Abstract
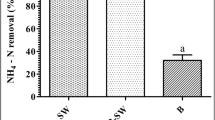
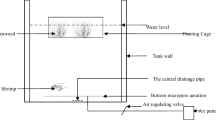
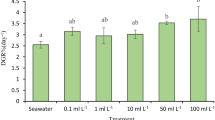
An indoor trial was conducted for 28 days to evaluate the effects and interactions of biofloc and seaweed Ulva lactuca in water quality and growth of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei in intensive system. L. vannamei (4.54 ± 0.09 g) were stocked in experimental tanks at a density 132 shrimp m−2 (566 shrimp m−3) and the U. lactuca was stocked at a density 0.46 kg m−2 (2.0 kg m−3). Biofloc with seaweed (BF-S) significantly reduced (P < 0.05) total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) by 25.9 %, nitrite–nitrogen (NO2–N) by 72.8 %, phosphate (PO 34 -P) by 24.6 %, and total suspended solids by 12.9 % in the water and significantly increased (P < 0.05) settleable solids by 34.2 % and final weight of shrimp by 6.9 % as compared to biofloc without seaweed. The BF-S can contribute by reducing nitrogen compounds (TAN and NO2–N), phosphate (PO 34 -P), and total suspended solids in water and increased final weight of shrimp.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LCM:
-
Marine Shrimp Laboratory
- TAN:
-
Total ammonia nitrogen
- NO2–N:
-
Nitrite–nitrogen
- PO 34 –P:
-
Phosphate
- TSS:
-
Total suspended solids
- SGR:
-
Specific growth rate
- FCR:
-
Feed conversion ratio
- BF-S:
-
Biofloc with seaweed
- BF-WS:
-
Biofloc without seaweed
- WBF-S:
-
Without biofloc with seaweed
- WBF-WS:
-
Without biofloc and without seaweed
- SS:
-
Settleable solids
References
Alencar R, Horta A Jr, Celino P, José J (2010) Cultivo de camarão branco Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone, 1931) com a macroalga Ulva Lacuata Linneaus (Chlorophyta) no tratamento de efluentes em sistema fechado de recirculação. Revista de Biologia e Ciências da Terra 10(1):117–137
Al-Hafedh YS, Alam A, Buschmann HA, Fitzsimmons KM (2012) Experiments on an integrated aquaculture system (seaweeds and marine fish) on the Red Sea coast of Saudi Arabia: efficiency comparison of two local seaweed species for nutrient biofiltration and production. Rev Aquac 4:21–31
Aminot A, Chaussepied M (1983) Manuel des analyses chimiques em milieu marin. C.N.E.X.O, Brest
A.P.H.A. (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. A. P. H. A., Washington
Avnimelech Y (2009) Biofloc technology—a pratical guide book. The world Aquaculture Society, Baton Rouge
Azim ME, Little DC (2008) The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 283:29–35
Baloi M, Arantes R, Schveitzer R, Magnotti C, Vinatea L (2013) Performance of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei raised in biofloc systems with varying levels of light exposure. Aquacul Eng 52:39–44
Bendschneider K, Robison RJ (1952) A new spectrophotometric method for the determination of nitrite in sea water. J Mar Res 11:87–96
Butterworth A (2010) Integrated multi-trophic aquaculture systems incorporating abalone and seaweeds. Nuffield Australia Farming Scholars. Fisheries Research and Development Corporation, Australia
Campos SS, Silva UL, Lúcio MZT, Correia ES (2007) Grow out of Litopenaues vannamei in microcosms fertilized with wheat bran without water exchange. Arch Zootec 56(215):181–190
Cohen JM, Samocha TM, Fox JM, Gandy RL, Lawrence AL (2005) Characterization of water quality factors during intensive raceway production of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei using limited discharge and biosecure management tools. Aquacul Eng 32:425–442
Copertino MS, Tormena T, Seeliger U (2009) Biofiltering efficiency, uptake and assimilation rates of Ulva clathrata (Roth) J. Agardh (Clorophyceae) cultivated in shrimp aquaculture waste water. J Appl Phycol 21:31–45
Cruz-Suárez LE, León A, Penã -Rodríguez A, Rodríguez-Penã G, Moll B, Ricque-Marie D (2010) Shrimp Ulva co-culture: a sustainable alternative to diminish the need for artificial feed and improve shrimp quality. Aquaculture 301:64–68
Du R, Liu L, Wang A, Wang Y (2013) Effects of temperature, algae biomass and ambient nutrient on the absorption of dissolved nitrogen and phosphate by Rodophyte Gracilaria asiatica. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 31(2):353–365
Ebeling JM, Timmons MB, Bisogni JJ (2006) Engineering analysis of the stoichiometry of photoautotrophic, autotrophic, and heterotrophic removal of ammonia-nitrogen in aquaculture systems. Aquaculture 257:346–358
