Abstract
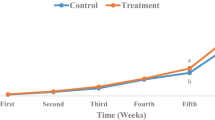
This experiment was carried out to investigate the potential probiotic properties of Bacillus subtilis and suitable methods of administration to the commercial feed in juvenile Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man) from 25 August to 25 November 2008. Putative Bacillus subtilis bacterium isolated from juvenile M. rosenbergii intestine was added to commercial prawn feed as a probiotic. Five types of diets were prepared by mixing B. subtilis at level of 108 cells g−1 with commercial feed using different methods consisting mixing, soaking, spraying and bathing. After 60 days, the prawns fed diets at soaking method treated group, showed a higher mean weight gain (2.09) or 328.84% increase in growth over control. There were significant differences (P < 0.05) in weight gain, feed intake and FCR among soaking method and other treated and control groups. There was significant difference (P < 0.05) in survival among treated and control groups, but no significant difference (P > 0.05) in water quality and biochemical composition among treated and control groups. Clearly, B. subtilis-treated diets appeared to enhance growth and survival of juveniles M. rosenbergii. It was concluded that the tested strain may be a promising probiotic for M. rosenbergii under soaking method of administration to the prawn commercial feed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham TJ, Babu CHS, Mondal S, Banerjee T (2007) Effects of dietary supplementation of commercial human probiotic and antibiotic on the growth rate and content of intestinal microflora in ornamental fishes. Bangladesh J Fish Res 11(1):57–63
Aly SM, Ahmed YA, Ghareeb AA, Mohamed MF (2008) Studies on Bacillus subtilis and Lactobacillus acidophilus as potential probiotics, on the immune response and resistance of Tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus) to challenge infections. Fish Shellfish Immunol 25:128–136
Anderson IG, Shamsudin MN, Nash G (1989) A preliminary study on the aerobic heterotrophic bacterial flora in giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, hatcheries in Malaysia. Aquaculture 81:213–223
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis of the association of official analytical chemists, 15th edn. AOAC, Arlington
Balcazar JL, de Blas I, Ruiz-Zarzuela I, Vendrell D, Muzquiz JL (2004) Probiotics: a tool for the future of fish and shellfish health management. J Aquac Trop 19:239–242
Bergey D, Sneath P, John H (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 1. Williams and Wilkins Company, Baltimore section 5
Chythanya R, Karunasagar I (2002) Inhibition of shrimp pathogenic vibrios by marine Pseudomonas 1-2 strain. Aquaculture 208:1–10
Colorni A (1985) A study on the bacterial flora of giant prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii, larvae fed with Artemia salina nauplii. Aquaculture 49:1–10
FAO (2007) The state of world fisheries and aquaculture 1998. Food and Agriculture Organization FAO, Rome, p 112
FAO/WHO (2001) Report of a joint FAO/WHO expert consoltation on evaluation of health and nutritional properties in food including powder milk with live lactic acid bacteria, Cordoba, Argentina
Felix N, Sudharsan M (2004) Effect of glycine betaine, a feed attractant affecting growth and feed conversion of juvenile freshwater prawn Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquac Nutr 10:193–197
Gildberg A, Mikkelsen H (1998) Effects of supplementing the feed to Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) fry with lactic acid bacteria and immuno-stimulating peptides during a challenge trial with Vibrio anguillarum. Aquaculture 167:103–113
Gildberg A, Johansen A, Bogwald J (1995) Growth and survival of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) fry given diets supplemented with fish protein hydrolysate and lactic acid bacteria during a challenge trial with Aeromonas salmonicida. Aquaculture 138:23–34
Gullian M, Rodriguez J (2002) Selection of probiotic bacteria and study of their immunostimulatory qualities of probiotic bacteria. Global Aquac Advocate 5:52–54
