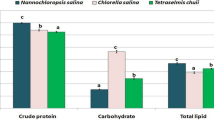
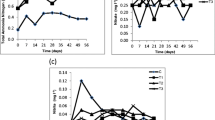
Abstract
The present work deals with the growth efficiency of Picochlorum maculatum and Oithona rigida in shrimp-cultured wastewater. In addition, the effects of wastewater (WW)-cultured P. maculatum and O. rigida on the growth and survival of Litopenaeus vannamei post-larvae (PLs) was studied and the results were compared with artificial culture media (ACM)-cultured P. maculatum and natural seawater (NSW)-cultured O. rigida. The results revealed that the high density obtained in microalgae and low in copepod using wastewater as a medium. Further, shrimp PLs fed with WW-cultured microalgae, and NSW-cultured copepod had specific growth rate and higher survival, but it was not significantly different (p > 0.05) from PL fed on ACM-cultured microalgae and WW-cultured copepod, indicate that P. maculatum has potential to be used as live feed for the hatchery rearing of L. vannamei PLs, in replacing microdiet. Further study is needed on optimization of wastewater-cultured copepod as a live feed to yield maximum growth and survival.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananth S, Santhanam P (2011) Laboratory culture and biochemical profile of marine copepod, Macrosetella gracilis (Dana). Aquaculture 12:49–55
Ananthi P (2012) Laboratary culture and application of marine copepod Oithona rigida for larval rearing of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) with special reference to astaxanthin development, M.Phil. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Ananthi P, Santhanam P, Nandakumar R, Ananth S, Jothiraj K, Dinesh Kumar S, Balaji Prasath B, Jayalakshmi T (2011) Production and utilization of marine copepods as live feed for larval rearing of tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon with special emphasis on astaxanthin enhancement. Indian J Nat Sci 2:494–503
Anderson RA (2005) Algal culturing techniques. Elsevier Academic Press, Burlington, Massachusetts
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis, 16th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington, DC
Becker EW (2007) Microalgae as a source of protein. Biotechnol Adv 25:207–210
Bligh EG, Dyer WJ (1959) A rapid method for total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol 37:911–917
Brooks RR, Presley BJ, Kaplan IR (1967) APDC-MIBK extraction system for the determination of trace metals in saline waters by atomic adsorption spectroscopy. Talanta 14:809–816
Brown MR (1991) The amino acid and sugar composition of 16 species of microalgae used in mariculture. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 145:79–99
Brown MR, Jeffrey SW, Volkman JK, Dunstan GA (1997) Nutritional properties of microalgae for mariculture. Aquaculture 151:315–331
Carbajal Miranda MJ, Sanchez Saavedray MDP, Simental Trinidad JA (2005) Effect of monospecific and mixed benthic diatom cultures on the growth of red abalone postlarvae Haliotis rufescens (Swainson 1822). J Shellfish Res 24:401–405
Dabrowski K (1984) The feeding of fish larvae: present ‘state of the art’ and perspective’s. Reprod Nutr Dev 24:807–823
Dave G (1989) Experiences with wastewater-cultured Daphnia in the start-feeding of rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri). Aquaculture 79:337–343
Derrien A, Coiffard LJ, Coiffard C, De Roeck-Holtzhauer Y (1998) Free amino acid analysis of five microalgae. J Appl Phycol 10:131–134
Dinesh Kumar S, Santhanam P, Lewis-Oscar F, Thajuddin N (2014) A dual role of marine microalga Chlorella sp. (PSDK01) in aquaculture effluent with emphasis on initial population density. Arab J Sci Eng 40:29–35
Dinesh Kumar S, Santhanam P, Jayalakshmi T, Nandakumar R, Ananth S, Shenbaga Devi A, Balaji Prasath B (2015) Ex-situ studies on excessive nutrients and heavy metals removal efficacy of marine microalga Chlorella marina (Butcher) for wastewater treatment. Indian J Mar Sci 44:43–50
Dubois M, Gills KA, Hamilton JK, Robert PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Evjemo OJ, Reitan IK, Olsen Y (2003) Copepods as live food organisms in the larval rearing of halibut larvae (Hippoglossus hippoglossus L.) with special emphasis on the nutritional value. Aquaculture 227:191–210
FAO (2007) Improving Penaeus monodon hatchery practices: manual based on experience in India. No. 446. Food & Agriculture Organisation
Fluchter J, Rembold H (1986) Soluble factor essential for metamorphosis of coregonid larvae has been partially purified from Artemia salina. Arch Hydrobiol 22:197–202
Folch JM, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1956) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
González-Davis O, Ponce-Rivas E, Sánchez-Saavedra M, Muñoz-Márquez ME, Gerwick WH (2012) Bioprospection of microalgae and cyanobacteria as biocontrol agents against Vibrio campbellii and their use in white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei culture. J World Aquac Soc 43:387–399
