Abstract
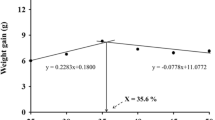
Three feeding trials were conducted to determine the optimal dietary protein levels for largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) of different sizes. Six isolipidic (12%) diets with different protein levels (46%, 48%, 50%, 52%, 54% and 56%) were tested to feed three size groups of fish for 56 days (Trial 1 and Trial 2) or 84 days (Trial 3). The initial body weights were approximately 10 g in Trial 1, 100 g in Trial 2, and 200 g in Trial 3, respectively. The fish in each size class were randomly distributed into 18 cages (1 m × 1 m × 1 m) in six groups (three replicates) and fed by hand to apparent satiation two times per day. At the end of the feeding trials, the fish grew to an average size of 26–36 g, 276–320 g, and 434–526 g, respectively. The weight gain (WG) showed an increasing trend with increasing dietary protein level up to 52%, 50%, and 48%, respectively, and then plateaued in all the three trials, which indicated that the minimum dietary protein requirements for largemouth bass decrease with increasing fish size. The feed efficiency (FE) in the three trials showed a similar trend to growth performance. Protein efficiency ratio (PER) tended to decline when dietary protein levels exceeded 48%, 50%, and 48% in the three trails, respectively. Broken-line regression analysis showed that the optimal dietary protein levels based on SGR for largemouth bass of different sizes (initial size 10, 100, and 200 g) were 51.6%, 50.5%, and 47.8%, respectively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam MS, Watanabe WO, Carroll PM (2008) Dietary protein requirements of juvenile black sea bass, Centropristis striata. J World Aquacult Soc 39:656–663
Anderson RJ, Kienholz EW, Flickinger SA (1981) Protein requirements of smallmouth bass and largemouth bass. J Nutr 111:1085–1097
AOAC (1990) Association of official analytical chemists. In: official methods of analysis, 15th edn Arlington, VA, USA
Árnason J, Björnsdottir R, Arnarsson I, Arnadottir GS, Thorarensen H, Fracalossi DM, Lall SP (2010) Protein requirements of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua L. Aquac Res 41:385–393
Brecka BJ, Wahl DH, Hooe ML (1996) Growth, survival, and body composition of largemouth bass fed various commercial diets and protein concentrations. The Progressive Fish-Culturist 58:104–110
Bright LA, Coyle SD, Tidwell JH (2005) Effect of dietary lipid level and protein energy ratio on growth and body composition of largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides. J World Aquacult Soc 36:129–134
Chen NS, Xiao WW, Liang QL, Zhou HY, Ma XL, Zhao M (2012) Effect of dietary lipid to protein ratios on growth performance, body composition and non-specific immunity of largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides). J Fish China 36:1270–1280 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Huang D, Wu YB, Lin YY, Chen JM, Wang Y (2017) Dietary protein and lipid requirements for juvenile largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoides. J World Aquacult Soc 48:782–790
Lee JK, Cho SH, Park SU, Kim KD, Lee SM (2003) Dietary protein requirement for young turbot (Scophthalmus maximus L.). Aquac Nutr 9:283–286
Lee SM, Park CS, Bang IC (2002) Dietary protein requirement of young Japanese flounder Paralichthys olivaceus. Fish Sci 68:158–164
Luo Z, Liu YJ, Mai KS, Tian LX, Tan XY (2004) Optimal dietary protein requirement of grouper Epinephelus coioides fed isoenergetic diets in floating net cages. Aquac Nutr 10:247–252
NRC (2011) Nutrient requirements of fish and shrimp. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Portz L, Cyrino JEP, Martino RC (2001) Growth and body composition of juvenile largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides in response to dietary protein and energy levels. Aquac Nutr 7:247–254
Shearer KD (1994) Factors affecting the proximate composition of cultured fishes with emphasis on salmonids. Aquaculture 119:63–88
Tidwell JH, Webster CD, Coyle SD (1996) Effects of dietary protein level on second year growth and water quality for largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) raised in ponds. Aquaculture 145:213–223
Tidwell JH, Coyle SD, Bright LA (2019) Largemouth bass aquaculture. In: Largemouth bass production in China, 5M published ltd. Sheffield, UK, pp 37–47
Ye CX, Wu YL, Sun ZZ, Wang AL (2016) Dietary protein requirement of juvenile obscure puffer, Takifugu obscurus. Aquac Res 48:2064–2073
Zhang JZ, Zhou F, Wang LL, Shao QJ, Xu ZR, Xu JZ (2010) Dietary protein requirement of juvenile black sea bream, Sparus macrocephalus. J World Aquacult Soc 41:151–164
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by R&D Projects in important areas of Guangdong Province, Studies and applications about key technology biosynithesis in antibiotic-free feeds (2019B020218003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
“All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.”
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, ZN., Qian, XQ. & Xie, SQ. Optimal dietary protein concentrations for largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides) of different sizes (10–500 g). Aquacult Int 28, 831–840 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00498-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00498-9