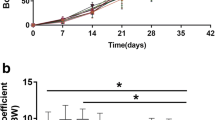
The effect of low dose dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT), omnipresent ecotoxicant and endocrine disruptor, on the functioning of the endocrine system is an urgent problem. We studied the effect of low dose DDT on thyroid status in rats. Rats receiving DDT in a dose of 1.890±0.086 μg/kg for 6 weeks showed increased concentrations of thyroid hormones, particularly triiodothyronine, and reduced level of thyrotropin. Longer exposure reduced the production of thyroid hormones. The dynamics of thyroid status parameters during DDT treatment in a low dose was similar to changes observed during the development of hypothyroidism induced by iodine deficiency.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hygienic Requirements to Foodstuff Safety and Nutritive Value [in Russian], SanPin 2.3.2.1078-01.2008.
I. I. Dedov, G. A. Gerasimov, and N. Yu. Sviridenko, Iodine Defi ciency Diseases in the Russian Federation (Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Prevention) [in Russian], Moscow (1999).
N. V. Yaglova, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 152, No. 2, 253-257 (2011).
N. V. Yaglova and V. V. Yaglov, Vestn. Ross. Akad. Med. Nauk, No. 3, 56-61 (2012).
M. Boas, U. Feldt-Rasmussen, and K. Main, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 355, No. 2, 240-248 (2012).
C. Capen, Prog. Clin. Biol. Res., 387, 173-191 (1994).
G. Daly and F. Wania, Environ. Sci. Technol., 39, No. 2, 385-398 (2005).
R. Delport, R. Bornman, U. Maclntyre, et al., Environ. Health Perspect., 119, No. 5, 647-651 (2011).
E. Diamanti-Kandarakis, J. P. Bourguignon, L. Guidice, et al., Endocr. Rev., 30, No. 4, 293-342 (2009).
J. Muñoz-Arnanz and B. Jimenez, Environ. Pollut., 159, No. 12, 3640-3646 (2011).
F. Santini, P. Vitti, G. Ceccarini, et al., J. Endocrinol. Invest., 26, No. 10, 950-955 (2003).
O. Tebourbi, D. Hallegue, M. Yakoubi, et al., Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol., 29, No. 3, 271-279 (2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 156, No. 12, pp. 720-722, December, 2013
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yaglova, N.V., Yaglov, V.V. Changes in Thyroid Status of Rats after Prolonged Exposure to Low Dose Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane. Bull Exp Biol Med 156, 760–762 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2443-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-014-2443-y