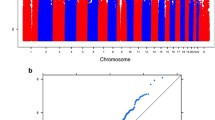
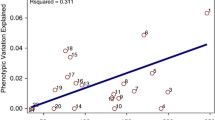
A genome-wide linkage scan of 795 microsatellite markers (761 autosomal, 34 X chromosome) was performed on Multidimensional Aptitude Battery subtests and verbal, performance and full scale scores, the WAIS-R Digit Symbol subtest, and two word-recognition tests (Schonell Graded Word Reading Test, Cambridge Contextual Reading Test) highly predictive of IQ. The sample included 361 families comprising 2–5 siblings who ranged in age from 15.7 to 22.2 years; genotype, but not phenotype, data were available for 81% of parents. A variance components analysis which controlled for age and sex effects showed significant linkage for the Cambridge reading test and performance IQ to the same region on chromosome 2, with respective LOD scores of 4.15 and 3.68. Suggestive linkage (LOD score>2.2) for various measures was further supported on chromosomes 6, 7, 11, 14, 21 and 22. Where location of linkage peaks converged for IQ subtests within the same scale, the overall scale score provided increased evidence for linkage to that region over any individual subtest. Association studies of candidate genes, particularly those involved in neural transmission and development, will be directed to genes located under the linkage peaks identified in this study.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abecasis, G. R. (2004). http://www.sph.umich.edu/csg/abecasis/Merlin/reference.html
Abecasis, G. R., Cherney, S. S., Cookson, W. O., and Cardon L. R. (2002). Merlin-rapid analysis of dense genetic maps using sparse gene flow trees. Nat. Genet. 30:97–101
Addington, A. M., Gornick, M., Duckworth, J., Sporn, A., Gogtay, N., Bobb, A., Greenstein, D., Lenane, M., Gochman, P., Baker, N., Balkissoon, R., Vakkalanka, R. K., Weinberger, D. R., Rapoport, J. L., and Straub, R. E. (2004). GAD1 (2q31.1), which encodes glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD(67)), is associated with childhood-onset schizophrenia and cortical gray matter volume loss. Mol. Psychiatry. Advance online publication 26 October
Bacchelli, E., Blasi, F., Biondolillo, M., Lamb, J. A., Bonora, E., Barnby, G., Parr, J., Beyer, K. S., Klauck, S. M., Poustka, A., Bailey, A. J., Monaco, A. P., and Maestrini E. (2003). Screening of nine candidate genes for autism on chromosome 2q reveals rare nonsynonymous variants in the cAMP-GEFII gene. Mol. Psychiatry 8:916–924
Beardsall, L., and Huppert, F. A. (1994). Improvement in NART word reading in demented and normal older persons using the Cambridge Contextual Reading Test. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 16:232–242
Cardon, L. R., Smith, S. D., Fulker, D. W., Kimberling, W.J., et al. (1994). Quantitative trait locus for reading disability of chromosome 6. Science 266:276–279
Casto, S. D., DeFries, J. C., and Fulker, D. W. (1995) Multivariate genetic analysis of Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children – Revised (WISC-R) factors. Behav. Genet. 25:25–32
Carroll, J. B. (1993). Human Cognitive Abilities: A Survey of Factor-Analytic Studies. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press
Cattell, R. B. (1963). Theory of fluid and crystallized intelligence: a critical experiment. J. Educ. Psychol. 54:1–22
Chorney, M. J., Chorney, K., Seese, N., Owen, M. J., Daniels, J., McGuffin, P., Thompson, L. A., Detterman, D. K., Benbow, C., Lubinski, D., Eley, T., and Plomin, R. (1998). A quantitative trait locus associated with cognitive ability in children. Psychol. Sci. 9:1–8
De Koning, D. J., Visscher, P. M., Knott, S. A., and Haley, C. S. (1998). A strategy for QTL detection in half-sib populations. Anim. Sci. 67:257–268
Fagerheim, T., Raeymaekers, P., Tonnessen, F. E., Pedersen, M., Tranebjaerg, L., and Lubs, H. A. (1999) A new gene (DYX3) for dyslexia is located on chromosome 2. J. Med. Genet. 36:664–669