Guillard RRL (1975) Culture of phytoplankton for feeding marine invertebrates. In: Smith WL, Chanley MH (eds) Culture of marine invertebrate animals. Plenum Press, New York, pp 29–60
Ip PF, Wong KH, Chen F (2004) Enhanced production of astaxanthin by the green microalga Chlorella zofingiensis in mixotrophic culture. Process Biochem 39:1761–1766
Jothiraj K (2012) Studies on biology, culture and efficacy of marine copepod Nannocalanus minor for fish larviculture. Ph.D. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Kathiresan M (2013) Composition and community structure of plankton from Muthupet coastal waters and application of marine copepod Oithona rigida for larval rearing of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Ph.D. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Khatoon H, Banerjee S, Yusoff FM, Shariff M (2009) Evaluation of indigenous marine periphytic Amphora, Navicula and Cymbella grown on substrate as feed supplement in Penaeus monodon postlarval hatchery system. Aquac Nutr 15:186–193
Khatoon H, Banerjee S, Yusoff FM, Shariff M (2013) Use of microalgal-enriched Diaphanosoma celebensis Stingelin, 1900 for rearing Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) postlarvae. Aquac Nutr 19:163–171
Kibria G, Nugegoda D, Fairclough R, Lam P, Bradley A (1999) Utilization of wastewater-grown zooplankton: nutritional quality of zooplankton and performance of silver perch Bidyanus bidyanus (Mitchell 1838) (Teraponidae) fed on wastewater-grown zooplankton. Aquac Nutr 5:221–227
Kiron V, Phromkunthong W, Huntley M, Archibald JA, Scheemaker G (2012) Marine microalgae from refinery as a potential feed protein source for Atlantic salmon, common carp and white leg shrimp. Aquac Nutr 18:521–531
Kovalenko EE, D’Abramo LR, Ohs CL, Buddington RK (2002) A successful microbound diet for the larval culture of freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquaculture 210:385–395
Kwak TJ, Zedler JB (1997) Food web analysis of southern California coastal wetlands using multiple stable isotopes. Oecologia 110:262–277
Laurence GC (1977) A bioenergetic model for the analysis of feeding and survival potential of winter flounder, Pseudopleuronectes americanus, larvae during the period from hatching to metamorphosis. Fish B-NOAA 75:529–546
Luis E, Conceicao C, Yuera M, Makridis P, Morais S, Dinis TM (2010) Live feeds for early stages of fish rearing. Aquac Res 41:613–640
Martin-Jezequel V, Poulet SA, Harris RP, Moal J, Samain JF (1988) Inter specific and intra specific composition and variation of free amino acids in marine phytoplankton. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 44:303–313
Moura Junior AM, Bezerra Neto E, Koening ML, Leça EE (2007) Chemical composition of three microalgae species for possible use in mariculture. Braz Arch Biol Technol 50:461–467
Munilla-Moran R, Stark JR, Barbout A (1990) The role of exogenous enzymes in digestion in cultured turbot larvae (Scoph- thalamus maximus L.). Aquaculture 88:337–350
Nageswara Rao I, Krupanidhi G (2001) Biochemical composition of zooplankton from the Andaman Sea. J Mar Biol Assoc India 43:49–56
Nandakumar R (2012) Laboratory culture of Macrosetella gracilis (Dana) and comparison of astaxanthin enrichment proficiency of different live feeds (copepods and Artemia nauplii) in pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) post larvae, M.Phil. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Nandakumar R (2015) Eco- biology, culture and live feed suitability of zooplankton for nursery rearing of ornamental fish Monodactylus argentus with special emphasis on marine copepod Nitocra affinis. Ph.D. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Nanton DA, Castell JD (1998) The effects of dietary fatty acids on the fatty acid composition of the harpacticoid copepod, Tisbe sp., for use as a live food for marine fish larvae. Aquaculture 163:251–261
Palmegiano GB, Agradi E, Forneris G, Gai F, Gasco L, Rigamonti E, Sicuro B, Zoccarato I (2005) Spirulina as a nutrient source in diets for growing sturgeon (Acipenser baeri). Aquac Res 36:188–195
Payne MF, Rippingale RJ (2000) Rearing west Australian seahorse, Hippocampus subelongatus, juveniles on copepod nauplii and enriched Artemia. Aquaculture 188:353–361
Payne MF, Rippingale RJ, Cleary JJ (2001) Cultured copepods as food for West Australian dhufish (Glaucosoma hebraicum) and pink snapper (Pagrus auratus) larvae. Aquaculture 194:137–150
Pillay TVR (1990) Aquaculture: principles and practices. Fishing New Books, England
Rajendran M (1973) A guide to the study of freshwater calanoids. J Madurai Uni India 1:1–86
Rajkumar M, Kumaraguru Vasagam KP (2006) Suitability of the copepod, Acartia clausi as a live feed for Seabass larvae (Lates calcarifer Bloch): compared to traditional live-food organisms with special emphasis on the nutritional value. Aquaculture 261:649–658
