Abstract
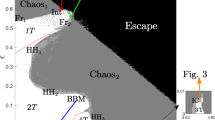
We explore the periodic orbits and the regions of quasi-periodic motion around both the primaries in the Saturn-Titan system in the framework of planar circular restricted three-body problem. The location, nature and size of periodic and quasi-periodic orbits are studied using the numerical technique of Poincare surface of sections. The maximum amplitude of oscillations about the periodic orbits is determined and is used as a parameter to measure the degree of stability in the phase space for such orbits. It is found that the orbits around Saturn remain around it and their stability increases with the increase in the value of Jacobi constant C. The orbits around Titan move towards it with the increase in C. At C=3.1, the pericenter and apocenter are 358.2 and 358.5 km, respectively. No periodic or quasi-periodic orbits could be found by the present method around the collinear Lagrangian point L 1 (0.9569373834…).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Broucke, R.A.: Periodic orbits in the restricted three-body problem with Earth-Moon masses. Technical Report, vol. 32, Jet Propulsion Lab., Pasadena, CA (1968)
Companys, V., et al.: Use of Earth-Moon Libration Points for Future Missions. AAS, vol. 404 (1995)
Contopoulos, G.: Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 435, 551 (1991)
Darwin, G.H.: Periodic Orbits. Scientific Papers, vol. 4. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1911)
Dutt, P., Sharma, R.K.: J. Guid. Control Dyn. 33, 1010 (2010)
Gomez, G., et al.: Study refinement of semi-analytical halo orbit theory. ESOC contract 8625/89, Final Report (1991a)
Gomez, G., et al.: In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics, ESA-SP-326, vol. 35, ESA (1991b)
Hagel, J.: Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 56, 267 (1992)
Hagel, J., Trenkler, T.: Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 56, 81 (1993)
Henon, M.: Annu. Astron. 28, 499 (1965a)
Henon, M.: Annu. Astron. 28, 9927 (1965b)
Henon, M.: Bull. Astron., Ser. 3 1, 57 (1965c)
Henon, M.: Bull. Astron., Ser. 3 2, 49 (1965d)
Huang, S.S.: Astron. J. 67, 304 (1962)
Jefferys, W.H.: Publ. Dep. Astron. Univ. Tex. Austin, Ser. II 3, 6 (1971)
Jefferys, W.H.: Celest. Mech. 30, 85 (1983)
Kolmen, E., et al.: New Trends in Astrodynamics and Applications III, vol. 886, pp. 68. American Inst. of Physics, Melville (2007)
Moulton, F.R.: Periodic Orbits. Carnegie Institute of Washington Publications, p. 161 (1920)
Poincare, H.: Les Methodes Nouvelles de la Mechanique Celeste, vol. 1, pp. 82. Gauthier-Villas, Paris (1892)
Ragos, O., et al.: Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 67, 251 (1997)
Rudolf, D., Sun, Y.S.: Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 67, 87 (1997)
Sharma, R.K., Subba Rao, P.V.: Celest. Mech. 13, 137–149 (1976)
Smith, R.H.: The onset of chaotic motion in the restricted problem of three bodies. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX (1991)
Smith, R.H., Szebehely, V.: Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 56, 409 (1993)
Stoer, J., Bulirsch, R.: Introduction to Numerical Analysis. Springer, Berlin (1983)
Stromgren, E.: O. Connaissance Actualle des Orbites dans le Problem des Trois Corps. Publications and Minor communications of Copenhagen Observatory, Publication 100, Copenhagen University, Astronomical Observatory, Denmark (1935)
Szebehely, V.: Theory of Orbits. Academic Press, San Diego (1967)
Winter, O.C.: Planetary and Space Science 48, 23 (2000)
Winter, O.C., Murray, C.D.: QMW Notes No. 16. Queen Marry and Westfield College, London, UK (1994a)
Winter, O.C., Murray, C.D.: QMW Notes No. 17. Queen Marry and Westfield College, London, UK (1994b)
Winter, O.C., Murray, C.D.: Astron. Astrophys. 319, 290 (1997a)
Winter, O.C., Murray, C.D.: Astron. Astrophys. 328, 304 (1997b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safiya Beevi, A., Sharma, R.K. Analysis of periodic orbits in the Saturn-Titan system using the method of Poincare section surfaces. Astrophys Space Sci 333, 37–48 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-011-0630-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-011-0630-0