependent apoptosis of human glioblastoma cells bearing mutant p53. BMC Biotechnol 2:6
Olson RD, Mushlin PS (1990) Doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: analysis of prevailing hypotheses. FASEB J 4:3076–3086
Park YD, Wu BN, Tian WX, Zhou HM (2002) Effects of osmolytes on unfolding of chicken liver fatty acid synthase. Biochem Mosc 67:914–917
Rattan SI, Clark BF (2005) Understanding and modulating ageing. IUBMB Life 57:297–304
Russell RJ, Ferguson JM, Hough DW, Danson MJ, Taylor GL (1997) The crystal structure of citrate synthase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus at 1.9 A resolution. Biochemistry 36:9983–9994
Sakamaki M, Igarashi H, Nishiyama Y, Hagiwara H, Ando J, Chishiki T, Curran BC, Katayama Y (2003) Effect of glycerol on ischemic cerebral edema assessed by magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurol Sci 209:69–74
Scheper W, Hol EM (2005) Protein quality control in Alzheimer’s disease: a fatal saviour. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 4:283–292
Shingarpure R, Davies KJ (2002) Protein turnover by the proteasome in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 32:1084–1089
Sivakama Sundari C, Raman B, Balasubramanian D (1999) Artificial chaperoning of insulin, human carbonic anhydrase and hen egg lysozyme using linear dextrin chains–a sweet route to the native state of globular proteins. FEBS Lett 443:215–219
Soti C, Csermely P (2002) Chaperones come of age. Cell Stress Chaperones 7:186–190
Soti C, Csermely P (2003) Aging and molecular chaperones. Exp Gerontol 38:1037–1040
Tamarappoo BK, Yang B, Verkman AS (1999) Misfolding of mutant aquaporin-2 water channels in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. J Biol Chem 274:34825–34831
Tanaka M, Machida Y, Niu S, Ikeda T, Jana NR, Doi H, Kurosawa M, Nekooki M, Nukina N (2004) Trehalose alleviates polyglutamine-mediated pathology in a mouse model of Huntington disease. Nat Med 10:148–154
Thomas AR, Oosthuizen V, Naude RJ (2005) Differential effects of detergents, fatty acids, cations and heating on ostrich skeletal muscle 20S proteasome. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 140:343–348
Tyner SD, Venkatachalam S, Choi J, Jones S, Ghebranious N, Igelmann H, Lu X, Soron G, Cooper B, Brayton C et al (2002) p53 mutant mice that display early ageing-associated phenotypes. Nature 415:45–53
Voziyan PA, Jadhav L, Fisher MT (2000) Refolding a glutamine synthetase truncation mutant in vitro: identifying superior conditions using a combination of chaperonins and osmolytes. J Pharm Sci 89:1036–1045
Wadhwa R, Takano S, Robert M, Yoshida A, Nomura H, Reddel RR, Mitsui Y, Kaul SC (1998) Inactivation of tumor suppressor p53 by mot-2, a hsp70 family member. J Biol Chem 273:29586–29591
Wagner BJ, Margolis JW (1993) Thermal stability and activation of bovine lens multicatalytic proteinase complex proteasome. Arch Biochem Biophys 307:146–152
Wang K, Spector A (2000) Alpha-crystallin prevents irreversible protein denaturation and acts cooperatively with other heat-shock proteins to renature the stabilized partially denatured protein in an ATP-dependent manner. Eur J Biochem 267:4705–4712
Xie Q, Matsunaga S, Shi X, Ogawa S, Niimi S, Wen Z, Tokuyasu K, Machida S (2003) Refolding and characterization of the functional ligand-binding domain of human lectin-like oxidized LDL receptor. Protein Expr Purif 32:68–74
Yazdanparast R, Khodagholi F, Khodagholi R (2005) Artificial chaperone-assisted refolding of chemically denatured alpha-amylase. Int J Biol Macromol 35:257–263
Yoshimoto N, Hashimoto T, Felix MM, Umakoshi H, Kuboi R (2003) Artificial chaperone-assisted refolding of bovine carbonic anhydrase using molecular assemblies of stimuli-responsive polymers. Biomacromol 4:1530–1538
Yu YL, Kumana CR, Lauder IJ, Cheung YK, Chan FL, Kou M, Fong KY, Cheung RT, Chang CM (1993) Treatment of acute cortical infarct with intravenous glycerol. A double-blind, placebo-controlled randomized trial. Stroke 24:1119–1124
Zhao Q, Wang J, Levichkin IV, Stasinopoulos S, Ryan MT, Hoogenraad NJ (2002) A mitochondrial specific stress response in mammalian cells. EMBO J 21:4411–4419
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Custer C. Deocaris and Syuichi Takano contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deocaris, C.C., Takano, S., Priyandoko, D. et al. Glycerol stimulates innate chaperoning, proteasomal and stress-resistance functions: implications for geronto-manipulation. Biogerontology 9, 269–282 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9136-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-008-9136-8