Abstract
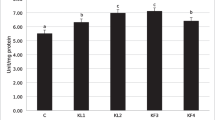
The current investigation was carried out to assess the efficacy of dietary garlic (GP) and/or chitosan (CH) powders to protect European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, against the adverse effects of zearalenone (ZEN) toxicity. Hence, ZEN (0.725 g/kg diet) was incorporated in a fish diet alone or with 30 g GP and/or 10 g CH/kg diet and the treatments were assigned as a control diet (T1), a control diet + ZEN (T2), a control diet + ZEN + GP (T3), a control diet + ZEN + CH (T4), and a control diet + ZEN + GP + CH (T5). Fish (30.7 ± 0.6 g) fed one of the tested diets up to apparent satiation thrice a day for 4 weeks. After the feeding trial, fish were intraperitoneally injected with pathogenic bacteria Vibrio alginolyticus for 14 days during which fish mortality was observed. The dietary ZEN inhibited fish growth and feed utilization; meanwhile, co-supplementation of GP and/or CH restored the reduced fish performance as a result of reducing the ZEN toxicity. The ZEN toxicity induced macrocytic hypochromic anemia in European sea bass; however, significant reductions were observed in values of red blood cells (RBCs), hemoglobin (Hb), hematocrit (Ht), and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) together with significant elevations in mean corpuscular volume (MCV) and mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) values in comparison with the control fish. Likewise, lymphopenia, monocytosis, leucopenia, eosinophilia, neutrophilia, and thrombocytopenia were the characteristic features of ZEN-toxicated fish with drastic reduction in white blood cells (WBCs) counts. Significant reductions in total protein, albumin, globulin, and lysozyme were also observed in fish serum due to ZEN toxicity. The co-supplementation of GP and/or CH to ZEN-fed fish elevated significantly values of RBCs, Hb, MCHC, and WBCs count with decreasing and increasing of its constituents. Significant rises in total protein, albumin, globulin, and lysozyme were observed with co-supplementation of GP and/or CH to ZEN-toxicated fish to be near these fed on the control diet. The ZEN toxicity also suppressed the fish immunity and subsequently elevated fish susceptibility to V. alginolyticus infection causing highest fish mortality as compared with other treatments. The co-supplementation of GP or CH to fish significantly enhanced their immunity causing a high relative percent of survival (RSP) of fish after bacterial infection (18.8 or 43.8%, respectively); meanwhile, fish fed both of GP and CH showed better RSP (68.8%). On the other hand, the co-supplementation of GP or CH reduced the ZEN residue (1.18 and 0.87 μg/kg dry weight) in fish muscles. These results show that CH was more effective than GP in enhancing fish immunity and protection against ZEN toxicity, whereas the co-supplementation of both GP and CH was most effective in protecting fish against ZEN toxicity resulting in lowest ZEN residue (0.53 μg/kg dry weight) in fish muscles.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbès S, Ouanes Z, Salah-Abbès JB, Houas Z, Oueslati R, Bacha H, Othman O (2006) The protective effect of hydrated sodium calcium aluminosilicate against haematological, biochemical and pathological changes induced by zearalenone in mice. Toxicon 47:567–574
Abbès S, Salah-Abbès JB, Sharafi H, Noghabi KA, Oueslati R (2012) Interaction of Lactobacillus plantarum MON03 with Tunisian Montmorillonite clay and ability of the composite to immobilize zearalenone in vitro and counteract immunotoxicity in vivo. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 34:944–950
Abdel-Ghany HM, Salem ME-S (2020) Effects of dietary chitosan supplementation on farmed fish: a review. Rev Aquac. https://doi.org/10.1111/raq.12326
Abdel-Tawwab M (2015) The use of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolium) in practical diets for Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus): resistance to waterborne copper toxicity. Aquac Res 46:1001–1006. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.12237
Abdel-Tawwab M (2016a) Feed supplementation to freshwater fish: experimental approaches. Lambert Academic Publishing, Berlin
Abdel-Tawwab M (2016b) Effect of feed availability on susceptibility of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) to environmental zinc toxicity: growth performance, biochemical response, and zinc bioaccumulation. Aquaculture 464:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2016.07.009
