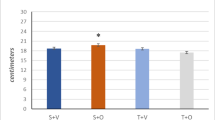
The effects of dynamic and static load on the intracellular concentrations of sodium \( \left({\mathrm{Na}}_{\mathrm{i}}^{+}\right) \) and potassium (K+i) in m. soleus and m. biceps, respectively, were studied in mice. Both dynamic (swimming for 60 min) and static (hanging on the grid for 40 min) load led to a 2-fold increase in \( {\mathrm{Na}}_{\mathrm{i}}^{+} \) level, a decrease in K+i concentration by 25-35%, and 3-4-fold increase in the \( {\mathrm{Na}}_{\mathrm{i}}^{+}/{\mathrm{K}}_{\mathrm{i}}^{+} \) ratio. These effects of dynamic and static loads on the studied parameters remained unchanged in mice subjected to regular physical exercise (swimming or hanging on the grid for 1 h a day over 4 weeks). Our results suggest that dissipation of sodium and potassium transmembrane gradients during physical exercise can be considered as a factor of regulation of functional activity of skeletal muscles, which includes changes in transcription and translation of myokines observed previously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kapilevich LV, Kabachkova AV, Zakharova AN, Lalaeva GS, Kironenko TA, Dyakova EYu, Orlov SN. Secretory Function of Skeletal Muscles: Producing Mechanisms and Myokines Physiological Effects. Uspekhi Fiziol. Nauk. 2016;47(2):7-26. Russian.
Danilov K, Sidorenko S, Milovanova K, Klimanova E, Kapilevich LV, Orlov SN. Electrical pulse stimulation decreases electrochemical Na+ and K+ gradients in C2C12 myotubes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017;493(2):875-878.
Gundersen K. Excitation-transcription coupling in skeletal muscle: the molecular pathways of exercise. Biol. Rev. 2011;86(3):564-600.
Kapilevich LV, Kironenko TA, Zaharova AN, Orlov SN, Kotelevtsev YV, Dulin NO. Skeletal muscle as an endocrine organ: role of [Na+]i/[K+]i-mediated excitation-transcription coupling. Genes Dis. 2015;2(4):328-336.
Łukaszuk B, Bialuk I, Górski J, Zajączkiewicz M, Winnicka MM, Chabowski A. A single bout of exercise increases the expression of glucose but not fatty acid transporters in skeletal muscle of IL-6 KO mice. Lipids. 2012;47(2):763-772.
Matchkov VV, Krivoi II. Specialized functional diversity and interactions of Na,K-ATPase. Front. Physiol. 2016;7. ID 179. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00179
Murphy KT, Nielsen OB, Clausen T. Analysis of exerciseinduced Na+-K+ exchange in rat skeletal muscle. Exp. Physiol. 2008;93(12):1249-1262.
Nikolić N, Görgens SW, Thoresen GH, Aas V, Eckel J, Eckardt K. Electrical pulse stimulation of cultured skeletal muscle cells as a model for in vitro exercise — possibilities and limitations. Acta Physiol. 2017;220(3):310-331.
Orlov SN, Hamet P. Salt and gene expression: evidence for Na+i,K+i-mediated signaling pathways. Pflugers Arch. 2015;467(3):489-498.
Pedersen BK, Febbraio MA. Muscle as an endocrine organ: focus on muscle-derived interleukin-6. Physiol. Rev. 2008; 88(4):1379-1406.
Popov DV, Lysenko EA, Bokov RO, Volodina MA, Kurochkina NS, Makhnovskii PA, Vyssokikh MY, Vinogradova OL. Effect of aerobic training on baseline expression of signaling and respiratory proteins in human skeletal muscle. Physiol. Rep. 2018;6(17). ID e13868. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.13868
Popov DV, Makhnovskii PA, Shagimardanova EI, Gazizova GR, Lysenko EA, Gusev OA, Vinogradova OL. Contactile activity-specific transcriptome response to acute endurance exercise and training in human skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2019;316(4):E604-E614.
Sidorenko S, Klimanova E, Milovanova K, Lopina OD, Kapilevich LV, Chibalin AV, Orlov SN. Transcriptomic changes in C2C12 myotubes triggered by electrical stimulation: Role of Ca2+i-mediated and Ca2+i-independent signaling and elevated [Na+]i/[K+]i ratio. Cell Calcium. 2018;76):72-86.
Sjøgaard G, Adams RP, Saltin B. Water and ion shifts in skeletal muscle of humans with intense dynamic knee extension. Am. J. Physiol. 1985;248(2, Pt 2):R190-R196.
Smolyaninova LV, Koltsova SV, Sidorenko SV, Orlov SN. Augemented gene expression triggered by Na+,K+-ATPase inhibition: role of Ca2+-mediated and -independent excitation-transcription coupling. Cell Calcium. 2017;68:5-13.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 169, No. 1, pp. 4-7, January, 2020
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapilevich, L.V., Milovanova, K.G., Sidorenko, S.V. et al. Effects of Dynamic and Static Loads on the Concentration of Sodium and Potassium in Murine Skeletal Muscles. Bull Exp Biol Med 169, 1–4 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04811-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-020-04811-y