Abstract
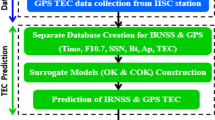
The total electron content (TEC) is the number of electrons present in a ray path between satellite and receiver. TEC affects the propagation of radio signal from satellite to receiver, which causes a ranging error. In the case of single frequency user receiver, the prediction of TEC helps to correct the range errors. TEC is measured using TEC unit (TECU), where \(1~\text{TECU} = 1 \times 10^{16}~\text{electrons}/\text{m}^{2}\). The vertical total electron content (VTEC) of the L1 band is estimated by using data collected from GPS receiver which is installed at the ACSCE station Bangalore. In this work, an ordinary kriging (OK)-based surrogate model algorithm and Matlab code is developed and used to predict the hourly basis ionospheric VTEC. Six parameters such as time, sun spot number (SSN), the solar flux index at 10.7 cm (F10.7), Kp and Ap and observed TEC are used to build the surrogate model. These parameters are related to the ionospheric diurnal variations, solar cycle and geomagnetic activities. In order to cover all regions of the world during different solar activity periods six input parameters are collected from low-, mid- and high-latitude regions during low, medium and high solar activity periods. The root mean square error (RMSE) of the OK-based surrogate model ranges from 0.6–3.6 TECU, and the correlation coefficient varies between 0.79–0.99 and range error varies from 0.04654–0.3017244 m at three regions.
The TEC prediction results from the OK-based surrogate model are compared with results obtained from (i) a genetic algorithm-based neural network (GA-NN), (ii) a back-propagation neural network (BP-NN) and (iii) the IRI-2012 model at the CHAN station. For a typical dataset the RMSE of the OK-based surrogate model is 4.523 TECU and the correlation coefficient is 0.9733. The RMSE values for the GA-NN, BP-NN and IRI-2012 models are 5.3529, 6.2913 and 6.7179 TECU and The correlation coefficients are 0.8343, 0.7869 and 0.7797, respectively. The OK model is also compared with a time series method for the CHAN station; it is observed that, for 3 days (7-1-2008 to 9-1-2008) prediction, the OK model gives a 75% result for \(\Delta \textit{TEC} <1~\text{TECU}\) condition, the time series method gives 39% for the same condition. The results indicate that the OK-based surrogate model is suitable for applications in ionospheric TEC predictions.


































Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharya, R., Roy, B., Sivaraman, M.R., Dasgupta, A.: Prediction of ionospheric total electron content using adaptive neural network with in-situ learning algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 47, 115–123 (2011)
Arikan, F., Erol, C.B., Arikan, O.: Regularized estimation of vertical total electron content from GPS data for a desired time period. IEEE (2004)
Arikan, F., Erol, C.B., Arikan, O.: Regularized estimation of TEC from GPS data for certain mid latitude stations and comparisons with IRI model. Adv. Space Res. 39(5), 867–874 (2007)
Badeke, R., Borries, C., Hoque, M.M., Minkwitz, D.: Empirical forecast of quiet time ionospheric Total Electron Content maps over Europe. Adv. Space Res. 61(12), 2881–2890 (2018)
Balu, R., Ulaganathan, S., Asproulis, N.: Effect of variogram types on surrogate model based optimisation of aircraft wing shapes. Proc. Eng. 38, 2713–2725 (2012)
Bilitza, D., McKinnell, L.-A., Reinisch, B., Fuller-Rowell, T.: The international reference ionosphere today and in the future. J. Geod. 85, 909–920 (2011)
Homam, M.J.: Prediction of total electron content of the ionosphere using neural network. UTM J. Technol. 78(5–8), 53–57 (2016)