Abdel-Tawwab M, Wafeek M (2010) Response of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fed dietary organic selenium to environmental cadmium toxicity. J World Aquac Soc 41:106–114
Abdel-Tawwab M, Mousa MAA, Abbass FE (2007) Growth performance and physiological response of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus (B.) fed organic selenium prior to the exposure to environmental copper toxicity. Aquaculture 272:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2007.09.004
Abdel-Tawwab M, Mousa MAA, Mohammed MA (2010) Use of live baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, in practical diet to enhance the growth performance of Galilee tilapia, Sarotherodon galilaeus (L.), and its resistance to environmental copper toxicity. J World Aquac Soc 41:214–223. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-7345.2010.00361.x
Abdel-Tawwab M, Sharafeldin KM, Mosaad MNM, Ismaiel NEM (2015) Coffee bean in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. diets: effect on growth performance, biochemical status, and resistance to waterborne zinc toxicity. Aquaculture 448:207–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2015.06.010
Abdel-Tawwab M, Sharafeldin KM, Ismaiel NEM (2018) Interactive effects of coffee bean supplementation and waterborne zinc toxicity on growth performance, biochemical variables, antioxidant activity and zinc bioaccumulation in whole body of common carp, Cyprinus carpio L. Aquac Nutr 24:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12540
Abou Khalil NS, Abd-Elkareem M, Sayed AH (2017) Nigella sativa seed protects against 4-nonylphenol-induced haematotoxicity in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822): oxidant/antioxidant rebalance. Aquac Nutr 23:1467–1474. https://doi.org/10.1111/anu.12522
Akhter N, Wu B, Memon AM, Mohsin M (2015) Probiotics and prebiotics associated with aquaculture: a review. Fish Shellfish Immunol 45:733–741
Alexander JB, Ingram GA (1992) Noncellular nonspecific defence mechanisms of fish. Annu Rev Fish Dis 2:249–279
Alpsoy L, Yalvac ME (2011) Key roles of vitamins A, C, and E in aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress. In: Vitamins & Hormones. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 287–305
Amend DF (1981) Potency Testing of Fish Vaccines. Fish Biologics: Serodiagnostics and Vaccines 49:447–454
Anater A, Manyes L, Meca G et al (2016) Mycotoxins and their consequences in aquaculture: a review. Aquaculture 451:1–10
Ashour TH (2014) Effect of thymoquinone supplement on erythrocyte indices and osmotic resistance in rat model of acute hemorrhagic anemia. Kasr El-Aini Med J 20:19–23
Ashour TH et al (2015) Thymoquinone therapy improves hyperglycemia, erythrocyte indices, erythropoietin production and erythrocyte osmotic resistance in rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Br J Med Med Res 5:350–361
Assayed ME (2010) Radioprotective effects of black seed (Nigella sativa) oil against hemopoietic damage and immunosuppression in gamma-irradiated rats. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol 32:284–296
Boyd CE, Tucker CS (2012) Pond aquaculture water quality management. Springer Science & Business Media, Berlin
Breyer KE, Getchell RG, Cornwell ER et al (2015) Efficacy of an extract from garlic, Allium sativum, against infection with the furunculosis bacterium, Aeromonas salmonicida, in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. J World Aquacult Soc 46:273–282. https://doi.org/10.1111/jwas.12195
Brown BA (1988) Routine hematology procedures. In: Hematology: principles and procedures (ed) Leo and Fabiger, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA. p 7–122
Burgos-Aceves MA, Lionetti L, Faggio C (2019) Multidisciplinary haematology as prognostic device in environmental and xenobiotic stress-induced response in fish. Sci Total Environ 670:1170–1183 doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.03.275
Cha S-H, Lee J-S, Song C-B, Lee K-J, Jeon Y-J (2008) Effects of chitosan-coated diet on improving water quality and innate immunity in the olive flounder, Paralichthys olivaceus. Aquaculture 278:110–118
Chakraborty SB, Hancz C (2011) Application of phytochemicals as immunostimulant, antipathogenic and antistress agents in finfish culture. Rev Aquac 3:103–119
Chen Y, Li M, Yuan L et al (2017) Growth, blood health, antioxidant status and immune response in juvenile yellow catfish Pelteobagrus fulvidraco exposed to α-ethinylestradiol (EE2). Fish Shellfish Immunol 69:1–5
