Abstract
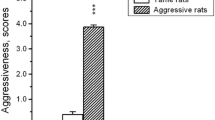
A comparative analysis of intermale aggression in the resident–intruder test was conducted with gray rats from a wild unselected population bred at the laboratory for three generations and gray rats selected for elimination (tame) and enhancement (aggressive) of aggressiveness towards human for 71–72 generations. Males from the laboratory line Wistar were used as neutral opponents. Rats from the tame line were characterized by reduced aggression manifest as longer attack latency, decreased number of attacks, upright postures, chases, kicks, and shorter total time of aggressive behavior compared to unselected males. There was no significant difference in the attack latency and the total time of aggression between rats of the aggressive line and unselected rats. A trend to decrease in the number of attacks, chases and upright postures and to increase in contribution of lateral threat postures to the total time of aggression was observed for males of the aggressive line. Plasma corticosterone in unselected males not presented with intruders and after their presentation was higher than in males of both selected lines. Comparative behavioral analysis of agonistic behaviors in rats from the aggressive and tame lines to opponents of different lines (Wistar, tame, aggressive) showed that the presence of an intruder from the aggressive line can enhance aggressive responses in residents from the tame line. Thus, selection for domestication of gray rats caused a significant attenuation of aggressive behavior without affecting the basic agonistic repertoire.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert FW, Shchepina O, Winter C, Rompler H, Teupser D, Palme R, Ceglarek U, Kratzsch J, Sohr R, Trut LN, Thiery J, Morgenstern R, Plyusnina IZ, Schoneberg T, Paabo S (2008) Phenotypic differences in rats selected for tameness and aggression are associated with differences in stress response. Horm Behav 53:413–421
Belyaev DK, Borodin PM (1982) The influence of stress on variation and its role in evolution. Biol Zent 100:705–714
Blanchard RJ, Blanchard DC (1977) Aggressive behavior in the rat. Behav Biol 21:197–224
Blanchard RJ, Fukunaga K, Blanchard DC, Kelley MJ (1975) Conspecific aggression in the laboratory rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89:1204–1209
Blanchard RJ, Wall PM, Blanchard DC (2003) Problems in the study of rodent aggression. Horm Behav 44:161–170
Boice R (1973) Some behavioral tests of domestication in Norway rats. Behaviour 3(4):198–231
Boice R (1999) Domestication. Psychol Bull 80(3):215–230
De Boer SF, Lesourd M, Mocaer E, Koolhaas JM (1999) Selective antiaggressive effects of alnespirone in resident–intruder test are mediated via 5-hydroxytryptamine 1A receptors: a comparative pharmacological study with 8-hydroxy-2-dipropylaminotetralin, ipsapirone, buspirone, eltoprazine, and WAY-100635. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288(3):1125–1133
De Boer SF, Van der Vegt BJ, Koolhaas JM (2003) Individual variation in aggression of feral rodent strains: a standard for the genetics of aggression and violence? Behav Genet 33(5):485–501
Guillot PV, Chapouthier G (1996) Intermale aggression and dark/light preference in ten inbred mouse strains. Behav Brain Res 77:211–213
Hale EB (1969) Domestication and the evolution of behavior. In: Hafez ESE (ed) The behavior of domestic animals. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 22–45
Haller J, Albert I, Macara GB (1997) Acute behavioral effects of corticosterone rhythm and the propensity to behave aggressively in male rats. J Neuroendocrinol 12:937–941
King HD (1939) Life processes in gray Norway rats during fourteen years in captivity. Am Anat Mem No 17. Cited from Robinson R (1965) Genetics of the Norway rat. Pergamon Press Ltd, Oxford, pp 1–804
Koolhaas JM, Schurman T, Wiepkema PR (1980) The organization of intraspecific agonistic behaviour in the rat. Prog Neurobiol 15(3):247–268
Koolhaas JM, de Boer SF, Coppens CM, Buwalda W (2010) Neuroendocrinology of coping styles: towards understanding the biology of individual variation. Front Neuroendocrinol 31(3):307–321
Kruk MR, Halasz J, Meelis W, Haller J (2004) Fast positice feedback between the adrenal stress response and a brain mechanism in aggressive behavior. Behav Neurosci 118:1062–1070
Lucion AB, de Almeida RMM (1991) Role of the intruder in the aggressive behaviour of colonies of wild rats (Rattus norvegicus). In: Animal models in psychopharmacology, advances in pharmacological sciences. Birkhauser Verlag, Basel, pp 347–356
Miczek KA, de Almeida RMM, Kravitz EA, Rissman EF, de Boer SF, Raine A (2007) Neurobiology of escalated aggression and violence. J Neurosci 27(44):11803–11806
Mikics E, Kruk MR, Haller J (2004) Genomic and non-genomic effects of glucocorticoids on aggressive behavior in male rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29(5):618–635
Moyer KE (1968) Kinds of aggression and their physiological basis. Commun Behav Biol 2:65–87
Murphy BE (1967) Some studies of the protein binding of steroids and their application to the routine micro and ultramicro measurements of various steroids in body fluids by competitive protein-binding radioassay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 27:973–990
