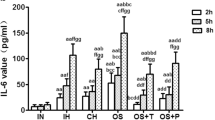
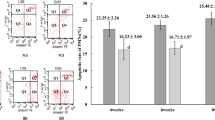
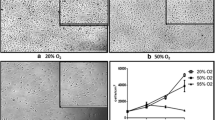
Abstract
We studied the effect of hypoxia on activation and stimulation of apoptosis in cultured endothelial cells. The effect of hypoxia was compared to that of apoptosis-inducing agents (tumor necrosis factor and bacterial lipopolysaccharide). Incubation of endothelial cells for 24 h under hypoxic conditions (2% O2, 5% CO2, and 93% N2) increased secretion of von Willebrand factor, but had no effect on the expression of cell adhesion molecule ICAM-1. Tumor necrosis factor and lipopolysaccharide did not stimulate secretion of von Willebrand factor, but significantly increased the expression of ICAM-1. These data attest to significant differences in the mechanisms of endothelium activation under hypoxic conditions and during treatment with tumor necrosis factor or lipopolysaccharide. Hypoxia stimulated apoptosis in endothelial cells, which was seen from the increase in the number of annexin V-binding cells and activation of caspase-3. Similar changes were revealed in the presence of tumor necrosis factor and lipopolysaccharide. Hence, damage to endothelial cells caused by hypoxia and these compounds is mediated by similar mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. V. Yanushevskaya, E. A. Barkevich, S. G. Khaspekova, et al., Gematol. Transfuziol., 50, No. 2, 20–25 (2005).
A. S. Antonov, M. A. Nikolaeva, T. S. Klueva, et al., Atherosclerosis, 59, No. 1, 1–19 (1986).
G. M. Cohen, Biochem. J., 326, No. 1, 1–16 (1997).
C. N. Lee, W. F. Cheng, M. C. Chang, et al., Apoptosis, 10, 887–894 (2005).
C. Michiels, T. Arnould, and Y. Remacle, Biochem. Biophys. Acta, 1497, No. 1, 1–10 (2000).
C. F. Maurus, D. Schmidt, M. K. Schneider, et al., Eur. J. Cardiothorac. Surg., 23, No. 6, 976–983 (2003).
D. J. Pinsky, Y. Naka, H. Liao, et al., J. Clin. Invest., 97, No. 2, 493–500 (1996).
O. Yu. Printseva, M. M. Peclo, and A. M. Grown, Am. J. Pathol., 140, No. 4, 889–896 (1992).
I. Vermes, C. Haanen, H. Steffens-Nakken, and C. Reutelingsperger, J. Immunol. Methods, 184, No. 1, 39–51 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
__________
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 144, No. 10, pp. 384–386, October, 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonova, O.A., Loktionova, S.A., Golubeva, N.V. et al. Damage and activation of endothelial cells during in vitro hypoxia. Bull Exp Biol Med 144, 504–506 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-007-0362-x
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-007-0362-x