Ekasari J, Crab R, Verstraete W (2010) Primary nutritional content of bioflocos cultures with different organic carbon sources and salinity. Hayati J Biosci 17(3):125–130
Emerenciano M, Ballester ELC, Cavalli RO, Wasielesky W Jr (2011) Effect of biofloc technology (BFT) on the early postlarval stage of pink shrimp Farfantepenaeus paulensis: growth performance, floc composition and salinity stress tolerance. Aquacul Int 19(5):891–901
Furtado PS, Poersch LH, Wasielesky W Jr (2011) Effect of calcium hydroxide, carbonate and sodium bicarbonate on water quality and zootechnical performance of shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei reared in bio-flocs technology (BFT) systems. Aquaculture 321:130–135
Gao L, Shan HW, Zhang TW, Bao WY, Ma S (2012) Effects of carbohydrate addition on Litopenaeus vannamei intensive culture in a zero-water exchange systems. Aquaculture 342–342:89–96
Hargreaves JA (1998) Nitrogen biogeochemistry of aquaculture ponds. Aquaculture 166:181–212
Hargreaves JA (2006) Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquacul Eng 34:344–363
Hari B, Madhusoodana KB, Varghese JT, Schrama JW, Verdegem MCJ (2006) The effect of carbohydrate addition on water quality and the nitrogen budget in extensive shrimp culture systems. Aquaculture 252:248–263
Izzati M (2011) The role of seaweeds Sargassum polycistum and Gracilaria verrucosa on growth performance and biomass production of tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodom Frab). J Coast Dev 14(3):235–241
Jackson C, Preston N, Thompson PJ, Burford M (2003) Nitrogen budget and effluent nitrogen components at an intensive shrimp farm. Aquaculture 218:397–411
Khoi LV, Fotedar R (2011) Integration of western king prawn (Penaeus latisulcatus Kishinouye, 1986) and green seaweed (Ulva lactuca Linaeus, 1753) in closed recirculating aquaculture system. Aquaculture 322–323:201–209
Koroleff F (1969) Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. Int Counc Expl Sea 9:19–22
Lobban CS, Harrison PJ, Duncan MJ (1985) The physiological ecology of seaweeds. Cambridge University Press, New York
Lombardi JV, Almeida MHL, Lima PRT, Sale BOJ, Paula EJ (2006) Cage polyculture of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei and the Philippines seaweed Kappaphycus alvarezii. Aquaculture 258:412–415
Mai H, Fotedar R, Fewtrell J (2010) Evaluation of Sargassum sp. as a nutrient-sink in an integrated seaweed-prawn (ISP) culture system. Aquaculture 310:91–98
Maia EP, Modesto GA, Brito LO, Gálvez AO (2012) Crescimento, sobrevivência e produção de Litopenaeus vannamei cultivado em sistema intensivo. Pesq Agropec Pernamb 17:15–19
Marinho-Soriano E, Nunes SO, Carneiro MAA, Pereira DC (2009) Nutrient’s removal from aquaculture wastewater using the seaweed Gracilaria birdiae. Biomass Bioenergy 33:327–331
Neal RS, Coyle SD, Tidwel JH, Boudreau BM (2010) Evaluation of stocking density and light level on the growth and survival of the pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei, reared in zero-exchange systems. J World Aquacul Soc 41(4):533–544
Peña Rodríguez A, León A, Moll B, Tapia-Salazar M, Nieto-López MG, Villarreal-Cavazos D, Ricque-Marie D, Cruz-Suárez LE (2010) Uso de Ulva clathrata en la nutrición del camarón blanco: revisión. In: Cruz-Suárez LE, Ricque-Marie D, Tapia-Salazar M, Nieto-López MG, Villarreal-Cavazos D, Gamboa-Delgado J (eds) Avances en nutrición acuícola, 10th edn. Universidad Autónoma de Nuevo León, Monterrey
Peña-Rodríguez A, Mawhinney TP, Ricque-Marie D, Cruz-Suárez LE (2011) Chemical composition of cultivated seaweed Ulva clathrata (Roth) C. Agardh. Food Chem 129:491–498
Portillo-Clark G, Casillas-Hernández R, Servín-Villegas R, Magallón-Barajas FJ (2012) Growth and survival of the juvenile yellowleg shrimp Farfantepenaeus californiensis cohabiting with the green feather alga Caulerpa sertularioides at different temperatures. Aquacul Res 44(1):22–30
Ramos R, Vinatea L, Andreatta ER, Costa RHR (2008) Tratamento de efluentes de tanques de criação de Litopenaeus vannamei por sedimentação e absorção de nutrientes pela macroalga Ulva fasciata. Bol Ins Pesca 34(3):345–353
Ramos R, Vinatea L, Santos J, Da Costa R (2010) Tratamiento de efluentes del cultivo de Litopenaeus vannamei mediante procesos de sedimentación, filtración y absorción. Lat Am J Aquat Res 38(2):188–200
Ray AJ, Lewis BL, Browdy CL, Leffler JW (2010) Suspended solids removal to improve shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) production and an evaluation of a plant-based feed in minimal-exchange, superintensive culture systems. Aquaculture 299:89–98
