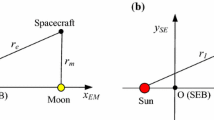
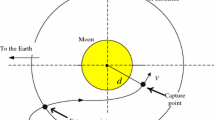
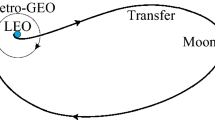
Abstract
In this paper, the lunar gravity assist (LGA) is investigated under the planar circular restricted three-body problem (PCRTBP) and two-body model. In the PCRTBP, the approximate expression of energy of the LGA in a small region of the Moon is derived. The expression uncovers the mechanism and mechanical process of the LGA in the framework of the PCRTBP. Based on the expression, the change of energy during the LGA is obtained and analyzed. To solve the limitation of the expressions and complete the research range of the LGA, a numerical methodology based on the patched-conic model is presented to analyze the LGA in a large region near the Moon. This numerical methodology cannot only obtain the change of energy but also may classify the trajectories before and after the LGA. As an application, we present a method to design a special kind of double LGA orbit. The design method synthesizes the preliminary results in the patched-conic model and the optimization in the PCRTBP. We can quickly obtain abundant double LGA orbits for the Earth–Moon transfer and interplanetary spaceflight.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broucke, R.A.: The celestial mechanics of the gravity assist. In: Proceedings of the AIAA/AAS Astrodynamics Conference, Minneapolis, pp. 83–85. AIAA, Washington, DC (1988)
Campagnola, S., Jehn, R., Van Damme, C.C.: Design of lunar gravity assist for the BepiColombo mission to Mercury. In: 14th AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Conference, Maui, Hawaii, Feb (2004). Paper AAS 04-130
Casalino, L., Colasurdo, G., Pasttrone, D.: Optimal low-thrust escape trajectories using gravity assist. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(5), 637–642 (1999a)
Casalino, L., Colasurdo, G., Pastrone, D.: Simple strategy for powered swingby. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(1), 156–159 (1999b)
Chen, Y., Baoyin, H.X., Li, J.F.: Accessibility of main-belt asteroids via gravity assists. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 37(2), 623–632 (2014)
Chobotov, V.A.: Orbital Mechanics. AIAA, Reston (2002)
Dunham, D., Davis, S.: Optimization of a multiple lunar-swingby trajectory sequence. J. Astronaut. Sci. 33(3), 275–288 (1985)
Felipe, G., Prado, A.F.B.A.: Classification of out of plane swing-by trajectories. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 22(5), 643–649 (1999)
Felipe, G., Prado, A.F.B.A.: Trajectories selection for a spacecraft performing a two-dimensional swingby. Adv. Space Res. 34(1), 2256–2261 (2004)
Helton, A.F., Strange, N.J., Longuski, J.M.: Automated Design of the Europa Orbiter Tour. J. Spacecr. Rockets 39(1), 17–22 (2002)
Kawaguchi, J., Yamakawa, H., Uesugi, T., Matsuo, H.: On making use of lunar and solar gravity assists in Lunar-A, Planet-B missions. Acta Astronaut. 35(9–11), 633–642 (1995)
Longuski, J.M., Williams, S.N.: Automated design of gravity-assist trajectories to Mars and the outer planets. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 52, 207–220 (1991)
Niehoff, J.C.: Gravity-assisted trajectories to solar-system. J. Spacecr. Rockets 3(9), 1351–1356 (1966)
Ocampo, C.A.: Transfers to Earth centered orbits via lunar gravity assist. Acta Astronaut. 52, 173–179 (2003)
Penzo, P.A.: A Survey and Recent Development of Lunar Gravity Assist. Space Studies Institute, Princeton University, Princeton (1998)
Prado, A.F.B.A.: Close-approach trajectories in the elliptic restricted problem. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 20(4), 797–802 (1997)
Shen, H.X., Casalino, L.: Indirect optimization of three-dimensional multiple-impulse Moon-to-Earth transfers. J. Astronaut. Sci. (2014). doi:10.1007/s40295-014-0018-9
Sohn, R.: Venus swingby mode for manned Mars missions. J. Spacecr. Rockets 1, 565–567 (1964)
Sohn, R.: Manned mars trips using Venus flyby modes. J. Spacecr. Rockets 3(2), 161–169 (1966)
Strange, N.J., Longuski, J.M.: Graphical method for gravity-assist trajectory design. J. Spacecr. Rockets 39(1), 9–16 (2002)
Szebehely, V.: Theory of Orbits. Academic Press, New York (1967)
Topputo, F.: On optimal two-impulse Earth–Moon transfers in a four-body model. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 117, 279–313 (2013)
Wilson, R.S., Howell, K.C.: Trajectory design in the Sun–Earth–Moon system using lunar gravity assists. J. Spacecr. Rockets 35(2), 191–198 (1998)
Yam, C.H., McConaghy, T.T., Chen, K.J., Longuski, J.M.: Design of low-thrust gravity-assist trajectories to the outer planets. In: International Astronautical Congress, Sep–Oct (2004). Paper IAC.04.A.6.02
Zimmer, S., Ocampo, C.: Analytical gradients for gravity assist trajectories using constant specific impulse engines. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 28(4), 753–760 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11432001 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 11402021. The authors also thank the Innovation Foundation of BUAA for Ph.D. Graduates and the China Scholarship Council (CSC) for fellowship support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, Y., Xu, S. Mechanical analysis of lunar gravity assist in the Earth–Moon system. Astrophys Space Sci 360, 55 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-015-2571-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-015-2571-5