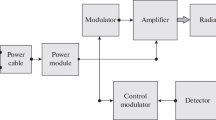
Effects of millimeter-wave electromagnetic radiation (40 GHz frequency, 0.01 mW power) on the spontaneous fi ring of convergent neurons of the spinal trigeminal nucleus and their responses to electrical stimulation of the dura mater were studied in neurophysiological experiments on rats. Irradiation of the area of cutaneous receptive fields of spinal trigeminal nucleus reversibly inhibited both spontaneous discharges and activity induced by electrical stimulation of the dura mater. The second and third exposures to electromagnetic radiation with an interval of 10 min were ineffective. These results suggest that suppression of neuronal excitability in the spinal trigeminal ganglion can be a mechanism of the anti-migraine effects of electromagnetic radiation observed in clinical practice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. V. Amelin, Yu. D. Ignatov, A. A. Skromets, and A. Yu. Sokolov, Migraine. Patogenesis, Clinics, Pharmotherapy: Manual for Therapists [in Russian], Moscow (2011).
O. V. Betskii, V. V. Kislov, and N. N. Lebedeva, Millimeter-Waves and Living Systems [in Russian], Moscow (2004).
E. R. Dzheldubaeva, and E. N. Chuyan, Antinociceptive Effects of Millimeter-Wave Radiation, Review, Experimental Data, and Summary of Results [in Russian], Saarbrucken (2012).
D. S. Medvedev, I. D. Molodtsova, and O. A. Yanova, Fundamental’nye Issledovaniya, No. 9-5, 866-870 (2013).
A. Yu. Sokolov, O. A. Lyubashina, Yu. D. Ignatov, et al., Med. Akad. Zh., 11, No. 2, 3-14 (2011).
S. Akerman, P. R. Holland, and J. Hoffmann, Cephalalgia, 33, No. 8, 577-592 (2013).
7. P. J. Goadsby, Ann. Indian Acad. Neurol., 15, Suppl. 1, S15-S22 (2012).
O. A. Lyubashina, A. Y. Sokolov, S. S. Panteleev, Neuroscience, 222, 29-37 (2012).
K. Messlinger, Exp. Brain Res., 196, No. 1, 179-193 (2009).
N. S. Novikova, T. B. Kazakova, V. J. Rogers, and E. A. Korneva, Neuro Endocrinol. Lett., 23, No. 4, 315-320 (2002).
A. G. Pakhomov, and P. R. Murphy, IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 28, No. 1, 34-40 (2000).
A. G. Pakhomov, H. K. Prol, S. P. Mathur, et al., Bio electromagnetics, 18, No. 4, 324-334 (1997).
R. B. Pelka, C. Jaenicke, and J. Gruenwald, Adv. Ther., 18, No. 3, 101-109 (2001).
A. A. Radzievsky, O. V. Gordiienko, S. Alekseev, et al., Bioelectromagnetics., 29, No. 4, 284-295 (2008).
T. I. Usichenko, H. Edinger, V. V. Gizhko, et al., Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med ., 3, No. 2, 201-207 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 160, No. 10, pp. 420-424, October, 2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sivachenko, I.B., Medvedev, D.S., Molodtsova, I.D. et al. Effects of Millimeter-Wave Electromagnetic Radiation on the Experimental Model of Migraine. Bull Exp Biol Med 160, 425–428 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3187-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-016-3187-7