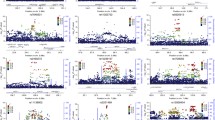
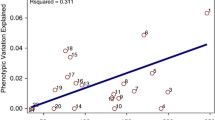
Intelligence, as measured by standardized psychological tests, has been shown to be highly heritable, though identifying specific genes influencing general intelligence has proven difficult. We conducted genome-wide linkage analyses to identify chromosomal regions containing genes influencing intelligence, as measured by WAIS full-scale IQ (FSIQ), performance IQ (PIQ) and verbal IQ (VIQ). Non-parametric multipoint linkage analyses were conducted with Merlin-regress software, using a sample of 1111 genotyped and phenotyped individuals from 201 families, ascertained as part of the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). The strongest evidence of linkage was obtained for FSIQ on chromosome 6 (LOD=3.28, 12 cM) near the marker D6S1006. This region was also implicated with suggestive linkage in a recently published genome screen of IQ in Australian and Dutch twin pairs, and it has been implicated in linkage studies of developmental dyslexia. Our findings provide further support that chromosome 6p contains gene(s) affecting intelligence.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis G. R., Cherny S. S., Cookson W. O. C., and Cardon L. R. (2000). Multipoint engine for rapid likelihood inference. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67 (Suppl): 1816
Antonarakis S. E., Blouin J. L., Pulver A. E., Wolyniec P., Lasseter V. K., Nestadt G., Kasch L., Babb R., Kazazian H. H., Dombroski B., Kimberland M., Ott J., Housman D., Karayiorgou M., MacLean C. J. (1995). Schizophrenia susceptibility and chromosome 6p24-22. Nat. Genet. 11:235–236
Bailer U., Leisch F., Meszaros K., Lenzinger E., Willinger U., Strobl R., Gebhardt C., Gerhard E., Fuchs K., Sieghart W., Kasper S., Hornik K., Aschauer H. N. (2000). Genome scan for susceptibility loci for schizophrenia. Neuropsychobiology 42:175–182
Boehnke M. (1991). Allele frequency estimation from pedigree data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 48:22–25
Bouchard T. J., and McGue M. (1981). Familial studies of intelligence: a review. Science 212:1055–1059
Bucholz K. K., Cadoret R., Cloninger C. R., Dinwiddie S. H., Hesselbrock V. M., Nurnberger J. J. I., Reich T., Schmidt I., Schuckit M. A. (1994). A new, semi-structured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: a report on the reliability of the SSAGA. J. Stud. Alcohol 55:149–158
Buyske, S., Bates, M. E., Gharani, N., Matise, T. C., Tischfield, J. A., and Manowitz P. (in press). Cognitive traits link to human chromosomal regions. Behav. Genet.
Cardon L. R., Smith S. D., Fulker D. W., Kimberling W. J., Pennington B. F., and DeFries J. S. (1994). Quantitative trait locus for reading disability on chromosome 6. Science 266:276–279
Cardon L. R., Smith S. D., Fulker D. W., Kimberling W. J., Pennington B. F., and DeFries J. S. (1995). Quantitative trait locus for reading disability: correction. Science 268:1553
Chorney M. J., Chorney K., Seese N., Owen M. J., Daniels J., McGuffin P., Thompson L. A., Detterman D. K., Benbow C., Lubinski D., Eley T. and Plomin R. (1998). A quantitative trait locus associated with cognitive ability in children. Psychol. Sci. 9:159–166
Cope N., Harold D., Hill G., Moskvina V., Stevenson J., Holmans P., Owen M. J., O’Donovan M. C., and Williams J. (2005). Strong evidence that KIAA0319 on chromosome 6p is a susceptibility gene for developmental dyslexia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 76:581–591
Comings D.E., Wu S., Rostamkhani M., McGue M., Lacono W.G., Cheng L.S. and MacMurray J.P. (2003). Role of the cholinergic muscarinic 2 receptor (CHRM2) gene in cognition. Mol. Psychiatry 8:10–11
Devlin B., Daniels M., and Roeder K., (1997). The heritability of IQ. Nature 388:468–471
Egan M. F., Goldberg T. E., Kolachana B. S., Callicott J. H., Mazzanti C. M., Straub R. E., Goldman D., Weinberger D. R. (2001). Effect of COMT Val108/158 Met genotype on frontal lobe function and risk for schizophrenia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:6917–6922
Fisher S. E., Marlow A. J., Lamb J., Maestrini E., Williams D. F., Richardson A. J., Weeks D. E., Stein J. F., and Monaco A. P. (1999). A quantitative-trait locus on chromosome 6p influences different aspects of developmental dyslexia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:146–156
Flint J. (1999). The genetic basis of cognition. Brain 122:2015–2031