Fisher, S. E., Francks, C., Marlow, A. J., MacPhie, I. L., Newbury, D. F., Cardon, L. R., Ishikawa-Brush, Y., Richardson, A. J., Talcott, J. B., Gayan, J., Olson, R. K., Pennington, B. F., Smith, S. D., DeFries, J. C., Stein, J. F., and Monaco, A. P. (2002). Independent genome-wide scans identify a chromosome 18 quantitative-trait locus influencing dyslexia. Nat Genet. 30:86–91
Gayan, J., Smith, S. D., Cherney, S. S., Cardon, L. R., Fulker, D. W., Brower, A. M., Olson, R. K., Pennington, B. F., and DeFries, J. C. (1999). Quantitative-trait locus for specific language and reading deficits on chromosome 6p. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:157–164
Gustafsson, J.-E. (1984). A unifying model for the structure of intellectual abilities. Intelligence 8:179–203
Horn, J. L., and Cattell, R. B. (1966). Refinement and test of the theory of fluid and crystallized general intelligences. J. Educ. Psychol. 57:253–270
Huntsman, M. M., Tran, B. V., Potkin, S. G., Bunney, W. E., Jr., and Jones, E. G. (1998). Altered ratios of alternatively spliced long and short gamma2 subunit mRNAs of the gamma-amino butyrate type A receptor in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95:15066–15071
Jackson, D. N. (1984). Manual for the Multidimensional Aptitude Battery. Port Huron, MI: Research Psychologists Press
Jackson, D. N. (1998). Multidimensional Aptitude Battery II. Port Huron, MI: Sigma Assessment Systems, Inc
Kaminen, N., Hannula-Jouppi, K., Kestila, M., Lahermo, P., Muller, K., Kaaranen, M., Myllyluoma, B., Voutilainen, A., Lyytinen, H., Nopola-Hemmi, J., and Kere, J. (2003). A genome scan for developmental dyslexia confirms linkage to chromosome 2p11 and suggests a new locus on 7q32. J. Med. Genet. 40:340–345
Kong, A., Gudbjartsson, D. F., Sainz, J., Jonsdottir, G. M., Gudjonsson, S. A., Richardsson, B., Sigurdardottir, S., Barnard, J., Hallbeck, B., Masson, G., Shlien, A., Palsson, S. T., Frigge, M. L., Thorgeirsson, T. E., Gulcher, J. R., and Stefansson, K. (2002). A high-resolution recombination map of the human genome. Nat. Genet. 31:241–247
Kruglyak, L., and Daly, M. J. (1998). Linkage thresholds for two-stage genome scans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 62: 994–997
Lander, E., and Kruglyak, L. (1995). Genetic dissection of complex traits: guidelines for interpreting and reporting linkage results. Nat. Genet. 11:241–247
Leal, S. M. (2003). Genetic maps of microsatellite and single-nucleotide polymorphism markers: are the distances accurate? Genet. Epidemiol. 24:243–252
Legare, M. E., Bartlett, F. S., II, and Frankel, W. N. (2000). A major effect QTL determined by multiple genes in epileptic EL mice. Genome. Res. 10:42–48
Luciano, M., Hine, E. J., Wright, M. J., Duffy, D. L., and Martin, N. G. (in preparation). Combined linkage and association tests of SCA1, MJD and DPRLA triplet repeat polymorphisms with cognitive phenotypes in a normal population of adolescent twins
Luciano, M., Wright, M. J., Geffen, G. M., Geffen, L. B., Smith, G. A., Evans, D. M., and Martin, N. G. (2003). A genetic two-factor model of the covariation among a subset of Multidimensional Aptitude Battery and WAIS-R subtests. Intelligence 31:589–605
Luciano, M., Wright, M. J., Geffen, G. M., Geffen, L. B., Smith, G. A., and Martin, N. G. (2004a). A genetic investigation of the covariation among inspection time, choice reaction time, and IQ subtest scores. Behav. Genet. 34:41–50
Luciano, M., Wright, M. J., and Martin, N. G. (2004b). Exploring the etiology of the association between birthweight and IQ in an adolescent twin sample. Twin. Res. 7:62–71
Martin, N. G., Boomsma, D. I., and Machin, G. A. (1997). A twin-pronged attack on complex traits. Nat. Genet. 17:87–392
Martin, N. G., and Eaves, L. J. (1977) The genetical analysis of covariance structure. Heredity 38:79–95
McClearn, G. E., Johansson, B., Berg, S., Pederson, N. L., Ahern, F., Petrill, S. A., and Plomin, R. (1997) Substantial genetic influence on cognitive abilities in twins 80 or more years old. Science 276:1560–1563
Nelson, H. E. (1982). National Adult Reading Test. Berkshire: NFER Nelson Publishing Company.