Rajthilak C, Santhanam P, Sivakumar J, Prem Kumar C, Perumal P (2013) Intensive culture of marine harpacticoid copepod Nitokra affinis (Gurney 1927) in aquaculture wastewater under laboratory condition-A new emphasis. Int J Res Sci Eng Technol 2:6158–6163
Raju P (2012) Comparative studies on growth, survival and fatty acid enrichment on Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone 1931) using enriched and un-enriched Artemia nauplii and marine copepod Oithona rigida. M.Phil. thesis, Bharathidasan University
Raymont JEG, Austin A, Ligfold E (1964) Biochemical studies on marine zooplankton. The biochemical composition of Neomysis integer. ICES J Mar Sci 28:354–363
Ricker WE (1979) Growth rates and models. In: Hoar WS, Randall DJ, Brett JR (eds) Fish physiology. Bio-energetics and Growth, vol VIII. Academic Press, New York, pp 677–743
Robert AA (2005) Algal culturing techniques: traditional microalgae isolation techniques. Elsevier, USA
Rohani-Ghadikolaei K, Abdolalian E, Hojatollah F, Masoud G, Ng WK (2013) The nutritional effect of Isochrysis galbana and Chaetoceros muelleri cultured with different seaweed extracts on the larval development, growth and survival of the marine shrimp, Penaeus indicus. Aquac Res 44:1444–1454
Sánchez-Saavedra MP, Voltolina D (2005) The growth rate, biomass production and composition of Chaetoceros sp. grown with different light sources. Aquac Eng 35:161–165
Sangha RS, Cruz AC, Chavez-Sanchez MC, Jones DA (2000) Survival and growth of Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) larvae fed a single dose of live algae and artificial diets with supplements. Aquac Res 31:683–689
Santhanam P (2002) Studies on the ecology, experimental biology and live-food suitability of copepod, Oithona rigida Giesbrecht from Parangipettai coastal environments (India) Ph.D. thesis, Annamalai University
Santhanam P, Perumal P (2012) Feeding, survival, egg production and hatching rate of the marine copepod Oithona rigida Giesbrecht (Copepoda: Cyclopoida) under experimental conditions. J Mar Biol Assoc India 54:38–44
Santhanam P, Perumal P (2013) Developmental biology of brackishwater copepod Oithona rigida Giesbrecht: a laboratory investigation. Indian J Mar Sci 42:236–243
Santhanam P, Perumal P, Rajkumar M (2004) Effect of feeding Artemia on growth and survival of P. monodon larvae. J Appl Fisher Aquacult 4:42–46
Sargent JR, Mc-Evoy LA, Bell JG (1997) Requirements presentation and sources of polyunsaturated fatty acids in marine fish larval feeds. Aquaculture 155:117–127
Stottrup JG (2000) The elusive copepods: their production and suitability in marine aquaculture. Aquac Res 31:703–711
Strickland SC, Parsons TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analyses. Bulletin of Fisheries Research Board of Canada, Ottawa
Sumitha AT (2006) Studies on biology, population growth and biochemical composition of freshwater cladoceran, Moina micrura (Crustacea: Cladocera: Moinidae), Ph.D. thesis, Madras University
Vengadeshperumal N, Damotharan P, Rajkumar M, Perumal P, Vijalakshimi S, Balasubramanian T (2010) Laboratory culture and biochemical characterization of the calanoid copepod, Acartia southwelli Sewell, 1914 and Acartia centrura Giesbretch, 1889. Adv Biol Res 4:97–107
Walne PR (1970) Studies on the food value of nineteen genera of algae to juvenile bivalves of the genera Ostrea, Crassostrea, Mercenaria, and Mytilis. Fish Invest 26:1–62
Wilson RP (2002) Amino acids and proteins. In: Halver JE, Hardy RW (eds) Fish nutrition. Academic Press, California
Yamamoto T, Marcouli PA, Unuma T, Akiama T (1994) Utilization of malt protein flour in fingerling rainbow trout diets. J Fish Sci 60:455–460
Yurkowski M, Tabachek JL (1979) Proximate and amino acid composition of some natural fish foods. In: Halver JE, Tiews K (eds) Proceedings of the world symposium on finfish nutrition and fish feed technology, vol 2, Hamburg 20 ± 23 June 1978. Heenemann, Hamburg, pp 435–448
Zelaya O, Davis DA, Rouse DB (2007) The influence of Artemia and algal supplements during the nursery phase of rearing Pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J World Aquac Soc 38:486–496
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to the Head, Department of Marine Science and authorities of Bharathidasan University, Tiruchirappalli, for the facilities provided. Authors are indebted to Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for Microalgae and Copepods culture facility provided through extramural project (BT/PR 5856/AAQ/3/598/2012). Authors (SDK & SA) thank the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India for fellowship provided.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dinesh Kumar, S., Santhanam, P., Ananth, S. et al. Evaluation of suitability of wastewater-grown microalgae (Picochlorum maculatum) and copepod (Oithona rigida) as live feed for white leg shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei post-larvae. Aquacult Int 25, 393–411 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0037-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-0037-6