Gayan J., Smith S. D., Cherny S. S., Cardon L. R., Fulker D. W., Brower A. M., Olson R. K., Pennington B. F., and DeFries J. S. (1999). Quantitative trait locus for specific language and reading deficits on chromosome 6. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:157–164
Green, P.H. (1990). Documentation for CRIMAP, version 2.4
Grigorenko E. L., Wood F. B., Meyer M. S., Hart L. A., Speed W. C., Shuster A., and Pauls D. L. (1997). Susceptibility loci for distinct components of developmental dyslexia on chromosome 6p and 15. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 60:27–39
Grigorenko E. L., Wood F. B., Meyer M. S., Hart L. A. and Pauls D. L. (2000). Chromosome 6p influences on different dyslexia-related cognitive process: further confirmation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 66:715–723
Grigorenko E. L., Wood F. B., Golovyan L., Meyer M., Romano C., Hart L. A. And Pauls D. L. (2003). Continuing the search for dyslexia genes on 6p. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genet. 118 B:89–98
Hesselbrock M., Easton C., Bucholz K. K., Schuckit M., Hesselbrock V. (1999). A validity study of the SSAGA – A comparison with the SCAN. Addiction 94:1361-1370
Hill L., Chorney M. J., Lubinski D., Thompson L. A., and Plomin R. (2002) A quantitative trait locus not associated with cognitive ability in children: a failure to replicate. Psychol. Sci. 13:561
Hovatta I., Lichtermann D., Juvonen H., Suvisaari J., Terwilliger J. D., Arajarvi R., Kokko-Sahin M.-L., Ekelund J., Lonnqvist J., Peltonen L. (1998). Linkage analysis of putative schizophrenia gene candidate regions on chromosomes 3p, 5q, 6p, 8p, 20p, and 22q in a population-based sampled Finnish family set. Mol. Psychiatry 3:452–457
Lander E., Kruglyak L. (1995). Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat. Genet. 11:241–247
Lindholm E., Ekholm B., Balciuniene J., Johansson G., Castensson A., Koisti M., Nylander P. O., Pettersson U., Adolfsson R., Jazin E. (1999). Linkage analysis of a large Swedish kindred provides further support for a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia on chromosome 6p23. Am. J. Med. Genet. 88:369–377
Luciano, M., Wright, M. J., Duffy, D. L., Wainwright, M. A., Evans, D. M., Geffen, G. M., Montgomery, G. W., and Martin, N. G. (in press). Genome-wide scan of IQ finds significant linkage to a quantitative trait locus on 2q. Behav. Genet.
Malhotra A. K., Kestler L. J., Mazzanti C., Bates J. A., Goldberg T., and Goldman D. (2002) A functional polymorphism in the COMT gene and performance on a test of prefrontal cognition. Am. J. Psychiatry 159:652–654
Maziade M., Roy M. A., Rouillard E., Bissonnette L., Fournier J. P., Roy A., Garneau Y., Montgrain N., Potvin A., Cliché, D., Dion C., Wallot H., Fournier A., Nicole L., Lavallee J. C., Merette C. (2001). A search for specific and common susceptibility loci for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder: a linkage study in 13 target chromosomes. Mol. Psychiatry 6:684–693
McGue M., Bouchard Jr. T. J., Iacono W. G., Lykken D..T. (1993). Behavioral genetics of cognitive ability: a life-span perspective. In: Plomin R., McClearn G. E. (eds). Nature, Nurture, and Psychology. American Psychological Association, Washington DC, pp. 59–76
McIntosh A. M., Harrison L. K., Forrester K., Lawrie S. M. and Johnstone E. C. (2005). Neuropsychological impairments in people with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder and their unaffected relatives. Br. J. Psychiatry 186:378–85
Paunio T., Tuulio-Henriksson A., Hiekkalinna T., Perola M., Varilo T., Partonen T., Cannon T.D., Lonnqvist J. and Peltonen L. (2004). Search for cognitive trait components of schizophrenia reveals a locus for verbal learning and memory on 4q and for visual working memory on 2q. Human Mol. Genet. 15:1693–1702
Payton A., Holland F., Diggle P., Rabbitt P., Horan M., Davidson Y., Gibbons L., Worthington J., Ollier W. E. R., and Pendleton N. (2003) Cathepsin D exon 2 polymorphism associated with general intelligence in a healthy older population. Mol. Psychiatry 8: 14-18
Petrill S. A. (2002). The case for general intelligence: a behavioral genetic perspective. In: Sternberg R. J. and Grigorenko E. L. (eds). The General Factor of Intelligence: How General is it?. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Mahwah NJ, pp. 281–298
Plomin R., DeFries J. C., McClearn G. E. and McGuffin P. (2001a) Behavioral genetics. 4th edition. Worth, London
Plomin R., Hill L., Craig I. W., McGuffin P., Purcell Sh., Sham P., Lubinski D., Thompson L. A., Fisher P. J., Turic D., and Owen M. J. (2001b). A genome-wide scan of 1842 DNA markers for allelic associations with general cognitive ability: a five-stage design using DNA pooling and extreme selected groups. Behav. Genet. 31:497–509
