Abstract
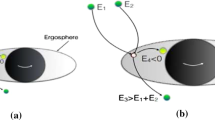
We study mechanism of formation of black holes (BHs) from collisions of particles in the vicinity of the supermassive black hole acting as a particle accelerator trough BSW (Banados-Silk-West) effect. Moreover, we also investigate BH-BH collision, in which stellar black holes colliding near the horizon of a rotating supermassive black hole can reach large values of the center-of-mass energy. This result implies that high arbitrary energy of collisions causes to be transformed into radiation energy and particles, which might bring possible visible signals through the astrophysical observations. We study the radiation energy from a collision of two accelerating stellar black holes and find a maximal value of the radiation energy to be nearly E rad ≈2.5⋅1056 erg for the ultrarelativistic value of v/c=0.99 from BH-BH collisions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdujabbarov, A.A., Tursunov, A.A., Ahmedov, B.J., Kuvatov, A.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 343, 173 (2013)
Amati, D., Ciafaloni, M., Veneziano, G.: Phys. Lett. B 197, 81 (1987)
Banados, M., Silk, J., West, S.M.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 103, 111102 (2009)
Banks, T., Fischler, W.: (2009). arXiv:hep-th/9906038
Grib, A.A., Pavlov, Yu.V.: Astropart. Phys. 20, 675 (2011a)
Grib, A.A., Pavlov, Yu.V.: Gravit. Cosmol. 17, 42 (2011b)
Hawking, S.W.: In: DeWitt, C., DeWitt, B.S. (eds.) Black Holes. Gordon and Breach, New York (1973)
Hooft, G.: Phys. Lett. B 198, 61 (1987)
Hills, J.G.: Nature 331, 687 (1988)
Jacobson, T., Sotiriou, T.P.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 104, 121101 (2010)
Larry, S., Čadez, A., DeWitt, B., Eppley, K.: Phys. Rev. D. 14, 2443 (1976)
Matthew, W., Choptuik, P., Frans, P.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(104), 111101 (2010)
Muzinich, I.J., Soldate, M.: Phys. Rev. D. 37, 359 (1988)
Patil, M., Joshi, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D 85, 104014 (2012)
Rezzolla, L., Takami, K.: Class. Quantum Gravity 30, 012001 (2013)
Sperhake, U., Cardoso, V., Pretorius, F., Berti, E., González, J.A.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 101(16), 161101 (2008)
Thorne, K.: Nonspherical gravitational collapse: a short review. In: Klauder, J. (ed.) Magic Without Magic: John Archibald Wheeler, p. 231. Freeman, San Francisco (1972)
Tillich, A.: Hyper-velocity Stars—a spectroscopic and kinematic study of blue stars. PhD Thesis, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität, Erlangen-Nürnberg, 149 pp (2010)
Zaslavskii, O.B.: Phys. Rev. D 82, 083004 (2010)
Zaslavskii, O.B.: Class. Quantum Gravity 28, 105010 (2011)
Wei, S.W., Liu, Y.X., Li, H.T., Chen, F.W.: J. High Energy Phys. 1012, 066 (2010a)
Wei, S.W., Liu, Y.X., Guo, H., Fu, C.-E.: Phys. Rev. D 82, 103005 (2010b)
Acknowledgements
This research is supported in part by the projects F2-FA-F113, FE2-FA-F134 of the UzAS and by the ICTP through the OEA-PRJ-29 project. BA and FA acknowledge the financial support from the Volkswagen Stiftung Foundation and thank the Max Planck Institute für GravitationsPhysik, Potsdam for the hospitality.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atamurotov, F., Ahmedov, B. & Shaymatov, S. Formation of black holes through BSW effect and black hole–black hole collisions. Astrophys Space Sci 347, 277–281 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-013-1527-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-013-1527-x