Abstract
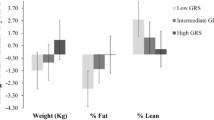
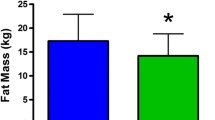
Genetic variations in the adrenergic receptor (ADR) have been associated with body composition in cross-sectional studies. Recent findings suggest that ADR variants may also modify body composition response to lifestyle. We assessed the role of ADR variants in body composition response to 12 months of resistance training versus control in previously sedentary postmenopausal women. Randomized trial completers were genotyped for A2B Glu9/12 by fragment length analysis, and B2 Gln27Glu and B3 Trp64Arg by TaqMan (n = 148, 54% hormone therapy users). Associations between genotypes and body composition, by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry, were analyzed using univariate models. There was no main effect of individual genes on change in body composition, however, gene × exercise interactions were observed for A2B Glu9/12 and B2 Gln27Glu on change in lean soft tissue (LST, p = 0.02); exercisers on the A2B Glu9− background gained LST compared to a loss among controls over 12 months (p < 0.05), with no significant intervention effect on the A2B Glu9+ background. Similarly, there was a significant LST gain with exercise on the B2 Glu27+ background compared to loss among controls and no intervention effect on the B2 Glu27− background. A non-significant association between total body fat (TBF) and B3 Trp64Arg persisted among sedentary controls only when intervention groups were separated (%TBF gain with B3 Arg64+ carriage, p = 0.03); exercisers lost TBF regardless of genotype. In summary, effect modification by lifestyle was demonstrated on ADRA2B, B2, and B3 genetic backgrounds. Individuals with certain ADR genotypes may be more vulnerable to adverse changes in body composition with sedentary behavior, thus these candidate genes warrant further study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison DB, Heo M, Faith MS, Pietrobelli A (1998) Meta-analysis of the association of the Trp64Arg polymorphism in the beta3 adrenergic receptor with body mass index. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 22(6):559–566
Arner P (1995) The beta 3-adrenergic receptor—a cause and cure of obesity? N Engl J Med 333(6):382–383
Arner P, Hoffstedt J (1999) Adrenoceptor genes in human obesity. J Intern Med 245(6):667–672
Booth FW, Chakravarthy MV, Spangenburg EE (2002) Exercise and gene expression: physiological regulation of the human genome through physical activity. J Physiol 543(Pt 2):399–411
Bouchard C (2008) Gene–environment interactions in the etiology of obesity: defining the fundamentals. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16(Suppl 3):S5–S10
Bouchard C, Agurs-Collins T (2008) Studying gene–behavior interactions: summary of recommendations. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16(Suppl 3):S95–S96
Bouchard C, Despres JP, Mauriege P (1993) Genetic and nongenetic determinants of regional fat distribution. Endocr Rev 14(1):72–93
Brodde OE (2008) Beta-1 and beta-2 adrenoceptor polymorphisms: functional importance, impact on cardiovascular diseases and drug responses. Pharmacol Ther 117(1):1–29
Collins S, Cao W, Robidoux J (2004) Learning new tricks from old dogs: beta-adrenergic receptors teach new lessons on firing up adipose tissue metabolism. Mol Endocrinol 18(9):2123–2131
Cussler EC, Going SB, Houtkooper LB, Stanford VA, Blew RM, Flint-Wagner HG, Metcalfe LL, Choi JE, Lohman TG (2005) Exercise frequency and calcium intake predict 4-year bone changes in postmenopausal women. Osteoporos Int 16(12):2129–2141
Dionne IJ, Turner AN, Tchernof A, Pollin TI, Avrithi D, Gray D, Shuldiner AR, Poehlman ET (2001) Identification of an interactive effect of beta3- and alpha2b-adrenoceptor gene polymorphisms on fat mass in Caucasian women. Diabetes 50(1):91–95
Frazer KA, Murray SS, Schork NJ, Topol EJ (2009) Human genetic variation and its contribution to complex traits. Nat Rev Genet 10(4):241–251
Garcia-Closas M, Egan KM, Abruzzo J, Newcomb PA, Titus-Ernstoff L, Franklin T, Bender PK, Beck JC, Le Marchand L, Lum A, Alavanja M, Hayes RB, Rutter J, Buetow K, Brinton LA, Rothman N (2001) Collection of genomic DNA from adults in epidemiological studies by buccal cytobrush and mouthwash. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 10(6):687–696
Garenc C, Perusse L, Rankinen T, Gagnon J, Leon AS, Skinner JS, Wilmore JH, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2001) The Trp64Arg polymorphism of the beta3-adrenergic receptor gene is not associated with training-induced changes in body composition: the HERITAGE Family Study. Obes Res 9(6):337–341
