Abstract
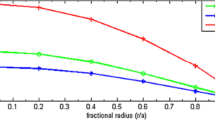
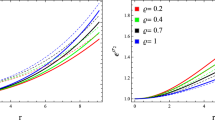
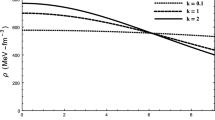
A family of charge analogues of a neutral solution with g 44=(1+Cr 2)6 has been obtained by using a specific electric intensity, which involves a parameter K. Both neutral and charged solutions are analysed physically subject to the surface density 2×1014 gm/cm3 (neutron star). The neutral solution is well behaved for 0.0<Ca 2≤0.10477 while its charge analogues are well behaved for a wide range of a parameter K (0≤K≤72) i.e. pressure, density, pressure-density ratio, velocity of sound is monotonically decreasing and the electric intensity is monotonically increasing in nature for the given range of the parameter K. The maximum mass and radius occupied by the neutral solution are 3.4126M Θ and 18.9227 km for Ca 2=0.10447 respectively. While the red shift at centre Z 0=0.9686 and red shift at the surface Z a =0.4612. For the charged solution, the maximum mass and radius are 5.6111M Θ and 17.2992 km respectively for K=3.0130 and Ca 2=0.2500, with the red shift Z 0=3.0113 and Z a =1.0538.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, R.C., Cohen, J.M.: Astrophys. J. 198, 507 (1975)
Adler, R.J.: J. Math. Phys. 15, 727 (1974)
Bijalwan, N., Gupta, Y.K.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 317, 251–260 (2008)
Bonnor, W.B.: Z. Phys. 160, 59 (1960)
Delgaty, M.S.R., Lake, K.: Comput. Phys. Commun. 115, 395 (1998)
Durgapal, M.C.: J. Phys. A 15, 2637 (1982)
Gupta, Y.K., Gupta, R.S.: Acta Phys. Pol. B 17, 855 (1986)
Gupta, Y.K., Kumar, M.: Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 37(1), 575 (2005a)
Gupta, Y.K., Kumar, M.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 299(1), 43–59 (2005b)
Gupta, Y.K., Maurya, S.K.: A class of charged analogues of Durgapal and Fuloria Superdense star. Astrophys. Space Sci. (2010a). doi:10.1007/s10509-010-4454
Gupta, Y.K., Maurya, S.K.: Astrophys. Space Sci. (2010b). doi:10.1007/s10509-010-0503-y
Gupta et al.: Int. J. Theor. Phys. 49, 854–860 (2010). doi:10.1007/s10773-010-0267-8
Heintzmann, H.: Z. Phys. 228, 489 (1969)
Ivanov, B.V.: Static charged perfect fluid sphere in general relativity. Phys. Rev. D 65, 104001 (2002)
Krasinski, A.: Inhomogeneous Cosmological Models. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1997)
Kuchowicz, B.: Astrophys. Space Sci. 33, L13 (1975)
Lemos, J.P.S., Zanchin, V.T.: arXiv:1004.3574v2 [gr-qc] (2010a)
Lemos, J.P.S., Zanchin, V.T.: Phys. Rev. D 81, 124016 (2010b)
Maharaj, S.D., Hansraj, S.: Charged analogue of Finch-Skea stars. Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 15, 1311–1327 (2006)
Maharaj, S.D., Komathiraj, K.: Classes of exact Einstein-Maxwell solutions. Gen. Relativ. Gravit. 39, 2079–2093 (2007a)
Maharaj, S.D., Komathiraj, K.: Tikekar superdense stars in electric fields. J. Math. Phys. 48, 042501 (2007b)
Maharaj, S.D., Komathiraj, K.: arXiv:0808.1998v1 [gr-qc] (2008)
Maharaj, S.D., Thirukkanesh, S.: Exact models for isotropic matter. Class. Quantum Gravity 23, 2697–2709 (2006a)
Maharaj, S.D., Thirukkanesh, S.: Generating potentials via difference equations. Math. Methods Appl. Sci. 29, 1943–1952 (2006b)
Maharaj, S.D., Thirukkanesh, S.: arXiv:0904.0781v1 [gr-qc] (2009)
Pant, N., et al.: Astrophys. Space Sci. (2010a). doi:10.1007/s10509-010-0453-4
Pant, N., et al.: Astrophys. Space Sci. (2010b). doi:10.1007/s10509-010-0509-5
Sharif, M., Abbas, G.: arXiv:1001.5316v1 [gr-qc] (2010)
Tolman, R.C.: Phys. Rev. 55, 364 (1939)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurya, S.K., Gupta, Y.K. A family of well behaved charge analogues of a well behaved neutral solution in general relativity. Astrophys Space Sci 332, 481–490 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0541-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10509-010-0541-5