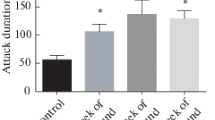
Stress-induced changes in the behavior of CBA and BALB/c mice were studied after 3-week ultrasound exposure (22-45 kHz). The mice of both lines demonstrated increased aggression in the resident—intruder and social interest paradigms and reduced number of social interactions in the social interest test. Elevated plus maze test showed a decrease in anxiety level in CBA mice and an increase in this parameter in BALB/c mice. Chronic exposure to ultrasound induced an increase in aggression level in mice of both lines that was not directly related to changes in anxiety level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bazovkina DV, Terenina EE, Kulikov AV. Effect of selective agonist of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors on defensive behavior in mice with different predisposition to catalepsy. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2010;150(2):225-228.
Kudryavtseva NN, Markel AL, Orlov YuL. Aggressive behavior: genetic and physiological mechanisms. Vavilovsk. Zh. Genetiki Selektsii. 2014;18(4-3):1133-1155. Russian.
Notova SV, Petrosienko ES. The problem of emotional stress and aggressiveness: theories of origin and methods of their study. Vestn. Orenburg. Gos. Univer. 2009(1):87-90. Russian.
Bronsard G, Bartolomei F. Rhythms, rhythmicity and aggression. J. Physiol. Paris. 2013;107(4):327-334.
Coppens CM, de Boer SF, Buwalda B, Koolhaas JM. Aggression and aspects of impulsivity in wild-type rats. Aggress Behav. 2014;40(4):300-308.
Costa AA, Morato S, Roque AC, Tinos R. A computational model for exploratory activity of rats with different anxiety levels in elevated plus-maze. J. Neurosci. Methods. 2014;236:44-50.
Haller J. The neurobiology of abnormal manifestations of aggression — a review of hypothalamic mechanisms in cats, rodents, and humans. Brain Res. Bull. 2013;93:97-109.
Kudryavtseva NN. Psychopathology of repeated aggression: a neurobiological aspect. Perspectives on the psychology of aggression. Morgan JP, ed. New York, 2006. P. 35-64.
Kudryavtseva NN, Smagin DA, Kovalenko I., Vishnivetskaya GB. Repeated positive fighting experience in male inbred mice. Nat. Protoc. 2014;9(11):2705-2717.
Newman WJ. Psychopharmacologic management of aggression. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 2012;35(4):957-972.
Rendon NM, Keesom SM, Amadi C, Hurley LM, Demas GE. Vocalizations convey sex, seasonal phenotype, and aggression in a seasonal mammal. Physiol. Behav. 2015;152(Pt A):143-150.
Stevenson PA, Rillich J. Isolation associated aggression — a consequence of recovery from defeat in a territorial animal. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e74965.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 163, No. 4, pp. 400-403, April, 2017
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlov, D.A., Gorlova, A.V., Ushakova, V.M. et al. Effects of Chronic Exposure to Ultrasound of Alternating Frequencies on the Levels of Aggression and Anxiety in CBA and BALB/c mice. Bull Exp Biol Med 163, 409–411 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3815-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-017-3815-x