Naumenko EV, Popova NK, Nikulina EM, Dygalo NN, Shishkina GT, Borodin PM, Markel AL (1989) Behavior, adrenocortical activity, and brain monoamines in Norway rats selected for reduced aggressiveness towards man. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 33:85–91
Neumann ID, Veenema AH, Beiderbeck DI (2010) Aggression and anxiety: social context and neurobiological links. Behav Neurosci 4(12):1–16
Oskina IN, Plyusnina IZ (2000) The hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal system during selection of animals for tame behavior. In: Shumnii VK, Markel AL (eds) Modern concepts of evolutionary genetics, vol 22–45. IC & G, Novosibirsk, pp 327–333 (Russian)
Oskina IN, Plyusnina IZ, Sysoletina AIu (2000) Effect of selection for behavior on the hypophyseal-adrenal function in the gray rats Rattus norvegicus during postnatal ontogenesis. Zh Evol Biokhim Fiziol 36:120–126 (Russian)
Oskina IN, Herbeck YuE, Shikhevich SG, Plyusnina IZ, Gulevich RG (2008) Alterations in the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal and immune systems during selection of animals for tame behavior. The Herald Vavilov Soc Genet Breed Sci 12:39–49
Parmigiani S, Palanza P, Rodgers J, Ferrari PF (1999) Selection, evolution of behavior and animal models in behavioral neuroscience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:957–970
Plyusnina IZ (2004) Locomotor activity–exploration or “panic”? Rossisky Fiziologichesky Zhurnal 90:84 (Russian)
Plyusnina IZ (2007) The behavior of wild grey rats at the modern step of domestication. Abstract 4 Russian conference on animal behaviour, Moscow, pp 596–597 (Russian)
Plyusnina IZ, Oskina IN (1997) Behavioral and adrenocortical responses to open-field test in rats selected for reduced aggressiveness toward humans. Physiol Behav 61(3):381–385
Plyusnina IZ, Solov’eva MYu (2010) Intraspecific intermale aggression in tame and aggressive grey rats. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlov 60(2):175–183 (Russian)
Plyusnina IZ, Trut LN, Karpushkeeva NI, Alekhina TA, Oskina IN (2003) Some behavioral and physiological characteristics of nonagouti mutation in gray rats during breeding for aggressiveness. Zh Vyssh Nerv Deiat Im I P Pavlov 53(5):613–621 (Russian)
Plyusnina IZ, Oskina IN, Tibeikina MA, Popova NK (2009) Cross-fostering effects on weight, exploratory activity, acoustic startle reflex and corticosterone stress response in Norway gray rats selected for elimination and for enhancement of aggressiveness towards human. Behav Genet 39:202–212
Popova NK, Kulikov AV, Nikulina EM, Kozlachkova EY, Maslova GB (1991) Serotonin metabolism and 5-HT receptors in Norway rats selected for low aggressiveness to man. Aggress Behav 17:207–213
Popova NK, Naumenko VS, Plyusnina IZ, Kulikov AV (2005) Reduction in 5-HT1A receptor density, 5-HT1A mRNA expression, and functional correlates for 5-HT1A receptors in genetically defined aggressive rats. J Neurosci Res 80(2):286–292
Poshivalov VP (1978) Ethological atlas for pharmacological study on rodents (mice, rats). VINITI, Moscow, pp 1–43
Price EO (1978) Genotype versus experience effects on aggression in wild and domestic Norway rats. Behaviour 64:340–353
Price EO (1984) Behavioral aspects of animal domestication. Q Rev Biol 59(1):1–32
Robertoux PL, Mortaud S, Perez-Diaz F, Tordjman S (1999) Measuring aggression in the mouse. In: Crusio WE, Gerlai RT (eds) Handbook of molecular-genetic techniques for brain and behavior research. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 696–709
Robinson R (1965) Genetics of the Norway rat. Pergamon Press Ltd, Oxford
Sgoifo A, De Boer SF, Haller J, Koolhaas JM (1996) Individual differences in plasma catecholamine and corticosterone stress responses of wild-type rats: relationship with aggression. Physiol Behav 60(6):1403–1407
Skutella T, Montkowski A, Stohr T, Probst JC, Landgraf R, Holsboer F, Jirikowski GF (1994) Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) antisense oligodeoxynucleotide treatment attenuates social defeat-induced anxiety in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 14(5):579–588
Takahashi LK, Blanchard RJ (1982) Attack and defense in laboratory and wild Norway and Black rats. Behav Process 7:49–62
Tinnikov AA, Bazhan NM (1984) Estimation of glucocorticoids in plasma and incubation medium by competitive binding of hormones by proteins without preliminary extraction. Lab Delo 12:709–713 Russian
Veenema AH, Neumann ID (2007) Neurobiological mechanisms of aggression and stress coping: a comparative study in mouse and rat selection lines. Brain Behav Evol 70:274–285
Veenema AH, Bredewold R, Neumann ID (2007) Opposite effects of maternal separation on intermale and maternal aggression in C57BL/6 mice: link to hypothalamic vasopressin and oxytocin immunoreactivity. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32:437–450
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to A. Fadeeva for help during preparation of the manuscript. We also thank R. Kozhemyakina for her assistance with experimental procedure. This study was supported by grant 08-04-01412 from the Russian Fund of Basic Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Stephen Maxson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plyusnina, I.Z., Solov’eva, M.Y. & Oskina, I.N. Effect of Domestication on Aggression in Gray Norway Rats. Behav Genet 41, 583–592 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9429-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9429-y