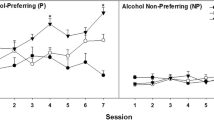
A genome scan of the F2 generation from an inbred alcohol-preferring (iP) and inbred alcohol-nonpreferring (iNP) rat cross identified a significant quantitative trait locus (QTL) on chromosome 4 with a lod score of 9.2. To confirm this QTL and to create animals for fine mapping of the QTL region, chromosome 4 reciprocal congenic strains were developed by transferring the chromosome 4 QTL interval into the respective iP or iNP backgrounds. The iP strain was crossed with the iNP strain to create iPiNP F1 animals, which were backcrossed to either iNP or iP animals to produce the N2 generation. Using marker-assisted selection, 10 generations of backcrossing were performed. The selection was followed by an intercross between the N10 animals to produce homozygous animals (N10F1), resulting in the finished congenic strains. Congenic strains in which the iP chromosome 4 QTL interval was transferred to the iNP (NP.P) and the iNP chromosome 4 QTL was transferred to the iP (P.NP) exhibited the expected effect on alcohol consumption of the donor strain. Development of these congenic strains further indicates that the chromosome 4 QTL region is, in part, responsible for the disparate alcohol consumption observed between the iP and iNP rats. These congenic animals will be an invaluable resource for fine mapping the QTL region and for the identification of the gene(s) that influences the drinking behavior of the iP and iNP rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beavis, W. D. (1994). The power and deceit of QTL experiments: lessons from comparative QTL studies. 49th Annual Corn & Sorghum Research Conference, Johnston, IA, pp. 250–266.
Bennett B., Beeson M., Gordon L., Carosone-Link P., Johnson T. E. (2002). Genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci specifying sedative/hypnotic sensitivity to ethanol: mapping with interval-specific congenic recombinant lines. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 26:1615–24
Bennett B., Johnson T. E. (1998). Development of congenics for hypnotic sensitivity to ethanol by QTL-marker-assisted counter selection. Mamm Genome. 9:969–974
Bice P., Foroud T., Bo R., Castelluccio P., Lumeng L., Li T. K., Carr L. G. (1998). Genomic screen for QTLs underlying alcohol consumption in the P and NP rat lines. Mamm. Genome 9:949–955
Carr L. G., Foroud T., Bice P., Gobbett T., Ivashina J., Edenberg H., Lumeng L., Li T. K. (1998). A quantitative trait locus for alcohol consumption in selectively bred rat lines. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 22:884–887
Cicero T. J. (1979). A critique of animal analogues of alcoholism. In: Majchrowicz E., Noble E. P. (eds), Biochemistry and Pharmacology of Ethanol Vol 2. Plenum Press, New York, pp 533–560
Crabbe J. C., Belknap J. K., Metten P., Grisel J. E., Buck K. J. (1998). Quantitative trait loci: mapping drug and alcohol-related genes. Adv. Pharmacol. 42:1033–7
Demarest K., Koyner J., McCaughran J. Jr, Hitzemann R. (2000). Mapping of a major QTL on mouse chromosome 2 for ethanol-induced locomotor activity in a heterogeneous stock population. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 24:96A
Fehr C., Shirley R. L., Belknap J. K., Crabbe J. C., Buck K. J. (2002) Congenic mapping of alcohol and pentobarbital withdrawal liability loci to a <1 centimorgan interval of murine chromosome 4: identification of Mpdz as a candidate gene. J. Neurosci. 22:3730–3738
Flaherty L. (1981). Congenic strains. In: Foster H. L., Small F. D., Fox F. G. (eds), The Mouse in Biomedical Research. Inc Academic Press, New York, pp 215–222
Flint J., Valdar W., Shifman S., Mott R. (2005). Strategies for mapping and cloning quantitative trait genes in rodents. Nat. Rev. Genet. 6:271–286
Garrett M. R., Rapp J. P. (2002a). Two closely linked interactive blood pressure QTL on rat chromosome 5 defined using congenic Dahl rats. Physiol. Genomics 8:81–86
Garrett M. R., Rapp J. P. (2002b) Multiple blood pressure QTL on rat Chromosome 2 defined by congenic Dahl rats. Mamm. Genome 13:41–44
Lander E. S., Schork N. J. (1994) Genetic dissection of complex traits. Science 265:2037–2048
Legare M. E., Frankel W. N. (2000) Multiple seizure susceptibility genes on chromosome 7 in SWXL-4 congenic mouse strains. Genomics 70:62–65
Legare M. E., Bartlett F. S. II, Frankel W. N. (2000) A major effect QTL determined by multiple genes in epileptic EL mice. Genome Res. 10:42–48
Li T.-K., Lumeng L., Doolittle D. P., Carr L. G. (1991). Molecular associations of alcohol seeking behavior in rat lines selectively bred for high and low voluntary ethanol drinking. Alcohol Alcohol Suppl. 1: 121–124
Lumeng L., Hawkins D. T., Li T.-K. (1997). New strains of rats with alcohol consumption and nonconsumption. In: Thurman R.G., Williamson J. R., Drott H., Chance B. (eds), Alcohol and Aldehyde Metabolizing Systems Vol 3. Academic Press, New York, pp. 537–44
Morel L., Blenman K. R., Croker B. P., Wakeland E. K. (2001). The major murine systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility locus, Sle1, is a cluster of functionally related genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:1787–1792
Shirley R. L., Walter N. A., Reilly M. T., Fehr C., Buck K. J. (2004). Mpdz is a quantitative trait gene for drug withdrawal seizures. Nat. Neurosci. 7:699–700
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carr, L.G., Habegger, K., Spence, J.P. et al. Development of Congenic Rat Strains for Alcohol Consumption Derived from the Alcohol-Preferring and Nonpreferring Rats. Behav Genet 36, 285–290 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9021-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9021-z