Abstract
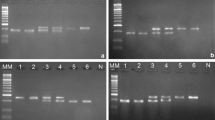
High consumer preference together with its polyculture potential has undoubtedly driven Rohu (Labeo rohita) and Catla (Catla catla) to top the list of the most preferred fishes among the Indian major carps. Commonly found in these fishes are hybrids that can be natural or man-made. Increasing emphasis on biodiversity issues has necessitated proper stock management of these through molecular genetics techniques. Also with few morphological differences that can be used to differentiate wild types and hybrids properly, the problem demands a straightforward molecular approach. Here, we report a simple PCR-based technique that can differentiate the hybrid variety from wild types easily using three different microsatellite markers. Three sets of primers were used to amplify three different microsatellite markers from the genomic DNA isolated from pectoral fins. When the PCR products using all three primer sets were analyzed, ‘hybrid–Rohu’ could be distinguished from wild types. Whereas the hybrid–Rohu DNA yielded specific PCR products with all three primer pairs, only two PCR products were obtained either from wild-type Catla DNA (by primer sets 1 and 2) or from wild-type Rohu DNA (by primer sets 1 and 3). This study clearly demonstrates that a simple PCR-based technique will help the fish breeders and hatcheries to identify and differentiate suspected hybrid–Rohu carp from the wild types within a few hours.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljanabi SM, Martinez I (1997) Universal and rapid salt-extraction of high quality genomic DNA for PCR based techniques. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4692–4693
Crooijmans RPMA, Bierbooms VAF, Komen J, Vander Poel JJ, Groenen MAM (1997) Microsatellite markers in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Anim Genet 28:129–134
Das P, Bharat A, Meher PK, Ray PP, Majumder D (2005) Isolation and characterization of polymorphic microsatellites in Labeo rohita and their cross-species amplification in related species. Mol Eco Notes 5:231–233
FAO Yearbook of Fishery Statistics (2005) FAO. Rome, Italy. No. 96/2
Ferguson MM (1995) Role of molecular genetic markers in the management of cultured fishes. In: Carvalho GR, Pitcher TJ (eds) Molecular genetics in fisheries. Chapman & Hall, London, p 81–103
Lal KK, Chauhan T, Mandal A, Singh RK, Khulbe L, Ponniah AG, Mohindra V (2004) Identification of microsatellite DNA markers for population structure analysis in Indian major carp, Cirrhinus mrigala (Hamilton-Buchanan, 1882). J Appl Ichtyol 20:87–91
Majumdar KC, Ravinder K, Nasaruddin K (1997) DNA fingerprinting in Indian major carps and tilapia by Bkm 2 (8) and M13 probes. Aquac Res 28:129–138
McConnell SKJ, Leamon J, Skibinski DOF, Mair GC (2001) Microsatellite markers from Indian major carp species Catla catla. Mol Eco Notes 1(3):115–116
Mohindra V, Mishra A, Palanichamy M, Ponniah AG (2001) Cross-species amplification of Catla catla microsatellite locus in Labeo rohita. Indian J Fish 48:103–108
Naish KA, Skibinski DOF (1998) Tetra nucleotide microsatellite loci for Indian major carp. J Fish Biol 53:886–889
Padhi BK, Ghosh SK, Mandal RK (1998) Characterization of MboI satellite in Cirrhina mrigala and Clarias batrachus (Pisces). Genome 41:34–39
Patel A, Das P, Swain SK, Meher PK, Jayasankar P, Sarangi N (2009) Development of 21 new microsatellite markers in Labeo rohita (Rohu). Anim Genet 40:251–254
Reddy PVGK (1999) Genetic resources of Indian major carps. In: Bartley D (ed) FAO fisheries technical paper no 387, Rome, p 76
Zhang SM, Reddy PVGK (1991) On the comparative karyomorphology of three Indian major carps, Catla catla (Ham.), Labeo rohita (Ham.) and Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.). Aquaculture 97:7–12
Zheng G, Zheng Y, Zhu X, Luo J, Xia S (1999) The genetic markers of Cirrhina molitorella, C. Mrigala and Labeo rohita from RAPD. J Shanghai Fish Univ 8:215–220
Acknowledgments
The present work was supported by a research grant from the UGC, Government of India (Grant No. PSJ-14/09-10), to Dr. S. Ghosh. Authors are thankful to the Department of Zoology, Ranchi College, Ranchi, India, for providing with the research facilities. Authors are obliged to the Department of Biotechnology, IIT Madras, to successfully complete a part of the research work in their laboratory. Authors are indebted to Dr. Prof. Firoz Ahmed, Vice-Chancellor, N. P. University, Daltangung, Jharkhand, India, for his valuable suggestions and critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allu, P.K.R., Chakraborty, B., Das, M. et al. PCR-based segregation of one hybrid variety of Labeo rohita and Catla catla from their wild-types. Aquacult Int 22, 775–782 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9705-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9705-y