Samocha TM, Patnaik S, Speed M, Ali AM, Burger JM, Almeida RV, Ayub Z, Harisanto M, Horowitz A, Brock DL (2007) Use of molasses as carbon source in limited discharge nursery and grow-out systems for Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquacul Eng 36:184–191
Samocha TM, Moris TC, Kim JS, Correia ES, Advent B (2011) Avanços recentes nas operações de raceways super-intensivos dominados por bioflocos e com renovação zero para produção do camarão branco do pacifico Litopenaeus vannamei. Revista da ABCC 13(2):62–67
Sánchez A, Sánchez-Rodríguez I, Casas-Valdez M (2012) The stable isotope of nitrogen in an experimental culture of Ulva spp. and its assimilation in the nutrition of white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, Baja California Sur, Mexico. J Appl Phycol 24:507–511
Selvin J, Manilal A, Sujith S, Kiran GS, Lipton AP (2011) Efficacy of marine green alga Ulva fasciata extract on the management of shrimp bacterial diseases. Lat Am J Aquat Res 39(2):197–204
Silva UL, Melo FP, Soares RB, Spanghero DBN, Correia ES (2009) Efeito da adição do melaço na relação carbono/nitrogênio no cultivo de camarão Litopenaeus vannamei na fase berçário. Acta Sci Biol Sci 31(4):337–343
Silva KR, Wasielesky W, Abreu PC (2013) Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in the biofloc production of the Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. J World Aquacul Soc 44(1):30–41
Tabarsa M, Rezaei M, Ramezanpour Z, Waaland JR (2012) Chemical compositions of the marine algae Gracilaria salicornia (Rhodophyta) and Ulva lactuca (Chlorophyta) as a potential food source. J Sci Food Agric 92(3):2500–2506
Taw N (2010) Biofloc technology expanding at white shrimp farms. Global Aquacul Adv 13(2):20–22
Thakur DP, Lin CK (2003) Water quality and nutrient budget in closed shrimp (Penaeus monodon) culture systems. Aquacul Eng 27:159–176
Thi DT, Mishima Y, Dinh DK (2012) Potential of Ulva sp. in biofiltration and bioenergy Production. J Vietnam Environ 3(1):55–59
Tsutsui I, Kanjanaworakul P, Srisapoome P, Aue-Umneoy D, Hamano K (2010) Growth of giant tiger prawn, Penaeus monodom Fabricus, under co-culture with a discarded filamentous seaweed Chaetomorpha ligustica (Kutzing), at an aquarium-scale. Aquacul Int 18:545–553
Van Wyk P (1999) Nutrition and feeding of Litopenaeus vannamei in intensive culture systems. In: Van Wyk P, Davis-Hodgkins M, Laramore R, Main KL, Mountain J, Scarpa J (eds) Farming marine shrimp in recirculating freshwater systems, 1st edn. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services-Harbor Branch Oceanic Institute, Florida
Van Wyk P, Scarpa J (1999) Water quality requirements and management. In: Van Wyk P, Davis-Hodgkins M, Laramore R, Main KL, Mountain J, Scarpa J (eds) Farming marine shrimp in recirculating freshwater systems, 1st edn. Florida Department of Agriculture and Consumer Services-Harbor Branch Oceanic Institute, Florida
Wasielesky W Jr, Atwood H, Stokes A, Browdy C (2006) Effect of natural production in a zero exchange suspended microbial floc based super-intensive system for white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 258:396–408
Xu WJ, Pan LQ, Zhao DH, Huang GJ (2012) Preliminary investigation into the contribution of bioflocs on protein nutrition of Litopenaues vannamei fed with different dietary protein levels in zero water exchange culture tanks. Aquaculture 350–353:147–153
Yokoyama H, Ishihi Y (2010) Bioindicator and biofilter function of Ulva spp. (Chlorophyta) for dissolved inorganic nitrogen discharged from a coastal fish farm—potential role in integrated multi-trophic aquaculture. Aquaculture 310:74–83
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Walter Seiffert and Leila Hayashi (LCM, UFSC, Brazil) for their contributions to this study. The authors are also grateful for the financial support provided by Coordination for the Improvement of Personnel in Higher Education (CAPES) and by the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq). Alfredo Olivera and Luis Vinatea are CNPq research fellows.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brito, L.O., Arantes, R., Magnotti, C. et al. Water quality and growth of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei (Boone) in co-culture with green seaweed Ulva lactuca (Linaeus) in intensive system. Aquacult Int 22, 497–508 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9659-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-013-9659-0