Garenc C, Perusse L, Chagnon YC, Rankinen T, Gagnon J, Borecki IB, Leon AS, Skinner JS, Wilmore JH, Rao DC, Bouchard C (2003) Effects of beta2-adrenergic receptor gene variants on adiposity: the HERITAGE Family Study. Obes Res 11(5):612–618
Going S, Lohman T, Houtkooper L, Metcalfe L, Flint-Wagner H, Blew R, Stanford V, Cussler E, Martin J, Teixeira P, Harris M, Milliken L, Figueroa-Galvez A, Weber J (2003) Effects of exercise on bone mineral density in calcium-replete postmenopausal women with and without hormone replacement therapy. Osteoporos Int 14(8):637–643
Hagstrom-Toft E, Enoksson S, Moberg E, Bolinder J, Arner P (1998) Beta-adrenergic regulation of lipolysis and blood flow in human skeletal muscle in vivo. Am J Physiol 275(6 Pt 1):E909–E916
Heinonen P, Koulu M, Pesonen U, Karvonen MK, Rissanen A, Laakso M, Valve R, Uusitupa M, Scheinin M (1999) Identification of a three-amino acid deletion in the alpha2B-adrenergic receptor that is associated with reduced basal metabolic rate in obese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(7):2429–2433
Hoffstedt J, Poirier O, Thorne A, Lonnqvist F, Herrmann SM, Cambien F, Arner P (1999) Polymorphism of the human beta3-adrenoceptor gene forms a well-conserved haplotype that is associated with moderate obesity and altered receptor function. Diabetes 48(1):203–205
Huttunen PM, Kortelainen L (1990) Long-term alcohol consumption and brown adipose tissue in man. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 60(6):418–424
Huttunen P, Hirvonen J, Kinnula V (1981) The occurrence of brown adipose tissue in outdoor workers. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 46(4):339–345
Jensen MD, Kanaley JA, Reed JE, Sheedy PF (1995) Measurement of abdominal and visceral fat with computed tomography and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. Am J Clin Nutr 61(2):274–278
Kirstein SL, Insel PA (2004) Autonomic nervous system pharmacogenomics: a progress report. Pharmacol Rev 56(1):31–52
Krief S, Lonnqvist F, Raimbault S, Baude B, Van Spronsen A, Arner P, Strosberg AD, Ricquier D, Emorine LJ (1993) Tissue distribution of beta 3-adrenergic receptor mRNA in man. J Clin Invest 91(1):344–349
Lenard NR, Berthoud HR (2008) Central and peripheral regulation of food intake and physical activity: pathways and genes. Obesity (Silver Spring) 16(Suppl 3):S11–S22
Macho-Azcarate T, Marti A, Gonzalez A, Martinez JA, Ibanez J (2002) Gln27Glu polymorphism in the beta2 adrenergic receptor gene and lipid metabolism during exercise in obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 26(11):1434–1441
Macho-Azcarate T, Marti A, Calabuig J, Martinez JA (2003) Basal fat oxidation and after a peak oxygen consumption test in obese women with a beta2 adrenoceptor gene polymorphism. J Nutr Biochem 14(5):275–279
Marti A, Corbalan MS, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Martinez JA (2002) TRP64ARG polymorphism of the beta 3-adrenergic receptor gene and obesity risk: effect modification by a sedentary lifestyle. Diabetes Obes Metab 4(6):428–430
McArdle WD, Katch FI, Katch VL (2007) Human energy expenditure during rest and physical activity. In: Keifer R, Kerrins R (eds) Exercise physiology: energy, nutrition, and human performance. Lippincott, Williams, and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 195–208
McCaffery JM, Papandonatos GD, Bond DS, Lyons MJ, Wing RR (2009) Gene × environment interaction of vigorous exercise and body mass index among male Vietnam-era twins. Am J Clin Nutr 89(4):1011–1018
McCole SD, Shuldiner AR, Brown MD, Moore GE, Ferrell RE, Wilund KR, Huberty A, Douglass LW, Hagberg JM (2004) Beta2- and beta3-adrenergic receptor polymorphisms and exercise hemodynamics in postmenopausal women. J Appl Physiol 96(2):526–530
Meirhaeghe A, Helbecque N, Cottel D, Amouyel P (1999) Beta2-adrenoceptor gene polymorphism, body weight, and physical activity. Lancet 353(9156):896
Metcalfe L, Lohman T, Going S, Houtkooper L, Ferreira D, Flint-Wagner H, Guido T, Martin J, Wright J, Cussler E (2001) Postmenopausal women and exercise for the prevention of osteoporosis: the Bone, Estrogen, and Strength Training (BEST) study. ACSM’s Health Fit J 5(3):6–14
Mustelin L, Silventoinen K, Pietilainen K, Rissanen A, Kaprio J (2009) Physical activity reduces the influence of genetic effects on BMI and waist circumference: a study in young adult twins. Int J Obes (Lond) 33(1):29–36
Phares DA, Halverstadt AA, Shuldiner AR, Ferrell RE, Douglass LW, Ryan AS, Goldberg AP, Hagberg JM (2004) Association between body fat response to exercise training and multilocus ADR genotypes. Obes Res 12(5):807–815
