Abstract
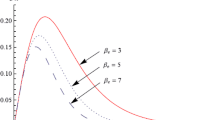
In collision-poor plasmas from space, e.g., the solar wind and planetary magnetospheres, the kinetic anisotropy of the plasma particles is expected to be regulated by the kinetic instabilities. Driven by an excess of ion (proton) temperature perpendicular to the magnetic field (\(T_{\perp}>T_{\parallel}\)), the electromagnetic ion-cyclotron (EMIC) instability is fast enough to constrain the proton anisotropy, but the observations do not conform to the instability thresholds predicted by the standard theory for bi-Maxwellian models of the plasma particles. This paper presents an extended investigation of the EMIC instability in the presence of suprathermal electrons which are ubiquitous in these environments. The analysis is based on the kinetic (Vlasov-Maxwell) theory assuming that both species, protons and electrons, may be anisotropic, and the EMIC unstable solutions are derived numerically providing an accurate description for conditions typically encountered in space plasmas. The effects of suprathermal populations are triggered by the electron anisotropy and the temperature contrast between electrons and protons. For certain conditions the anisotropy thresholds exceed the limits of the proton anisotropy measured in the solar wind considerably restraining the unstable regimes of the EMIC modes.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bale, S.D., Kasper, J.C., Howes, G.G., Quataert, E., Salem, C., Sundkvist, D.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 211101 (2009)
Feldman, W.C., Asbridge, J.R., Bame, S.J., Montgomery, M.D., Gary, S.P.: J. Geophys. Res. 80, 418 (1975)
Fried, B.D., Conte, S.D.: The Plasma Dispersion Function. Academic Press, New York (1961)
Gary, S.P.: Theory of Space Plasma Microinstabilities. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993)
Gary, S.P., Lee, M.A.: J. Geophys. Res. 99, 11297 (1994)
Gary, S.P., Montgomery, M.D., Feldman, W.C., Forslund, D.W.: J. Geophys. Res. 81, 1241 (1976)
Gary, S.P., Skoug, R.M., Steinberg, J.T., Smith, C.W.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 28, 2759 (2001)
Hellberg, M.A., Mace, R.L., Cattaert, T.: Space Sci. Rev. 121, 127 (2005)
Hellberg, M.A., Mace, R.L., Baluku, T.K., Kourakis, I., Saini, N.S.: Phys. Plasmas 16, 094701 (2009)
Hellinger, P., Trávníček, P.: J. Geophys. Res. 110, A04210 (2005)
Hellinger, P., Trávníček, P., Kasper, J.C., Lazarus, A.J.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L09101 (2006)
Henning, F.D., Mace, R.L.: Phys. Plasmas 21, 042905 (2014)
Isenberg, P.A., Maruca, B.A., Kasper, J.C.: Astrophys. J. 773, 164 (2013)
Kennel, C.F., Petschek, H.E.: J. Geophys. Res. 71, 1 (1966)
Kennel, C.F., Scarf, F.L.: J. Geophys. Res. 73, 6149 (1968)
Kourakis, I., Sultana, S., Hellberg, M.A.: Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion 54, 124001 (2012)
Lazar, M.: Astron. Astrophys. 547, A94 (2012)
Lazar, M., Schlickeiser, R., Shukla, P.K.: Phys. Plasmas 15, 042103 (2008)
Lazar, M., Poedts, S., Schlickeiser, R.: Astron. Astrophys. 534, A116 (2011)
Lazar, M., Poedts, S., Fichtner, H.: Astron. Astrophys. 582, A124 (2015)
Lazar, M., Fichtner, H., Yoon, P.H.: Astron. Astrophys. 589, A39 (2016)
Lepping, R.P., Acǔna, M.H., Burlaga, L.F., et al.: Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207 (1995)
Leubner, M., Schupfer, N.: J. Geophys. Res. 105, 27387 (2000)
Livadiotis, G., McComas, D.J.: Space Sci. Rev. 175, 183 (2013)
Mace, R.L., Sydora, R.D., Silin, I.: J. Geophys. Res. 116, A05206 (2011)
Maksimovic, M., Pierrard, V., Riley, P.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 24, 1151 (1997)
Maksimovic, M., Zouganelis, I., Chaufray, J.Y., Issautier, K., Scime, E.E., Littleton, J.E., et al.: J. Geophys. Res. 110, A09104 (2005)
Matteini, L., Landi, S., Hellinger, P., Pantellini, F., Maksimovic, M., Velli, M., Goldstein, B.E., Marsch, E.: Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L20105 (2007)
Michno, M.J., Lazar, M., Yoon, P.H., Schlickeiser, R.: Astrophys. J. 781, 49 (2014)
Newbury, J.A., Russell, C.T., Phillips, J.L., Gary, S.P.: J. Geophys. Res. 103, 9553 (1998)
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., et al.: Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55 (1995)
Pierrard, V., Lazar, M.: Sol. Phys. 267, 153 (2010)
Shaaban, M.S., Lazar, M., Poedts, S., Elhanbaly, A.: Astrophys. J. 814, 34 (2015)
Štverák, Š., Trávníček, P., Maksimovic, M., Marsch, E., Fazakerley, A.N., Scime, E.E.: J. Geophys. Res. 113, A03103 (2008)
Summers, D., Thorne, R.M.: Phys. Fluids, B Plasma Phys. 3, 1835 (1991)
Vasyliunas, V.M.: J. Geophys. Res. 73, 2839 (1968)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the use of WIND SWE (Ogilvie et al. 1995) ion data, and WIND MFI (Lepping et al. 1995) magnetic field data from the SPDF CDAWeb service: http://cdaweb.gsfc.nasa.gov/. The authors acknowledge support from the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. These results were obtained in the framework of the projects GOA/2015-014 (KU Leuven), G0A2316N (FWO-Vlaanderen), and C 90347 (ESA Prodex 9). The research leading to these results has also received funding from IAP P7/08 CHARM (Belspo), and the European Commission’s Seventh Framework Programme FP7-PEOPLE-2010-IRSES-269299 project-SOLSPANET (www.solspanet.eu). This project has received funding from the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration under grant agreement SHOCK 284515. S.M. Shaaban would like to thank the Egyptian Ministry of Higher Education for supporting his research activities and would like to acknowledge the discussions and suggestions of Prof. S.A. Elwakil.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shaaban, S.M., Lazar, M., Poedts, S. et al. Effects of suprathermal electrons on the proton temperature anisotropy in space plasmas: Electromagnetic ion-cyclotron instability. Astrophys Space Sci 361, 193 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2782-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-016-2782-4