Plomin R. (2003). Genetics, genes, genomics, and g. Mol. Psychiatry 8:1–5
Posthuma, D., Luciano, M., De Geus, E. J. C., Wright, M. J., Slagboom, P. E., Montgomery, G. W., Boomsma, D. I., and Martin, N. G. (2005). A genome wide scan for intelligence identifies quantitative trait loci on 2q and 6p. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 77:318–326
Reich T. (1996). A genomic survey of alcohol dependence and related phenotypes: results from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 20:133A–137A
Reich, T., Edenberg, H. J., Goate, A., Williams, J. T., Rice, J. P., Van Eerdewegh, P., Foroud, T., Hesselbrock, V., Schuckit, M. A., Bucholz, K., Porjesz, B., Li, T. K., Conneally, P. M., Nurnberger, J. I. Jr., Tischfield, J.A., Crowe, R. R., Cloninger, C. R., Wu, W., Shears, S., Carr, K., Crose, C., Willig, C., and Begleiter, H. (1998). Genome-wide search for genes affecting the risk for alcohol dependence. Am. J. Med. Genet. 81:207–215
Schwab S. G., Hallmayer J., Albus M., Lerer B., Eckstein G. N., Borrmann M., Segman R. H., Hanses C., Freymann J., Yakir A., Trixler M., Falkai P., Rietschel M., Maier W., Wildenauer D. B. (2000). A genome-wide autosomal screen for schizophrenia susceptibility loci in 71 families with affected siblings: support for loci on chromosome 10p and 6. Mol. Psychiatry 5(6):638–649
Sham P. C., Purcell S., Cherny S. S. and Abecasis G. R. (2002). Powerful regression-based quantitative-trait linkage analysis of general pedigrees. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:238–253
Straub R. E., Jiang Y., MacLean C. J., Ma Y., Webb B. T., Myakishev M. V., Harris-Kerr C., Wormley B., Sadek H., Kadambi B., Cesare A. J., Gibberman A., Wang X., O’Neill F. A., Walsh D., and Kendler K. S. (2002). Genetic variation in the 6p22.3 Gene DTNBP1, the human ortholog of the mouse dysbindin gene, is associated with schizophrenia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:337–348
Suarez B. K., Hampe C. L. and Van Eerdewegh P. (1994). Problems of replicating linkage claims in psychiatry. In: Gershon E. S. and Cloninger C. R. (eds). Genetic Approaches to Mental Disorders. American Psychiatric Press, Washington, DC
Wainwright, M. A., Wright, M. J., Luciano, M., Montgomery, G. W., Geffen, G. M., and Martin, N. G. (in press). A linkage study of academic skills defined by the Queensland Core Skills Test. Behav. Genet.
Wechsler D. (1981). Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale – Revised. The Psychological Corporation, New York
Wechsler D. (1997). WAIS-III Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wiltshire S., Cardon L. R. and McCarthy M. I. (2002). Evaluating the results of genomewide linkage scans of complex traits by locus counting. Am. J. Human Genet. 71:1175–1182
Acknowledgments
The Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) (Principal Investigator: H. Begleiter; Co-Principal Investigators: L. Bierut, H. Edenberg, V. Hesselbrock, B. Porjesz) includes nine different centers where data collection, analysis, and storage take place. The nine sites and Principal Investigators and Co-Investigators are: University of Connecticut (V. Hesselbrock); Indiana University (H. Edenberg, J. Nurnberger Jr., P.M. Conneally, T. Foroud); University of Iowa (S. Kuperman, R. Crowe); SUNY HSCB (B. Porjesz, H. Begleiter); Washington University in St. Louis (L. Bierut, A. Goate, J. Rice); University of California at San Diego (M. Schuckit); Howard University (R. Taylor); Rutgers University (J. Tischfield); Southwest Foundation (L. Almasy). Zhaoxia Ren serves as the NIAAA Staff Collaborator. This national collaborative study is supported by the NIH Grant U10AA08401 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA) and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA). Partial support was also provided by NCRR Grant M01-RR06192 to the University of Connecticut School of Medicine GCRC.
In memory of Theodore Reich, M.D., Co-Principal Investigator of COGA since its inception and one of the founders of modern psychiatric genetics, we acknowledge his immeasurable and fundamental scientific contributions to COGA and the field.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dick, D.M., Aliev, F., Bierut, L. et al. Linkage Analyses of IQ in the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) Sample. Behav Genet 36, 77–86 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9009-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9009-8