Naeve, G. S., Ramakrishnan, M., Kramer, R., Hevroni, D., Citri, Y., and Theill, L. E. (1997) Neuritin: a gene induced by neural activity and neurotrophins that promotes neuritogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94:2648–2653
Pedersen, N. L., Plomin, R., and McClearn, G. E. (1994). Is there a G beyond g? (Is there genetic influence on specific cognitive abilities independent of genetic influence on general cognitive ability?). Intelligence 18:133–145
Petrill, S. A., Luo, D., Thompson, L. A., and Detterman, D. K. (1996a) The independent prediction of general intelligence by elementary cognitive tasks: genetic and environmental influences. Behav. Genet. 26:135–147
Petrill, S. A., Plomin, R., McClearn, G. E., Smith, D. L., Vignetti, S., Chorney, M. J., Chorney, K., Thompson, L. A., Detterman, D. K., Benbow, C., Lubinski, D., Daniels, J., Owen M. J., and McGuffin, P. (1996b) DNA markers associated with general and specific cognitive abilities. Intelligence 23:191–203
Petryshen, T. L., Kaplan, B. J., Hughes, M. L., Tzenova, J., and Field, L. L. (2002) Supportive evidence for the DYX3 dyslexia susceptibility gene in Canadian families. J. Med. Genet. 39:125–126
Plomin, R. (1999) Genetics and general cognitive ability. Nature 402: C25–C29
Plomin, R., Hill, L., Craig, I. W., McGuffin, P., Purcell, S., Sham, P. C., Thompson, L. A., Fisher, P. J., Turic, D., and Owen, M. J. (2001) A genome-wide scan of 1842 DNA markers for allelic associations with general cognitive ability: a five-stage design using DNA pooling and extreme selected groups. Behav. Genet. 31:497–509
Plomin, R., McClearn, G. E., Smith, D. L., Skuder, P., Vignetti, S., Chorney, M. J., Chorney, K., Kasarda, S., Thompson, L. A., Detterman, D. K., Petrill, S. A., Daniels, J., Owen, M. J., and McGuffin, P. (1995) Allelic associations between 100 DNA markers and high versus low IQ. Intelligence 21:31–48
Plomin, R., McClearn, G. E., Smith, D. L., Vignetti, S., Chorney, M. J., Chorney, K., Venditti, C. P., Kasarda, S., Thompson, L. A., Detterman, D. K., Daniels, J., Owen, M., and McGuffin, P. (1994) DNA markers associated with high versus low IQ: the IQ quantitative trait loci (QTL) project. Behav. Genet. 24:107–118
Plomin, R., Turic, D. M., Hill, L., Turic, D. E., Stephens, M., Williams, J., Owen, M. J., and O’Donovan, M. C. (2004) A functional polymorphism in the succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 family, member A1) gene is associated with cognitive ability. Mol. Psychiatry 9:582–586
Posthuma, D., Luciano, M., Geus, E. J. d., Wright, M. J., Slagboom, E., Montgomery, G. W., Boomsma, D. I., and Martin N. G. (2005). A genome-wide scan for IQ in two independent samples identifies quantitative trait loci on 2q and 6p. Am J Hum Genet. 77:318–326
Rabionet, R., Jaworski, J. M., Ashley-Koch, A. E., Martin, E. R., Sutcliffe, J. S., Haines, J. L., Delong, G. R., Abramson, R. K., Wright, H. H., Cuccaro, M. L., Gilbert, J. R., and Pericak-Vance, M. A. (2004) Analysis of the autism chromosome 2 linkage region: GAD1 and other candidate genes. Neurosci. Lett. 372: 209–214
Rietveld, M. J. H., van Baal, C., Dolan, C. V., and Boomsma, D. I. (2000) Genetic factor analyses of specific cognitive abilities in 5-year-old Dutch children. Behav. Genet. 30: 29–40
Rijsdijk, F. V., Vernon, P. A., and Boomsma, D. I. (1998) The genetic basis of the relation between speed-of-information-processing and IQ. Behav. Brain Res. 95:77–84
Roberts, S. B., MacLean, C. J., Neale, M. C., Eaves, L. J., and Kendler, K. S. (1999) Replication of linkage studies of complex traits: an examination of variation in location estimates. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65: 876–884
Rujescu, D., Hartmann, A. M., Gonnermann, C., Moller, H. J., and Giegling, I. (2003) M129V variation in the prion protein may influence cognitive performance. Mol. Psychiatry 8:937–941
Singer, S., Rossi, S., Verzosa, S., Hashim, A., Lonow, R., Cooper, T., Sershen, H., and Lajtha, A. (2004) Nicotine-induced changes in neurotransmitter levels in brain areas associated with cognitive function. Neurochem. Res. 29: 1779–1792
Spelman, R. J., Coppieters, W., Karim, L., van Arendonk, J. A., and Bovenhuis, H. (1996) Quantitative trait loci analysis for five milk production traits on chromosome six in the Dutch Holstein-Friesian population. Genetics 144: 1799–1808
SPSS (1989–2003). SPSS 12.0.2 for Windows. SPSS Inc