Gullian M, Thompson F, Rodriguez J (2004) Selection of probiotic bacteria and study of their immunostimulatory effect in Penaeus vannamei. Aquaculture 233:1–14
Irianto A, Austin B (2002) Probiotics in Aquaculrture. J Fish Dis 25:633–642
Keysami MA, Saad CR, Daud HM, Sijam K, Alimon AR (2005) A Preliminary study to isolation and identification of the aerobic putative bacterial flora in juvenile giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man). Kustem 4th annual seminar held at Primula Beach Resort, Kuala Terengganu, Malaysia during May 2–3, 2005. Abstract book, p 78
Keysami MA, Saad CR, Daud HM, Sijam K, Alimon AR (2007) Effect of Bacillus subtilis on grouth development and survival of larva Macrobracum rosenbergii (de Man). Aquac Nutr 13:131–136
Meunpol O, Lopinyosiri K, Menasveta P (2003) The effects of ozone and probiotics on the survival of black tiger shrimp (Penaeus monodon). Aquaculture 220:437–448
New MB (2005) Freshwater prawn farming: global status, recent research and a glance at the future. Aquac Res 36:210–230
New MB, Valenti WC, Tidwell JH D, Abramo LR, Kutty MN (2010) Freshwater prawns biology and farming. Blackwell science, Oxford, p 550
Nikoskelainen S, Ouwehand A, Salminen S, Bylund G (2001) Protection of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss from furunculosis by Lactobacillus rhamnosus. Aquaculture 198:229–236
Ringo E, Gatesoupe FJ (1998) Lactic acid bacteria in fish: a review. Aquaculture 160:177–203
Robertson PAW, O’Dowd C, Burrells C, Williams P, Austin B (2000) Use of Carnobacterium sp. as a probiotic for Atlantic salmon Salmo salar L. and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss, Walbaum. Aquaculture 185:235–243
Rumsey GL, Hughes SG, Kinsella JL (2007) Use of dietary yeast Saccaromyces cerevisae nitrogen by Lake Trout. J World Aquac Soc 21(3):205–209
Salinas I, Cuesta A, Estteban MA, Meseguer J (2005) Dietary administration of Lactobacillus delbrueckii and Bacillus subtilis, single or combined, on gilthead sea bream cellular innate immune responses. Fish Shellfish Immunol 19:67–77
Scan (2003) Opinion of the scientific committee on animal nutrition on the criteria for assessing the safety of microorganisms resistant to antibiotics of human clinical and veterinary importance. European Commission Health and Consumer Protection Directorate-General
Sokal RR, Rohlf FJ (1995) Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. Freeman, New York
Sotomayure MA, Balcazar JL (2003) Inhibition of shrimp pathogenic Vibrios by mixture of probiotic strain. Rev Aquat 19:9–15
Sugita H, Okamo R, Suzuki Y, Iwai D, Mizukami M, Akiyama N, Matsuura S (2002) Antibacterial abilities of intestinal bacteria from larval and juvenile Japanese flounder against fish pathogens. Fish Sci 68:1004–1011
Venkat HK, Sahu NP, Jain KK (2004) Effect of feeding Lactobacillus-based probiotics on the gut microflora, growth and survival of postlarva of Macrobrachium rosenbergii(de Man). Aquac Res 35:501–507
Verschuere L, Rombaut G, Huys G, Dhont J, Sorgeloos P, Verstraete W (2000) Probiotic bacteria as biological control agents in aquaculture, review. Microbiol Mol Biol 64:655–671
Vine NG, Leukes WD, Kaiser H, Daya S, Baxter J, Hecht T (2004) Competition for attachment of aquaculture candidate probiotic and pathogenic bacteria on fish intestinal mucus. J Fish Dis 27:319–326
Wang X, Li H, Zhang X, Li Y, Ji W, Xu H (2000) Microbial flora in the digestive tract of adult penaeid shrimp (Penaeus chinensis). J Ocean Univ Qingdao 30:493–498
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the staff of Microbiology and Aquaculture Laboratory and Hatchery unit in Faculty of Agriculture (UPM) for use of equipments and their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Keysami, M.A., Mohammadpour, M. & Saad, C.R. Probiotic activity of Bacillus subtilis in juvenile freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man) at different methods of administration to the feed. Aquacult Int 20, 499–511 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9481-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-011-9481-5