Chistiakov DA, Hellemans B, Volckaert FAM (2007) Review on the immunology of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 117:1–16
Čonková E, Laciaková A, Pástorová B, Seidel H, Kováč G (2001) The effect of zearalenone on some enzymatic parameters in rabbits. Toxicol Lett 121:145–149
Dawood MAO, Koshio S, Esteban MÁ (2018) Beneficial roles of feed additives as immunostimulants in aquaculture: a review. Rev Aquac 10:950–974
Di Marco P, Priori A, Finoia MG, Massari A, Mandich A, Marino G (2008) Physiological responses of European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax to different stocking densities and acute stress challenge. Aquaculture 275:319–328
Döll S, Baardsen G, Muller P, Koppe W, Stubhaug I, Danicke S (2010) Effects of increasing concentrations of the mycotoxins deoxynivalenol, zearalenone or ochratoxin A in diets for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) on growth performance and health. In: 14th International Symposium on Fish Nutrition and Feeding, Qingdao, China
Dügenci SK, Arda N, Candan A (2003) Some medicinal plants as immunostimulant for fish. J Ethnopharmacol 88:99–106
Dytham C (2011) Choosing and using statistics: a biologist’s guide. Blackwell Science Ltd., London
El-Sayed HS, Barakat KM (2016) Effect of dietary chitosan on challenged Dicentrarchus labrax post larvae with Aeromonas hydrophila. Russ J Mar Biol 42:501–508
Engstad RE, Robertson B, Frivold E (1992) Yeast glucan induces increase in activity of lysozyme and complement mediated haemolytic activity in Atlantic salmon blood. Fish Shellfish Immunol 2:287–297
European Commission (2006) The presence of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, ochratoxin A, T-2 and HT-2 and fumonisins in products intended for animal feeding. Off. J. Eur. Un. 2006:L229/7–L229/9
European Food Safety Authority (2004) Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Contaminants in Food Chain on a request from the Commission related to zearalenone as undesirable substance in animal feed. EFSA J 89:1–35
Faggio C, Fedele G, Arfuso F et al (2014) Haematological and biochemical response of Mugil cephalus after acclimation to captivity. Cah Biol Mar 55:31–36
Fazio F, Marafioti S, Torre A et al (2013) Haematological and serum protein profiles of Mugil cephalus: effect of two different habitats. Ichthyol Res 60:36–42
Foysal J, Alam M, Momtaz F, Chaklader R, Siddik MAB, Cole A, Fotedar R, Rahman M (2019) Dietary supplementation of garlic (Allium sativum) modulates gut microbiota and health status of tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) against Streptococcus iniae infection. Aquac Res 50:2107–2116. https://doi.org/10.1111/are.14088
Galina J, Yin G, Ardo L, Jeney Z (2009) The use of immunostimulating herbs in fish. An overview of research. Fish Physiol Biochem 35:669–676
Ghehdarijani MS, Hajimoradloo A, Ghorbani R, Roohi Z (2016) The effects of garlic-supplemented diets on skin mucosal immune responses, stress resistance and growth performance of the Caspian roach (Rutilus rutilus) fry. Fish Shellfish Immunol 49:79–83
Gonçalves RA, Schatzmayr D, Hofstetter U, Santos GA (2017) Occurrence of mycotoxins in aquaculture: preliminary overview of Asian and European plant ingredients and finished feeds. World Mycotoxin J 10:183–194
Gonçalves RA, Naehrer K, Santos GA (2018) Occurrence of mycotoxins in commercial aquafeeds in Asia and Europe: a real risk to aquaculture? Rev Aquac 10:263–280
Gopalakannan A, Arul V (2006) Immunomodulatory effects of dietary intake of chitin, chitosan and levamisole on the immune system of Cyprinus carpio and control of Aeromonas hydrophila infection in ponds. Aquaculture 255:179–187
Grinde B (1989) Lysozyme from rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, as an antibacterial agent against fish pathogens. J Fish Dis 12:95–104
Guo JJ, Kuo CM, Chuang YC et al (2012) The effects of garlic-supplemented diets on antibacterial activity against Streptococcus iniae and on growth in orange-spotted grouper, Epinephelus coioides. Aquaculture 364:33–38
Hamed HS, Abdel-Tawwab M (2017) Ameliorative effect of propolis supplementation on alleviating bisphenol-A toxicity: growth performance, biochemical variables, and oxidative stress biomarkers of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) fingerlings. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 202:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2017.08.001