Kenpankho, P., Watthanasangmechai, K., Supnithi, P., Tsugawa, T., Maruyama, T.: Comparison of GPS TEC measurements with IRI TEC prediction at the equatorial latitude station, Chumphon, Thailand. Earth Planets Space 63, 365–370 (2011)
Krishnan, S.R., Seelamantula, C.S.: On the selection of optimum Savitzky-Golay filters. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 61(2), 380–391 (2013)
Lanyi, G.E., Roth, T.: A comparison of mapped and measured total ionospheric electron content using global positioning system and beacon satellite observations. Radio Sci. 23, 483–492 (1998)
Li, X., Guo, D.: Modeling and prediction of ionospheric total electron content by time series analysis. In: 2nd International Conference on Advanced Computer Control. IEEE Press, New York (2010)
Montagnac, M., Jouhaud, J.C., Sagaut, P., Laurenceau, J.: A surrogate-model based multidisciplinary shape optimization method with application to a 2d subsonic airfoil. Comput. Fluids 36, 520–529 (2007)
Mukesh, R., Lingadurai, K., Selvakumar, U.: Kriging methodology for surrogate-based airfoil shape optimization. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 39(10), 7363–7373 (2014)
Murayama, M., Jeong, S., Yamamoto, K.: Efficient optimization design method using kriging model. J. Aircr. 42, 413–420 (2005)
Nayirl, H., Arikan, F., Arikan, O., Erol, C.B.: GPS/TEC estimation with IONOLAB method. 1-4244-1057-6/07, IEEE (2007)
Norsuzila, Y., Abdullah, M., Ismail, M., Ibrahim, M., Zakaria, Z.: Total electron content (TEC) and estimation of positioning error using Malaysia data. In: Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, vol. I, WCE 2010 (2010)
Panda, S.K., Gedam, S.S., Shuanggen, J.: Ionospheric TEC Variations at Low Latitude Indian Region. IntechOpen, China (2015)
Poole, A.W.V., McKinnell, L.-A.: On the predictability of foF2 using neural networks. Radio Sci. 35, 225–234 (2000)
Radzol, A.R.M., Lee, K.Y., Mansor, W., Azman, A.: Optimization of Savitzky-Golay smoothing filter for salivary surface enhanced Raman spectra of non structural protein 1. IEEE (2014)
Sharma, K., Dabas, R.S., Ravindran, S.: Study of total electron content variations over equatorial and low latitude ionosphere during extreme solar minimum. Astrophys. Space Sci. 341(2), 277–286 (2012)
Shyy, Wei, Tushar, G., Vaidyanathan, R., Queipo, N.V., Haftka, R.T., Tucker, P.K.: Surrogate-based analysis and optimization. Prog. Aerosp. Sci. 41, 1–28 (2005)
Song, R., Zhang, X., Zhou, C., Liu, J., He, J.: Predicting TEC in China based on the neural networks optimized by genetic algorithm. Adv. Space Res. 62, 745–759 (2018)
Srilatha Indira Dutt, V.B.S., Gowsuddin, S.: Ionospheric delay estimation using Klobuchar algorithm for single frequency GPS receivers. Int. J. Adv. Res. Electron. Commun. Eng. 2, 202–207 (2013)
Sun, S., Egerstedt, M.B., Martin, C.F.: Control theoretic smoothing splines. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 45(12), 2271–2279 (2000)
Wu, W.-C., Wang, T.-H., Chiu, C.-T.: Edge curve scaling and smoothing with cubic spline interpolation for image up scaling. In: IEEE Workshop on Signal Processing Systems (2013)
Ya’acob, N., Abdullah, M., Ismail, M.: GPS total electron content (TEC) prediction at ionosphere layer over the equatorial region. In: Bouras, C.J. (ed.) Trends in Telecommunications Technologies. IntechOpen, Europe (2010)
Acknowledgement
The research work presented in this paper has been carried out under the project entitled “Surrogate model for ionospheric studies using IRNSS/GPS Data”, funded by SAC, ISRO, Ahmadabad.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukesh, R., Soma, P., Karthikeyan, V. et al. Prediction of ionospheric vertical total electron content from GPS data using ordinary kriging-based surrogate model. Astrophys Space Sci 364, 15 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3502-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-019-3502-7