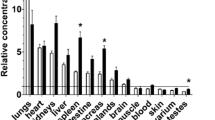
Abstract
Blood ammonia concentration increased in the portal vein (by 1.4 times) and inferior vena cava (caudal to the renal vein inflow, by 2.2 times; and cranial to the hepatic vein inflow, by 2.5 times) of rats 3 h after intragastric administration of 16.57 M ethanol solution (446 mmol/kg, ≈ 1.4 LD50/48 h). Ammonia concentration in mixed blood samples (post-decapitation) increased by 39%. The rate of ammonia accumulation was 3-fold higher in an intraperitoneal lavage solution. Three-hour exposure of ethanol-treated animals to atmospheric ammonia (0.84–1.07 mg/liter, i.e. ≈ 1/8LC50 for intact rats) was followed by a 2.4-fold increase in blood ammonia concentration as compared to specimens of the ethanol group. Ammonia inhalation potentiated the lethal effect of ethanol (dose variation factor 0.81), suppressed external respiration, and decreased oxygen consumption. Our results indicate that kinetic changes in endogenous ammonia have an adverse effect on the outcome of alcohol intoxication in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hazardous Industrial Substances, Eds. N. V. Lazarev and I. D. Gadaskina [in Russian], Leningrad (1977), Vol. 3, 7th Edition, p. 89.
V. L. Rejniuk, T. V. Schafer, R. V. Ovsep'yan, and Ju. Ju. Ivnitsky, Byull. Eksp. Biol. Med., 143, No. 6, 634–637 (2007).
T. V. Schafer, Ju. Ju. Ivnitsky, and V. N. Malakhovsky, Ibid., 135, No. 4, 419–422 (2003).
N. K. Aagaard, T. Thogersen, T. Grofte, et al., Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res., 28, No. 5, 697–701 (2004).
K. Adachia, T. Matsuhashia, Yu. Nishizawaa, et al., Biochem. Pharmacol., 50, No. 9, 1391–1399 (1995).
Ju. Ju. Ivnitsky, V. L. Rejniuk, T. V. Schafer, and V. N. Malakhovsky, Toxicol., 224, 184–190 (2006).
V. Mohanachari, K. S. Reddy, and K. Indira, Toxicol. Lett., 20, No. 2, 225–228 (1984).
M. C. Vemuri and K. Indira, Biochem. Med. Metab. Biol., 36, No. 1, 8–13 (1986).
A. Watanabe and Y. Kuwabara, Res. Exp. Med. (Berl.), 194, No. 3, 157–164 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Byulleten' Eksperimental'noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 145, No. 6, pp. 688–690, June, 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rejniuk, V.L., Schafer, T.V. & Ivnitsky, J.J. Ammonia potentiates the lethal effect of ethanol on rats. Bull Exp Biol Med 145, 741–743 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-008-0191-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-008-0191-6