Hansen JA, Welsh PG, Lipton J, Suedkamp MJ (2002) The effects of long-term cadmium exposure on the growth and survival of juvenile bull trout (Salvelinus confluentus). Aquat Toxicol 58:165–174
Harikrishnan R, Balasundaram C, Heo M-S (2011) Impact of plant products on innate and adaptive immune system of cultured finfish and shellfish. Aquaculture 317:1–15
Harikrishnan R, Kim J-S, Balasundaram C, Heo M-S (2012) Immunomodulatory effects of chitin and chitosan enriched diets in Epinephelus bruneus against Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Aquaculture 326:46–52
Harris JC, Cottrell S, Plummer S, Lloyd D (2001) Antimicrobial properties of Allium sativum (garlic). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 57:282–286
Henry RJ (1964) Colorimetric determination of total protein. Clin Chem Harper Row Publ, New York 181
Hooft JM, Bureau DP (2017) Evaluation of the efficacy of a commercial feed additive against the adverse effects of feed-borne deoxynivalenol (DON) on the performance of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 473:237–245
Hu SX (2001) Vitamin C helps to overcome aflatoxin poisoning. Foreign Livest (Pigs Birds) 4:14–17
Hussein HS, Brasel JM (2001) Toxicity, metabolism, and impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Toxicology 167:101–134
Irkin LC, Yigit M, Yilmaz S, Maita M (2014) Toxicological evaluation of dietary garlic (Allium sativum) powder in European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax juveniles. Food Nutr Sci 5:989
Jiang SZ, Yang ZB, Yang WR et al (2011) Effects of purified zearalenone on growth performance, organ size, serum metabolites, and oxidative stress in postweaning gilts. J Anim Sci 89:3008–3015
Jiang SZ, Yang ZB, Yang WR et al (2012) Effect on hepatonephric organs, serum metabolites and oxidative stress in post-weaning piglets fed purified zearalenone-contaminated diets with or without Calibrin-Z. J Anim Physiol Anim Nutr (Berl) 96:1147–1156
Kalyankar AD, Gupta RK, Bansal N et al (2013) Effect of garlic (Allium sativum) against Aeromonas hydrophila and health management of swordtail, Xiphophorus helleri. J Environ Sci Sustain 1:41–48
Kamali Najafabad M, Imanpoor MR, Taghizadeh V, Alishahi A (2016) Effect of dietary chitosan on growth performance, hematological parameters, intestinal histology and stress resistance of Caspian kutum (Rutilus frisii kutum Kamenskii, 1901) fingerlings. Fish Physiol Biochem 42:1063–1071
Kholife MM, Moawad AA, Diab AM, Abeer EMS (2019) Mycological examination of fish feed stuff with special reference to mycotoxin production. Slov Vet Res 56(Suppl 22):303–312
Kotb AM, Abd-Elkareem M, Abou Khalil NS, Sayed AH (2018) Protective effect of Nigella sativa on 4-nonylphenol-induced nephrotoxicity in Clarias gariepinus (Burchell, 1822). Sci Total Environ 619–620:692–699
Lee J-Y, Gao Y (2012) Review of the application of garlic, Allium sativum, in aquaculture. J World Aquac Soc 43:447–458
Lewis SM (2006) Reference ranges and normal values. Dacie Lewis Pract Haematol 10:11–24
Maaroufi K, Chekir L, Creppy EE, Ellouz F, Bacha H (1996) Zearalenone induces modifications of haematological and biochemical parameters in rats. Toxicon 34:535–540
Maron DF, Smith TJS, Nachman KE (2013) Restrictions on antimicrobial use in food animal production: an international regulatory and economic survey. Glob Health 9:48
Másson M, Holappa J, Hjálmarsdóttir M, Rúnarsson ÖV, Nevalainen T, Järvinen T (2008) Antimicrobial activity of piperazine derivatives of chitosan. Carbohydr Polym 74:566–571
Matejova I, Svobodova Z, Vakula J, Mares J, Modra H (2017) Impact of mycotoxins on aquaculture fish species: a review. J world Aquac Soc 48:186–200
Nair SC, Salomi MJ, Panikkae B, Panikkar KR (1991) Modulatory effects of Crocus sativus and Nigella sativa extracts on cisplatin-induced toxicity in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 31:75–83
Ndong D, Fall J (2011) The effect of garlic (Allium sativum) on growth and immune responses of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus x Oreochromis aureus). J Clin Immunol Immunopathol Res 3:1–9
Nya EJ, Austin B (2009) Use of garlic, Allium sativum, to control Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 32:963–970
Nya EJ, Dawood Z, Austin B (2010) The garlic component, allicin, prevents disease caused by Aeromonas hydrophila in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum). J Fish Dis 33:293–300
Pridgeon JW, Klesius PH (2012) Major bacterial diseases in aquaculture and their vaccine development. Anim Sci Rev 7:1–16