Stober, G., Meyer, J., Nanda, I., Wienker, T. F., Saar, K., Knapp, M., Jatzke, S., Schmid, M., Lesch, K. P., and Beckmann, H. (2000) Linkage and family-based association study of schizophrenia and the synapsin III locus that maps to chromosome 22q13. Am. J. Med. Genet. 96: 392–397
Toyooka, K., Muratake, T., Tanaka, T., Igarashi, S., Watanabe, H., Takeuchi, H., Hayashi, S., Maeda, M., Takahashi, M., Tsuji, S., Kumanishi, T., and Takahashi, Y. (1999) 14–3-3 protein eta chain gene (YWHAH) polymorphism and its genetic association with schizophrenia. Am. J. Med. Genet. 88: 164–167
Tsai, S. J., Hong, C. J., Yu, Y. W., and Chen, T. J. (2004) Association study of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Val66Met polymorphism and personality trait and intelligence in healthy young females. Neuropsychobiology 49:13–16
van Wezel, T., Ruivenkamp, C. A., Stassen, A. P., Moen, C. J., and Demant, P. (1999) Four new colon cancer susceptibility loci, Scc6 to Scc9 in the mouse. Cancer Res. 59:4216–4218
Vink, J. M., and Boomsma, D. I. (2002) Gene finding strategies. Biol. Psychol. 61:53–71
Wainwright, M. A., Wright, M. J., Geffen, G. M., Geffen, L. B., Luciano, M., Martin, N. G. (2004) Genetic and environmental sources of covariance between reading tests used in neuropsychological assessment and IQ subtests. Behav. Genet. 34:365–376
Wainwright, M. A., Wright, M. J., Geffen, G. M., Luciano, M., and Martin, N. G. (2005) The genetic basis of academic achievement on the Queensland Core Skills Test and its shared genetic variance with IQ. Behav. Genet. 35:133–145
Ward, L. C., Ryan, J. J., and Axelrod, B. N. (2000) Confirmatory factor analyses of the WAIS-III standardization data. Psychol. Assess. 12:341–345
Wiltshire, S., Cardon, L. R., and McCarthy, M. I. (2002) Evaluating the results of genomewide linkage scans of complex traits by locus counting. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 71:1175–1182
Wright, M. J., De Geus, E., Ando, J., Luciano, M., Posthuma, D., Ono, Y., Hansell, N. K., Van Baal, C., Hiraishi, K., Hasegawa, T., Smith, G., Geffen, G., Geffen, L., Kanba, S., Miyake, A., Martin, N., and Boomsma, D. (2001) Genetics of cognition: outline of collaborative twin study. Twin Res. 4:48–56
Yalcin, B., Willis-Owen, S. A., Fullerton, J., Meesaq, A., Deacon, R. M., Rawlins, J. N., Copley, R. R., Morris, A. P., Flint, J., and Mott, R. (2004) Genetic dissection of a behavioral quantitative trait locus shows that Rgs2 modulates anxiety in mice. Nat. Genet. 36:1197–1202
Zeng, Z., Fan, P., Rand, E., Kyaw, H., Su, K., Madike, V., Carter, K. C., and Li, Y. (1998) Cloning of a putative human neurotransmitter receptor expressed in skeletal muscle and brain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 242:575–578
Zhu, G., Duffy, D. L., Eldridge, A., Grace, M., Mayne, C., O’Gorman, L., Aitken, J. F., Neale, M., Hayward, N. K., Green, A. C., and Martin, N. G. (1999) A major quantitative-trait locus for mole density is linked to the familial melanoma gene CDKN2A: a maximum-likelihood combined linkage and association analysis in twins and their sibs. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 65:483–492
Zhu, G., Evans, D. M., Duffy, D. L., Montgomery, G. W., Medland, S. E., Gillespie, N. A., Ewen, K. R., Jewell, M., Liew, Y. W., Hayward, N. K., Sturm, R. A., Trent, J. M., and Martin, N. G. (2004) A genome scan for eye color in 502 twin families: most variation is due to a QTL on chromosome 15q. Twin Res. 7:197–210
Acknowledgments
We should like to thank the twins and their parents for their co-operation, Manuel Ferreira and Sarah Medland for assistance with data simulations and linkage analysis, Anjali Henders for blood processing and Megan Campbell for DNA extraction. Phenotype collection was funded by ARC grants (A79600334, A79906588, A79801419, DP0212016, DP0343921) and genotyping by the Australian NHMRC’s Program in Medical Genomics (NHMRC–219178) and the Center for Inherited Disease Research (CIDR; Director, Dr Jerry Roberts) at The Johns Hopkins University. CIDR is fully funded through a federal contract from the National Institutes of Health to The Johns Hopkins University (Contract Number N01-HG-65403). Dr Luciano is supported by an Australian Research Council Postdoctoral Fellowship (DP0449598).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luciano, M., Wright, M., Duffy, D. et al. Genome-wide Scan of IQ Finds Significant Linkage to a Quantitative Trait Locus on 2q. Behav Genet 36, 45–55 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9003-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-005-9003-1