Pietri-Rouxel F, St John Manning B, Gros J, Strosberg AD (1997) The biochemical effect of the naturally occurring Trp64-->Arg mutation on human beta3-adrenoceptor activity. Eur J Biochem 247(3):1174–1179
Rankinen T, Perusse L, Rauramaa R, Rivera MA, Wolfarth B, Bouchard C (2004) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2003 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(9):1451–1469
Rankinen T, Zuberi A, Chagnon YC, Weisnagel SJ, Argyropoulos G, Walts B, Perusse L, Bouchard C (2006) The human obesity gene map: the 2005 update. Obesity (Silver Spring) 14(4):529–644
Sivenius K, Lindi V, Niskanen L, Laakso M, Uusitupa M (2001) Effect of a three-amino acid deletion in the alpha2B-adrenergic receptor gene on long-term body weight change in Finnish non-diabetic and type 2 diabetic subjects. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25(11):1609–1614
Small KM, Liggett SB (2001) Identification and functional characterization of alpha(2)-adrenoceptor polymorphisms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22(9):471–477
Small KM, Brown KM, Forbes SL, Liggett SB (2001) Polymorphic deletion of three intracellular acidic residues of the alpha 2B-adrenergic receptor decreases G protein-coupled receptor kinase-mediated phosphorylation and desensitization. J Biol Chem 276(7):4917–4922
Small KM, McGraw DW, Liggett SB (2003) Pharmacology and physiology of human adrenergic receptor polymorphisms. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:381–411
Tarkovacs G, Blandizzi C, Vizi ES (1994) Functional evidence that alpha 2A-adrenoceptors are responsible for antilipolysis in human abdominal fat cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 349(1):34–41
Teixeira PJ, Going SB, Houtkooper LB, Metcalfe LL, Blew RM, Flint-Wagner HG, Cussler EC, Sardinha LB, Lohman TG (2003) Resistance training in postmenopausal women with and without hormone therapy. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(4):555–562
Umekawa T, Yoshida T, Sakane N, Kogure A, Kondo M, Honjyo H (1999) Trp64Arg mutation of beta3-adrenoceptor gene deteriorates lipolysis induced by beta3-adrenoceptor agonist in human omental adipocytes. Diabetes 48(1):117–120
Wagoner LE, Craft LL, Singh B, Suresh DP, Zengel PW, McGuire N, Abraham WT, Chenier TC, Dorn GW, Liggett S B II (2000) Polymorphisms of the beta(2)-adrenergic receptor determine exercise capacity in patients with heart failure. Circ Res 86(8):834–840
Wolfarth B, Bray MS, Hagberg JM, Perusse L, Rauramaa R, Rivera MA, Roth SM, Rankinen T, Bouchard C (2005) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2004 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37(6):881–903
Yao L, Delmonico MJ, Roth SM, Hand BD, Johns J, Conway J, Douglass L, Hurley BF (2007) Adrenergic receptor genotype influence on midthigh intermuscular fat response to strength training in middle-aged and older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 62(6):658–663
Zhang H, Li X, Huang J, Li Y, Thijs L, Wang Z, Lu X, Cao K, Xie S, Staessen JA, Wang JG (2005a) Cardiovascular and metabolic phenotypes in relation to the ADRA2B insertion/deletion polymorphism in a Chinese population. J Hypertens 23(12):2201–2207
Zhang HF, Li XL, Xie SF, Zhu J, Wang ZZ, Liang LR, Cao KJ, De W, Yuan L, Huang J (2005b) ADRA2B gene insertion/deletion polymorphism and artery compliance. Chin Med J (Engl) 118(21):1797–1802
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health Grant AR39559 and the 2005 Gatorade Sports Science Institute Student Grant Award. Calcium supplements and Scope mouthwash were donated by Mission Pharmacal and Proctor and Gamble, respectively. We thank Betsy Wertheim and Elizabeth Jacobs for their critical review of the manuscript and participants and staff of the Bone Estrogen and Strength Training Study. We also thank Dr. Michael Hogan and staff for the use of their equipment and genotyping expertise. The supporters of this research will not benefit from the results of the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by David Allison.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bea, J.W., Lohman, T.G., Cussler, E.C. et al. Lifestyle Modifies the Relationship Between Body Composition and Adrenergic Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms, ADRB2, ADRB3 and ADRA2B: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Controlled Trial of Physical Activity Among Postmenopausal Women. Behav Genet 40, 649–659 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9361-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9361-1