Ragland SA, Criss AK (2017) From bacterial killing to immune modulation: recent insights into the functions of lysozyme. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006512
Sahu S, Das BK, Mishra BK et al (2007) Effect of Allium sativum on the immunity and survival of Labeo rohita infected with Aeromonas hydrophila. J Appl Ichthyol 23:80–86
Salah-Abbès JB, Abbès S, Ouanes Z et al (2008) Tunisian radish extract (Raphanus sativus) enhances the antioxidant status and protects against oxidative stress induced by zearalenone in balb/c mice. J Appl Toxicol 28:6–14
Salah-Abbès JB, Abbès S, Ouanes Z et al (2009) Isothiocyanate from the Tunisian radish (Raphanus sativus) prevents genotoxicity of zearalenone in vivo and in vitro. Mutat Res 677:59–65
Saleh NE, Michael FR, Toutou MM (2015) Evaluation of garlic and onion powder as phyto-additives in the diet of sea bass (Dicentrarcus labrax). Egypt J Aquat Res 41:211–217
Saurabh S, Sahoo PK (2008) Lysozyme: an important defence molecule of fish innate immune system. Aquac Res 39:223–239
Schäperclaus W (1992) Fish diseases. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Sehonova P, Svobodova Z, Dolezelova P et al (2018) Effects of waterborne antidepressants on non-target animals living in the aquatic environment: a review. Sci Total Environ 631:789–794
Shoemaker CA, Evans JJ, Klesius PH (2000) Density and dose: factors affecting mortality of Streptococcus iniae infected tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 188:229–235
Shoemaker C, Xu D-H, LaFrentz B, LaPatra S (2015) Overview of fish immune system and infectious diseases. Diet Nutr Addit fish Heal Wiley, Canada, pp 1–24
Su Y, Sun Y, Ju D et al (2018) The detoxification effect of vitamin C on zearalenone toxicity in piglets. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:284–292
Talpur AD, Ikhwanuddin M (2012) Dietary effects of garlic (Allium sativum) on haemato-immunological parameters, survival, growth, and disease resistance against Vibrio harveyi infection in Asian sea bass, Lates calcarifer (Bloch). Aquaculture 364:6–12
Tort L (2011) Stress and immune modulation in fish. Dev Comp Immunol 35:1366–1375
Van Kampen EJ, Zijlstra WG (1961) Standardization of hemoglobinometry II. The hemiglobincyanide method. Clin Chim Acta 6:538–544
Vaseeharan B, Thaya R (2014) Medicinal plant derivatives as immunostimulants: an alternative to chemotherapeutics and antibiotics in aquaculture. Aquac Int 22:1079–1091
Warth B, Parich A, Atehnkeng J, Bandyopadhyay R, Schuhmacher R, Sulyok M, Krska R (2012) Quantitation of mycotoxins in food and feed from Burkina Faso and Mozambique using a modern LC-MS/MS multitoxin method. J Agric Food Chem 60:9352–9363
Wei W, Jiao-Jie M, Chuan-Chuan Y, Xiao-Hui L, Hong-Ru J, Bing S, Feng-Qin L (2012) Simultaneous determination of masked deoxynivalenol and some important type B trichothecenes in Chinese corn kernels and corn-based products by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Agric Food Chem 60:11638–11646
Wootton IDP (1974) Micro-analysis in medical biochemistry. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Woźny M, Dobosz S, Obremski K, Hliwa P, Gomułka P, Łakomiak A, Brzuzan P (2015) Feed-borne exposure to zearalenone leads to advanced ovarian development and limited histopathological changes in the liver of premarket size rainbow trout. Aquaculture 448:71–81
Woźny M, Obremski K, Hliwa P, Gomułka P, Różyński Rafałand Wojtacha PFM, Segner H, Brzuzan P (2019) Feed contamination with zearalenone promotes growth but affects the immune system of rainbow trout. Fish Shellfish Immunol 84:680–694
Zaki MA, Salem ME-S, Gaber MM, Nour AM (2015) Effect of chitosan supplemented diet on survival, growth, feed utilization, body composition & histology of sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). World J Eng Technol 3:38
Zinedine A, Soriano JM, Molto JC, Manes J (2007) Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: an oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem Toxicol 45:1–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of fish were followed by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel-Tawwab, M., Khalifa, E., Diab, A.M. et al. Dietary garlic and chitosan alleviated zearalenone toxic effects on performance, immunity, and challenge of European sea bass, Dicentrarchus labrax, to Vibrio alginolyticus infection. Aquacult Int 28, 493–510 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00477-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-019-00477-0